Dollarization refers to a country adopting a foreign currency, typically the U.S. dollar, as its legal tender to stabilize the economy and curb inflation. Currency unions involve multiple countries agreeing to share a common currency, like the Eurozone's euro, facilitating trade and economic integration among member states. Explore the advantages and challenges of dollarization versus currency unions to understand their impact on economic stability and growth.
Why it is important
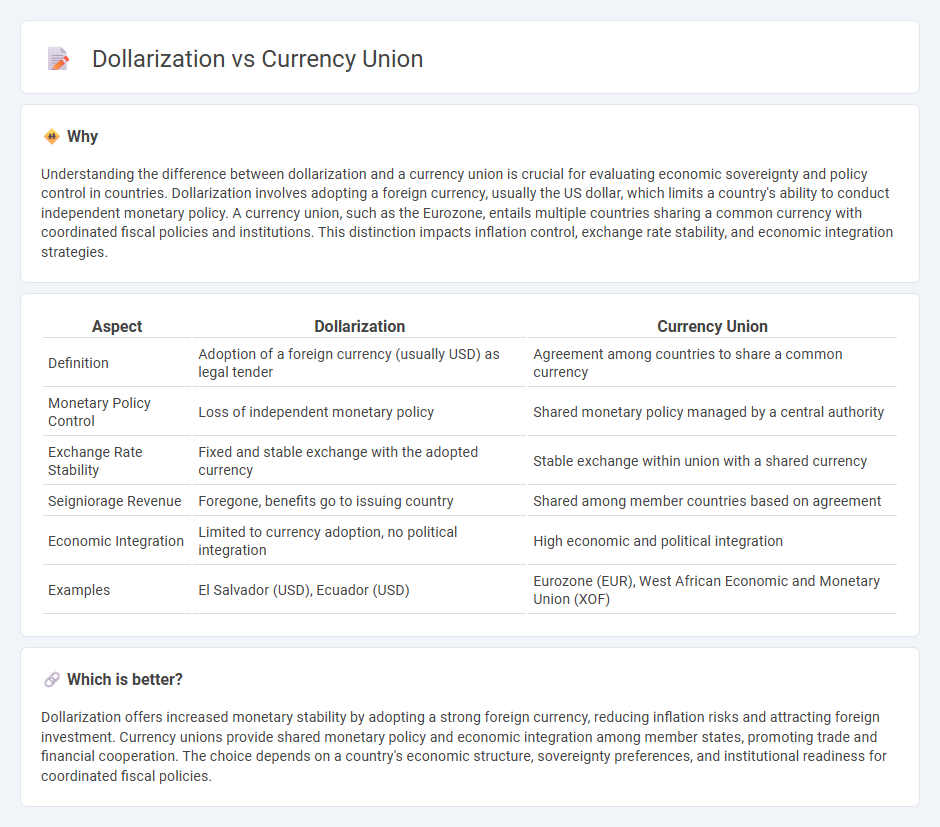
Understanding the difference between dollarization and a currency union is crucial for evaluating economic sovereignty and policy control in countries. Dollarization involves adopting a foreign currency, usually the US dollar, which limits a country's ability to conduct independent monetary policy. A currency union, such as the Eurozone, entails multiple countries sharing a common currency with coordinated fiscal policies and institutions. This distinction impacts inflation control, exchange rate stability, and economic integration strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dollarization | Currency Union |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adoption of a foreign currency (usually USD) as legal tender | Agreement among countries to share a common currency |
| Monetary Policy Control | Loss of independent monetary policy | Shared monetary policy managed by a central authority |
| Exchange Rate Stability | Fixed and stable exchange with the adopted currency | Stable exchange within union with a shared currency |
| Seigniorage Revenue | Foregone, benefits go to issuing country | Shared among member countries based on agreement |
| Economic Integration | Limited to currency adoption, no political integration | High economic and political integration |
| Examples | El Salvador (USD), Ecuador (USD) | Eurozone (EUR), West African Economic and Monetary Union (XOF) |
Which is better?
Dollarization offers increased monetary stability by adopting a strong foreign currency, reducing inflation risks and attracting foreign investment. Currency unions provide shared monetary policy and economic integration among member states, promoting trade and financial cooperation. The choice depends on a country's economic structure, sovereignty preferences, and institutional readiness for coordinated fiscal policies.
Connection
Dollarization occurs when a country adopts a foreign currency, often the US dollar, to stabilize its economy and control inflation, closely linking its economic performance to the currency's issuer. Currency unions involve multiple countries sharing a common currency, such as the Eurozone using the euro, which facilitates trade and monetary policy coordination among member states. Both mechanisms reduce exchange rate volatility and foster economic integration by aligning monetary policies and enhancing financial stability across borders.
Key Terms
Monetary Policy
A currency union involves multiple countries adopting a shared currency and coordinating their monetary policies through a central authority like the European Central Bank, enabling unified interest rate decisions and inflation targeting. Dollarization occurs when a country unilaterally adopts a foreign currency, such as the US dollar, losing independent monetary policy control and relying on the foreign currency issuer's monetary decisions. Explore how these frameworks impact economic stability and sovereign monetary autonomy in greater detail.
Exchange Rate
Currency unions involve multiple countries adopting a shared currency managed by a common central authority, ensuring fixed exchange rates among member states that facilitate trade stability and reduce transaction costs. Dollarization occurs when a country unilaterally adopts a foreign currency, typically the US dollar, relinquishing control over its monetary policy and exposing the economy to exchange rate risks tied to the foreign currency's fluctuations. Explore how these monetary frameworks impact economic sovereignty and exchange rate stability further.
Legal Tender
A currency union establishes a shared currency with full legal tender status across member countries, ensuring uniform monetary policy and legal consistency. Dollarization occurs when a country adopts a foreign currency, like the US dollar, as legal tender without formal integration into the issuing country's monetary system. Explore the implications of legal tender status in currency arrangements to understand their economic and legal impacts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com