Shinrin-yoku tourism emphasizes immersive forest bathing experiences that enhance mental well-being, attracting visitors seeking relaxation and nature therapy. Eco-tourism focuses on sustainable travel practices that conserve biodiversity and support local communities through environmentally responsible activities. Explore the unique economic benefits and environmental impacts of these complementary tourism trends.
Why it is important
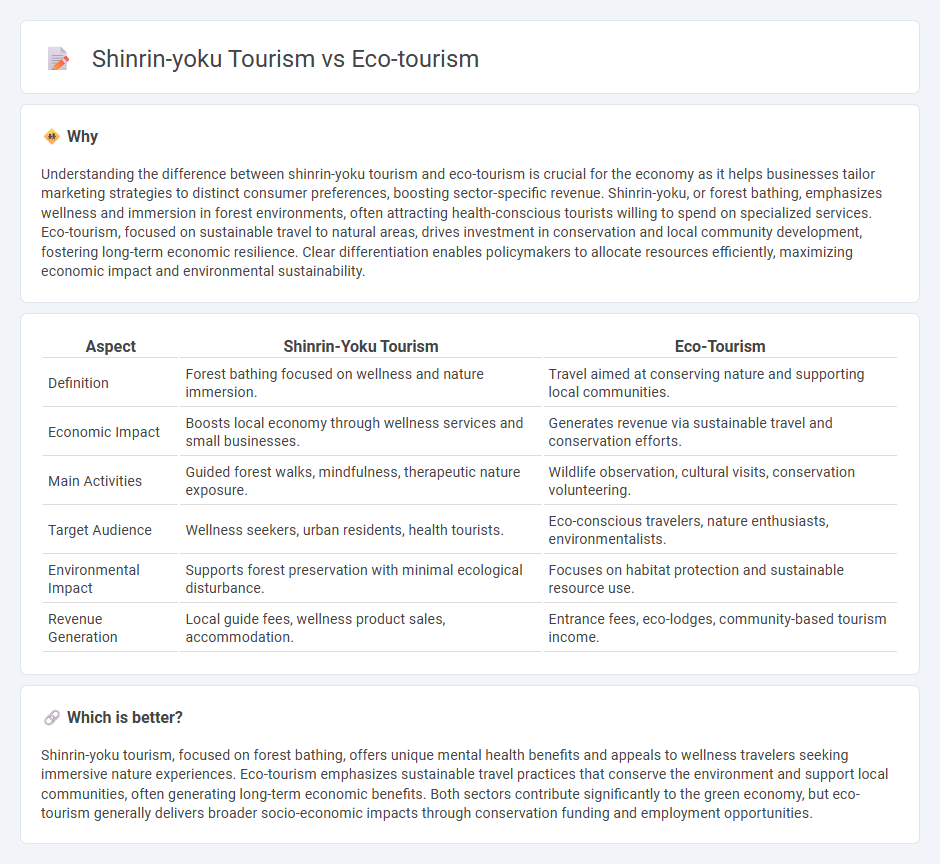
Understanding the difference between shinrin-yoku tourism and eco-tourism is crucial for the economy as it helps businesses tailor marketing strategies to distinct consumer preferences, boosting sector-specific revenue. Shinrin-yoku, or forest bathing, emphasizes wellness and immersion in forest environments, often attracting health-conscious tourists willing to spend on specialized services. Eco-tourism, focused on sustainable travel to natural areas, drives investment in conservation and local community development, fostering long-term economic resilience. Clear differentiation enables policymakers to allocate resources efficiently, maximizing economic impact and environmental sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shinrin-Yoku Tourism | Eco-Tourism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forest bathing focused on wellness and nature immersion. | Travel aimed at conserving nature and supporting local communities. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local economy through wellness services and small businesses. | Generates revenue via sustainable travel and conservation efforts. |
| Main Activities | Guided forest walks, mindfulness, therapeutic nature exposure. | Wildlife observation, cultural visits, conservation volunteering. |
| Target Audience | Wellness seekers, urban residents, health tourists. | Eco-conscious travelers, nature enthusiasts, environmentalists. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports forest preservation with minimal ecological disturbance. | Focuses on habitat protection and sustainable resource use. |
| Revenue Generation | Local guide fees, wellness product sales, accommodation. | Entrance fees, eco-lodges, community-based tourism income. |
Which is better?
Shinrin-yoku tourism, focused on forest bathing, offers unique mental health benefits and appeals to wellness travelers seeking immersive nature experiences. Eco-tourism emphasizes sustainable travel practices that conserve the environment and support local communities, often generating long-term economic benefits. Both sectors contribute significantly to the green economy, but eco-tourism generally delivers broader socio-economic impacts through conservation funding and employment opportunities.
Connection
Shinrin-yoku tourism, known as forest bathing, boosts local economies by attracting eco-tourists seeking nature-based wellness experiences, increasing demand for sustainable accommodations and guided tours. Eco-tourism promotes conservation efforts and supports rural communities through responsible travel practices that align with the principles of shinrin-yoku. Both contribute to economic development by fostering environmental awareness and creating jobs in eco-friendly sectors.
Key Terms
Sustainable Development
Eco-tourism promotes conservation efforts and supports local communities by encouraging responsible travel to natural areas, emphasizing biodiversity preservation and cultural respect. Shinrin-yoku tourism, or forest bathing, enhances mental and physical health through immersive nature experiences, prioritizing well-being alongside environmental mindfulness. Discover how these sustainable tourism practices contribute uniquely to achieving Sustainable Development Goals.
Local Economic Impact
Eco-tourism emphasizes sustainable travel that supports conservation efforts and benefits local communities by creating jobs and promoting local businesses. Shinrin-yoku tourism, or forest bathing, drives economic growth through wellness-centered experiences, increasing demand for guided tours, accommodation, and local artisanal products in forest areas. Explore how these tourism models uniquely contribute to local economies and foster sustainable development.
Value-added Services
Eco-tourism emphasizes environmental education and conservation efforts, offering guided nature tours, wildlife observation, and sustainable lodging to enhance visitor experience. Shinrin-yoku tourism, or forest bathing, provides therapeutic services such as mindfulness sessions, sensory walks, and stress relief workshops designed to promote mental well-being and physical health. Explore how these value-added services can elevate your travel experience by integrating nature, wellness, and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What Is Ecotourism - Ecotourism is defined as responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of local people, supports conservation financially, and promotes environmental and cultural awareness through education and interpretation.
Ecotourism - Wikipedia - Ecotourism is nature-based tourism aimed at conservation and environmental education with minimal impact, often financially benefiting host communities and promoting awareness of natural habitats and local cultures.
Ecotourism and Sustainable Tourism | GSTC - Ecotourism is a sustainable, ethical form of nature-based tourism focusing on low-impact, educational experiences that support conservation and provide economic and social benefits to local communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com