Shadow bailouts often involve hidden financial support to prevent economic collapse without public disclosure, while debt restructuring rearranges existing debt terms to enhance repayment feasibility for struggling entities. Shadow bailouts can obscure financial risk, complicating market transparency, whereas debt restructuring promotes long-term economic stability by adjusting obligations to sustainable levels. Explore the intricate impacts of these approaches on global economic resilience and policy-making.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between shadow bailouts and debt restructuring is crucial for evaluating economic recovery strategies and their impact on national debt levels. Shadow bailouts often involve covert financial support to prevent systemic collapse without transparent accountability, whereas debt restructuring legally modifies debt terms to enhance payment feasibility. Accurate knowledge helps policymakers and investors assess financial risks, maintain market stability, and promote sustainable economic growth. Distinguishing these concepts ensures effective fiscal management and safeguards taxpayer interests.
Comparison Table
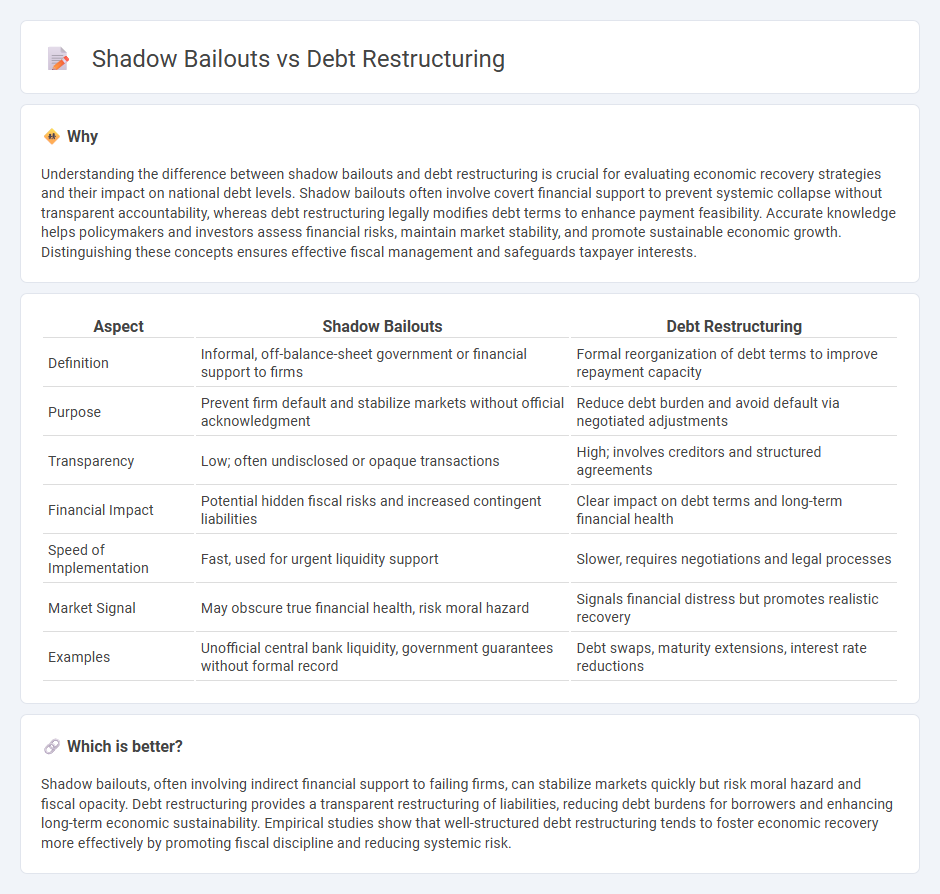
| Aspect | Shadow Bailouts | Debt Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal, off-balance-sheet government or financial support to firms | Formal reorganization of debt terms to improve repayment capacity |
| Purpose | Prevent firm default and stabilize markets without official acknowledgment | Reduce debt burden and avoid default via negotiated adjustments |
| Transparency | Low; often undisclosed or opaque transactions | High; involves creditors and structured agreements |
| Financial Impact | Potential hidden fiscal risks and increased contingent liabilities | Clear impact on debt terms and long-term financial health |
| Speed of Implementation | Fast, used for urgent liquidity support | Slower, requires negotiations and legal processes |
| Market Signal | May obscure true financial health, risk moral hazard | Signals financial distress but promotes realistic recovery |
| Examples | Unofficial central bank liquidity, government guarantees without formal record | Debt swaps, maturity extensions, interest rate reductions |
Which is better?
Shadow bailouts, often involving indirect financial support to failing firms, can stabilize markets quickly but risk moral hazard and fiscal opacity. Debt restructuring provides a transparent restructuring of liabilities, reducing debt burdens for borrowers and enhancing long-term economic sustainability. Empirical studies show that well-structured debt restructuring tends to foster economic recovery more effectively by promoting fiscal discipline and reducing systemic risk.
Connection
Shadow bailouts occur when governments or financial institutions secretly provide financial support to struggling companies, avoiding public scrutiny and formal approval processes. Debt restructuring involves renegotiating the terms of debt agreements to improve a company's financial stability, often coordinated behind the scenes in shadow bailout scenarios to prevent defaults from triggering systemic risks. These practices connect by stabilizing distressed firms and financial markets without the transparency of official interventions, potentially exposing taxpayers to hidden fiscal risks.
Key Terms
Insolvency
Debt restructuring involves renegotiating the terms of existing debt to restore a company's financial stability during insolvency, often including extended payment schedules or reduced interest rates. Shadow bailouts refer to indirect government interventions that provide financial support without formal recognition, potentially distorting insolvency proceedings and market discipline. Explore the impacts of these mechanisms on corporate recovery and economic resilience for deeper insights.
Off-balance-sheet support
Debt restructuring involves renegotiating terms to manage existing obligations, while shadow bailouts provide off-balance-sheet support through indirect financial assistance or guarantees that do not appear on official debt statements. Off-balance-sheet support can mask the true financial risk and complicate fiscal transparency, making it harder for investors to assess a country's or corporation's actual liabilities. Explore the mechanisms and impacts of these financial strategies for a deeper understanding.
Moral hazard
Debt restructuring involves renegotiating the terms of debt to avoid default, while shadow bailouts refer to indirect government support without official acknowledgment. Both mechanisms carry significant moral hazard risks by potentially encouraging irresponsible borrowing and lending behaviors. Explore further to understand how these financial interventions impact economic stability and regulatory frameworks.
Source and External Links
Debt Restructuring - Definition, Reason, Achieve - Debt restructuring is the process where a financially distressed company renegotiates its debt obligations with creditors to improve liquidity and avoid bankruptcy, often by altering payment terms or converting debt to equity.
Debt Restructuring: What It Is and How It Works | LendingTree - Debt restructuring involves modifying existing debt agreements, such as loan modifications, payment deferrals, or interest reductions, to better fit a debtor's current financial situation and avoid penalties or default.
Debt Restructuring Pros and Cons: Key Benefits and Risks - Common debt restructuring methods include loan modification, debt settlement, and refinancing, which aim to make repayments more manageable but may affect credit scores and require proof of hardship.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com