De-risking involves strategically reducing exposure to high-risk assets or markets to protect financial stability, while disinvestment refers to the complete withdrawal of investments from specific sectors, companies, or regions. Both approaches aim to manage financial risk, but de-risking focuses on mitigation, whereas disinvestment often signals a strong ethical, political, or economic stance. Explore these strategies further to understand their impact on global economic trends.
Why it is important
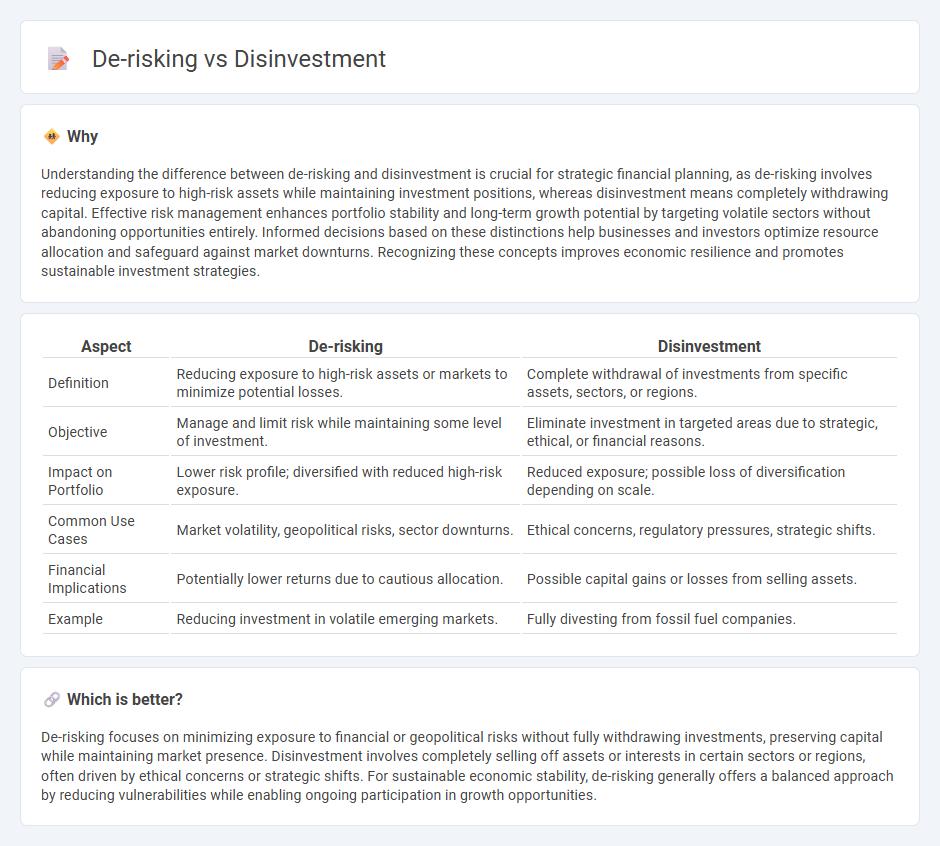
Understanding the difference between de-risking and disinvestment is crucial for strategic financial planning, as de-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets while maintaining investment positions, whereas disinvestment means completely withdrawing capital. Effective risk management enhances portfolio stability and long-term growth potential by targeting volatile sectors without abandoning opportunities entirely. Informed decisions based on these distinctions help businesses and investors optimize resource allocation and safeguard against market downturns. Recognizing these concepts improves economic resilience and promotes sustainable investment strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-risking | Disinvestment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to high-risk assets or markets to minimize potential losses. | Complete withdrawal of investments from specific assets, sectors, or regions. |
| Objective | Manage and limit risk while maintaining some level of investment. | Eliminate investment in targeted areas due to strategic, ethical, or financial reasons. |
| Impact on Portfolio | Lower risk profile; diversified with reduced high-risk exposure. | Reduced exposure; possible loss of diversification depending on scale. |
| Common Use Cases | Market volatility, geopolitical risks, sector downturns. | Ethical concerns, regulatory pressures, strategic shifts. |
| Financial Implications | Potentially lower returns due to cautious allocation. | Possible capital gains or losses from selling assets. |
| Example | Reducing investment in volatile emerging markets. | Fully divesting from fossil fuel companies. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on minimizing exposure to financial or geopolitical risks without fully withdrawing investments, preserving capital while maintaining market presence. Disinvestment involves completely selling off assets or interests in certain sectors or regions, often driven by ethical concerns or strategic shifts. For sustainable economic stability, de-risking generally offers a balanced approach by reducing vulnerabilities while enabling ongoing participation in growth opportunities.
Connection
De-risking and disinvestment are interrelated strategies employed by investors and companies to mitigate financial exposure in volatile markets. De-risking involves reducing risk by altering portfolios or operational practices, often leading to disinvestment, which is the deliberate withdrawal of capital from specific assets or sectors deemed high-risk. Both approaches aim to enhance financial stability and redirect resources toward more secure, sustainable economic opportunities.
Key Terms
Asset Sale
Disinvestment involves selling assets or subsidiaries to raise capital or streamline operations, whereas de-risking focuses on reducing exposure to specific financial or operational risks by exiting high-risk markets or sectors. Asset sales in disinvestment often target non-core or underperforming units to optimize balance sheets, while de-risking may include asset sale strategies aimed at minimizing potential losses and enhancing stability. Explore deeper insights into how strategic asset sales impact corporate risk profiles and financial health.
Risk Mitigation
Disinvestment involves the strategic sale or liquidation of assets to reduce exposure and improve liquidity, often targeting underperforming or non-core holdings. De-risking focuses on minimizing potential risks through diversification, hedging, or restructuring without necessarily divesting assets, aiming to stabilize returns and protect against market volatility. Explore detailed strategies on how disinvestment and de-risking effectively mitigate financial and operational risks.
Capital Allocation
Disinvestment involves the strategic withdrawal of investments from non-core or underperforming assets to optimize capital allocation and enhance portfolio efficiency. De-risking focuses on reallocating capital toward lower-risk opportunities to safeguard assets and ensure steady returns amid market uncertainties. Explore detailed strategies to master capital allocation through disinvestment and de-risking.
Source and External Links
What Is Disinvestment and How Can It Impact Your Portfolio? - Disinvestment is the process of reducing or eliminating investments in a company, asset or industry for financial, ethical, or environmental reasons, often shifting capital away partially rather than complete withdrawal.
What Is Disinvestment? Meaning, Types and Examples - Disinvestment involves selling or liquidating assets by governments or companies to reallocate resources, improve efficiency, or generate funds, with types including strategic and minority disinvestment.
Disinvestment: Definition, When it Happens (+ Example) - Disinvestment occurs when governments or organizations sell assets or subsidiaries motivated by factors like asset maximization, political agendas, legal requirements, or opportunistic offers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com