Neobank stacking leverages multiple digital banking platforms to optimize financial services, offering users enhanced flexibility and tailored benefits compared to traditional challenger banks, which operate as standalone entities disrupting legacy banking models. By integrating various neobanks, consumers can diversify accounts, maximize rewards, and manage finances more efficiently through specialized features such as zero-fee transactions and real-time spending analytics. Explore the evolving landscape of digital banking to understand how neobank stacking reshapes personal finance management beyond challenger bank offerings.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and challenger banks is crucial for optimizing financial management strategies and maximizing digital banking benefits. Neobank stacking involves using multiple digital-only banks to diversify financial services, while challenger banks are full-service digital banks disrupting traditional finance with advanced technology. This distinction helps consumers and businesses choose the right banking model for tailored financial products, better fees, and improved user experience. Knowledge of these differences can enhance decision-making in digital banking adoption, impacting economic behavior and market competition.
Comparison Table
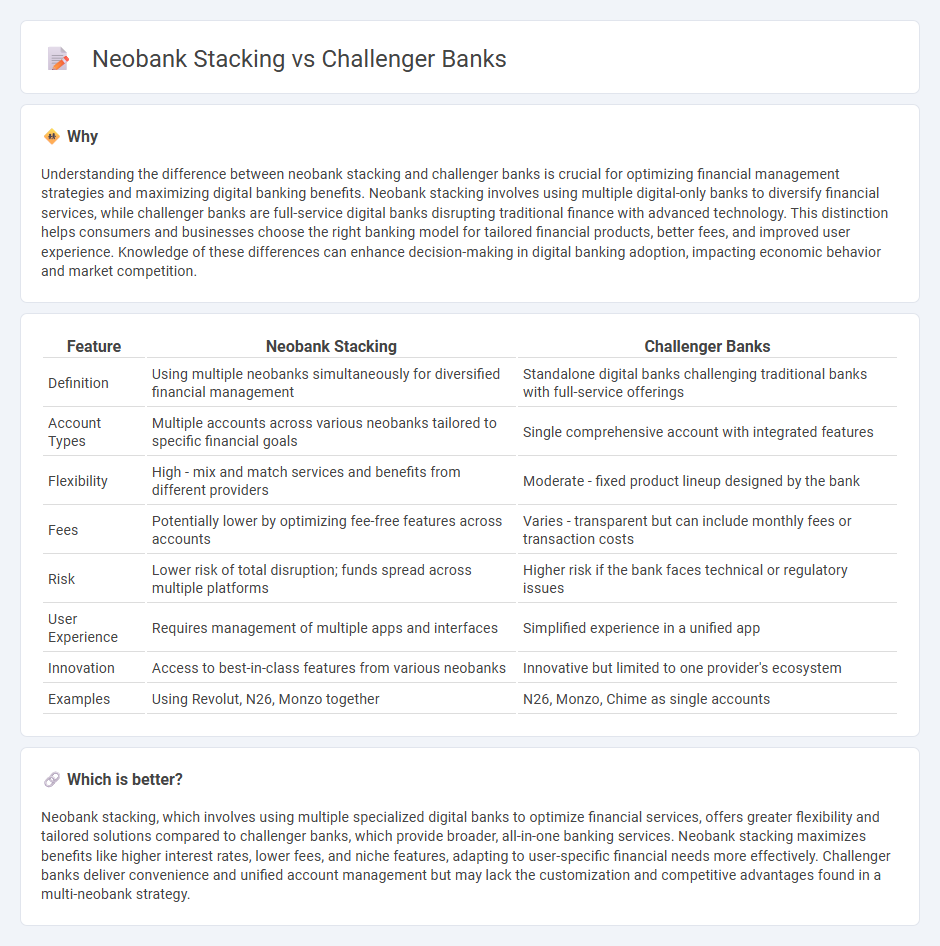
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Challenger Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using multiple neobanks simultaneously for diversified financial management | Standalone digital banks challenging traditional banks with full-service offerings |
| Account Types | Multiple accounts across various neobanks tailored to specific financial goals | Single comprehensive account with integrated features |
| Flexibility | High - mix and match services and benefits from different providers | Moderate - fixed product lineup designed by the bank |
| Fees | Potentially lower by optimizing fee-free features across accounts | Varies - transparent but can include monthly fees or transaction costs |
| Risk | Lower risk of total disruption; funds spread across multiple platforms | Higher risk if the bank faces technical or regulatory issues |
| User Experience | Requires management of multiple apps and interfaces | Simplified experience in a unified app |
| Innovation | Access to best-in-class features from various neobanks | Innovative but limited to one provider's ecosystem |
| Examples | Using Revolut, N26, Monzo together | N26, Monzo, Chime as single accounts |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking, which involves using multiple specialized digital banks to optimize financial services, offers greater flexibility and tailored solutions compared to challenger banks, which provide broader, all-in-one banking services. Neobank stacking maximizes benefits like higher interest rates, lower fees, and niche features, adapting to user-specific financial needs more effectively. Challenger banks deliver convenience and unified account management but may lack the customization and competitive advantages found in a multi-neobank strategy.
Connection
Neobank stacking involves customers using multiple neobanks to optimize financial benefits such as cashback and lower fees, creating an interconnected ecosystem that enhances user experience. Challenger banks, often operating as neobanks, pioneer innovative digital banking services that drive this trend, offering diverse products tailored to specific customer needs. The synergy between neobank stacking and challenger banks accelerates financial inclusion, promotes competition, and reshapes traditional banking models worldwide.
Key Terms
Digital Banking Platforms
Challenger banks leverage advanced digital banking platforms to offer personalized financial services with robust security and user-friendly interfaces, often integrating AI-driven tools for enhanced customer insight. Neobank stacking relies on modular digital banking platforms allowing users to combine multiple specialized neobanks, optimizing financial management through seamless app integration and real-time data synchronization. Explore the evolving landscape of digital banking platforms to understand which approach maximizes financial innovation and user experience.
Regulatory Licensing
Challenger banks and neobanks differ significantly in regulatory licensing, with challenger banks operating under full banking licenses that enable them to offer a wider range of financial services and hold customer deposits securely. Neobanks often function under partnerships with licensed banks or hold specialized e-money licenses, limiting their scope but allowing faster market entry and lower operational costs. Explore how these licensing structures impact consumer protections and service innovation in the evolving digital banking landscape.
Value-added Services Integration
Challenger banks and neobanks differentiate significantly in value-added services integration, with challenger banks often expanding offerings through partnerships in areas like budgeting tools, insurance, and investment platforms, enhancing customer retention and engagement. Neobanks prioritize streamlined, tech-first interfaces that embed value-added services such as personalized financial insights and instant credit scoring directly within the app, delivering seamless experiences tailored for digital-native users. Explore how these strategic approaches transform user engagement and financial ecosystem innovation.
Source and External Links
Challenger Banks Explained: Trends and Opportunities - Ulam Labs - Challenger banks are digital-first financial institutions aiming to disrupt traditional banks by offering innovative, customer-centric digital banking services, with the global market expected to grow from USD 118 billion in 2023 to over USD 2.5 trillion by 2031, driven by major players like Monzo, Revolut, and Nubank.
The Rise of Challenger Banks: Are the Apps Taking Over? - FT Partners - Challenger banks have become formidable global competitors to traditional banks by leveraging technology and customer-focused services, prompting incumbents to launch fintech brands and collaborate with fintech providers to defend their market share.
Challenger Bank Definition - FinTech Weekly - Challenger banks, often called neobanks, are typically small, modern retail banks that challenge established financial institutions by using advanced financial technologies and focusing more on customer needs, with significant regulatory changes enabling their growth since 2010.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com