Shinrin-yoku tourism leverages Japan's extensive forest ecosystems to offer stress reduction and mental wellness benefits through immersive nature experiences, driving economic growth in rural areas. Medical tourism attracts international patients seeking advanced healthcare services, boosting revenue in urban healthcare sectors and fostering global medical collaborations. Explore how these distinct tourism models impact economic development and sustainability worldwide.
Why it is important
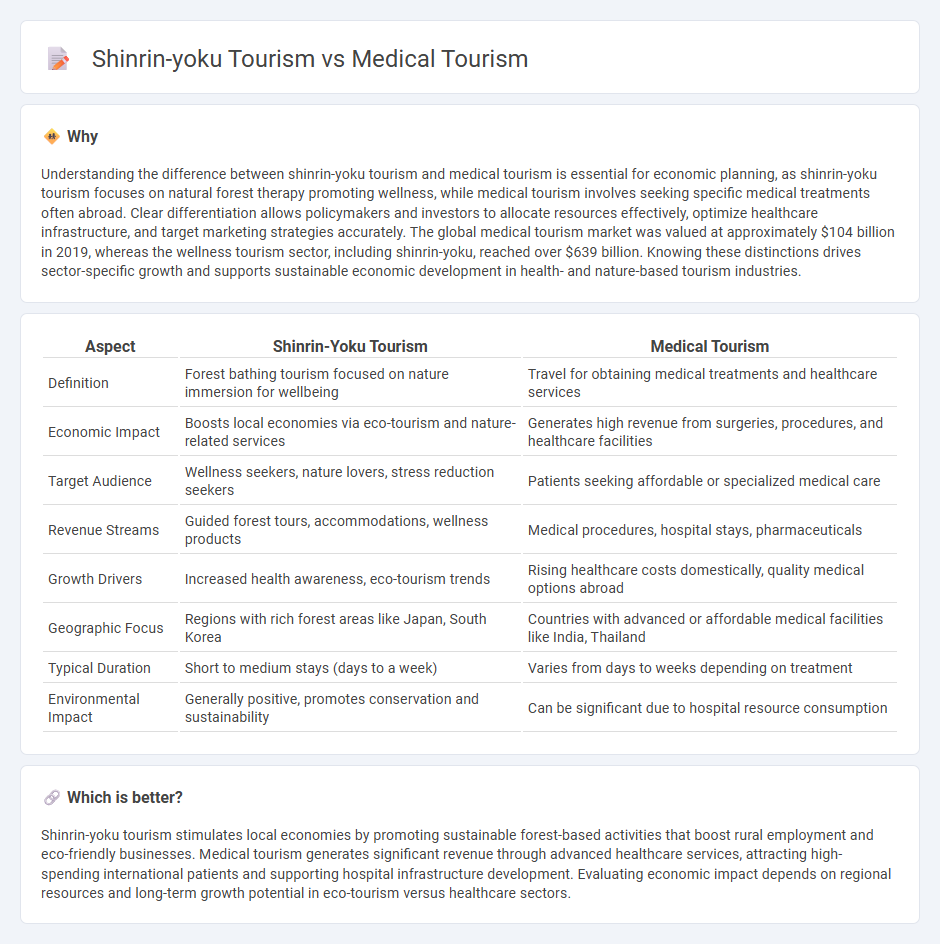
Understanding the difference between shinrin-yoku tourism and medical tourism is essential for economic planning, as shinrin-yoku tourism focuses on natural forest therapy promoting wellness, while medical tourism involves seeking specific medical treatments often abroad. Clear differentiation allows policymakers and investors to allocate resources effectively, optimize healthcare infrastructure, and target marketing strategies accurately. The global medical tourism market was valued at approximately $104 billion in 2019, whereas the wellness tourism sector, including shinrin-yoku, reached over $639 billion. Knowing these distinctions drives sector-specific growth and supports sustainable economic development in health- and nature-based tourism industries.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shinrin-Yoku Tourism | Medical Tourism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forest bathing tourism focused on nature immersion for wellbeing | Travel for obtaining medical treatments and healthcare services |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local economies via eco-tourism and nature-related services | Generates high revenue from surgeries, procedures, and healthcare facilities |
| Target Audience | Wellness seekers, nature lovers, stress reduction seekers | Patients seeking affordable or specialized medical care |
| Revenue Streams | Guided forest tours, accommodations, wellness products | Medical procedures, hospital stays, pharmaceuticals |
| Growth Drivers | Increased health awareness, eco-tourism trends | Rising healthcare costs domestically, quality medical options abroad |
| Geographic Focus | Regions with rich forest areas like Japan, South Korea | Countries with advanced or affordable medical facilities like India, Thailand |
| Typical Duration | Short to medium stays (days to a week) | Varies from days to weeks depending on treatment |
| Environmental Impact | Generally positive, promotes conservation and sustainability | Can be significant due to hospital resource consumption |
Which is better?
Shinrin-yoku tourism stimulates local economies by promoting sustainable forest-based activities that boost rural employment and eco-friendly businesses. Medical tourism generates significant revenue through advanced healthcare services, attracting high-spending international patients and supporting hospital infrastructure development. Evaluating economic impact depends on regional resources and long-term growth potential in eco-tourism versus healthcare sectors.
Connection
Shinrin-yoku tourism, centered around forest bathing experiences, contributes significantly to the wellness economy by attracting travelers seeking nature-based health benefits. Medical tourism overlaps with shinrin-yoku by incorporating natural healing environments into treatment plans, enhancing patient recovery and wellbeing. Both industries stimulate local economies through increased demand for healthcare services, hospitality, and sustainable natural attractions.
Key Terms
Revenue generation
Medical tourism generates significant revenue by attracting patients seeking specialized treatments, with the global medical tourism market valued at approximately $104 billion in 2023. Shinrin-yoku tourism, centered around forest bathing experiences, contributes to wellness tourism growth projected to reach $919 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for mental health and stress reduction services. Explore more about how these distinct tourism sectors contribute economically while promoting health and well-being.
Healthcare cost savings
Medical tourism offers significant healthcare cost savings by enabling patients to access high-quality treatments at a fraction of domestic prices, particularly for procedures like cardiac surgery, dental care, and cosmetic operations. Shinrin-yoku tourism, or forest bathing, while not a direct medical procedure, contributes to healthcare savings by promoting mental well-being and reducing stress-related illnesses, thus potentially decreasing the need for costly medical interventions. Explore deeper insights on how these tourism types uniquely impact healthcare economics and personal wellness.
Sustainable local development
Medical tourism promotes sustainable local development by generating revenue through healthcare services, supporting local jobs in hospitals, clinics, and hospitality sectors. Shinrin-yoku tourism enhances environmental conservation and community well-being by encouraging forest preservation and eco-friendly travel, fostering a symbiotic relationship between visitors and nature. Explore the distinct impacts of these tourism types on sustainable local development to understand their long-term benefits.
Source and External Links
Medical tourism - Wikipedia - Medical tourism is the practice of traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment, often for surgeries or procedures unavailable, unaffordable, or less accessible in the home country, with popular destinations like Thailand attracting millions of patients annually and generating billions in revenue.
Medical Tourism - Medical tourism involves traveling internationally to access healthcare services that are cheaper or unavailable domestically, with treatments costing 40-80% less than in the US, driven by high costs, wait times, and increased global travel options.
Medical Tourism: What Is Health Tourism & Where Is It Popular? - Originally associated with patients from less-developed countries seeking advanced care, medical tourism now increasingly includes developed country patients traveling to low-cost destinations for elective, cosmetic, fertility, and other treatments, saving thousands of dollars.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com