De-risking focuses on minimizing exposure to economic uncertainties by diversifying supply chains and investment portfolios, thereby reducing potential losses without severing global ties. Decoupling involves a more drastic separation of economic systems or markets, often driven by geopolitical tensions, aiming to create independent and self-sufficient economies. Explore the key differences and strategic implications of de-risking versus decoupling in today's dynamic global economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-risking and decoupling is crucial for effective economic strategy and risk management in global markets. De-risking involves reducing exposure to specific financial or geopolitical risks without severing economic ties, while decoupling refers to the deliberate separation of economic dependencies between countries. Grasping these concepts helps businesses and policymakers optimize investment decisions and maintain stability amid geopolitical tensions. Recognizing their distinct impacts enables more precise responses to international financial challenges and trade policies.
Comparison Table
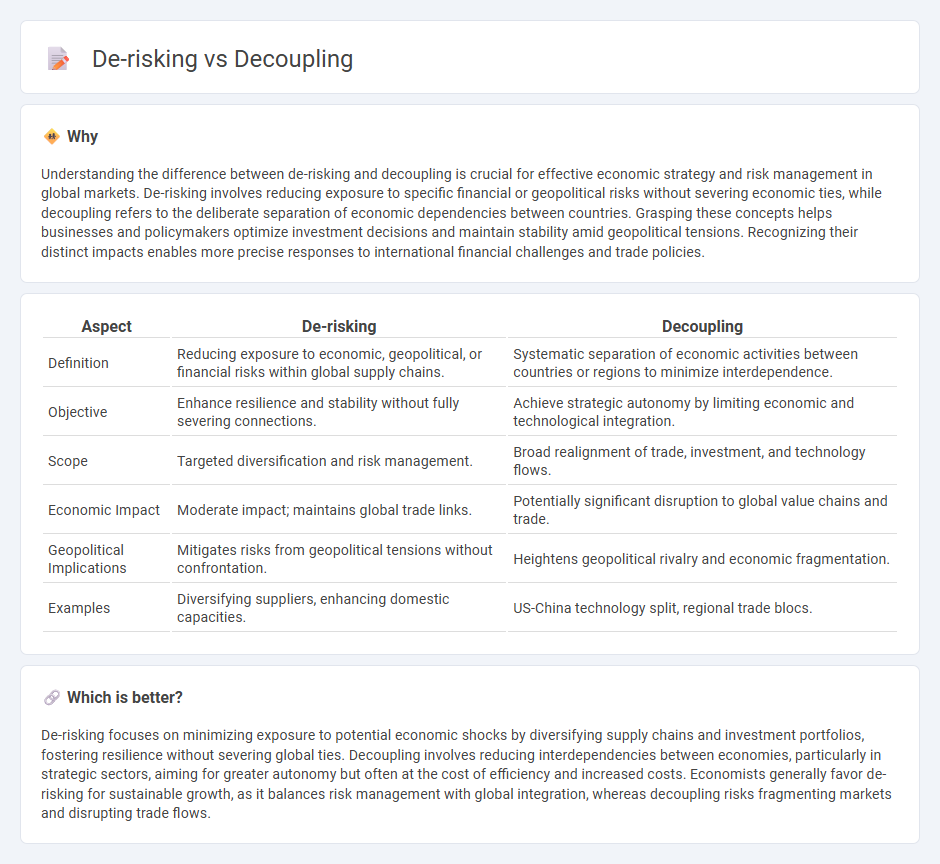
| Aspect | De-risking | Decoupling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to economic, geopolitical, or financial risks within global supply chains. | Systematic separation of economic activities between countries or regions to minimize interdependence. |
| Objective | Enhance resilience and stability without fully severing connections. | Achieve strategic autonomy by limiting economic and technological integration. |
| Scope | Targeted diversification and risk management. | Broad realignment of trade, investment, and technology flows. |
| Economic Impact | Moderate impact; maintains global trade links. | Potentially significant disruption to global value chains and trade. |
| Geopolitical Implications | Mitigates risks from geopolitical tensions without confrontation. | Heightens geopolitical rivalry and economic fragmentation. |
| Examples | Diversifying suppliers, enhancing domestic capacities. | US-China technology split, regional trade blocs. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on minimizing exposure to potential economic shocks by diversifying supply chains and investment portfolios, fostering resilience without severing global ties. Decoupling involves reducing interdependencies between economies, particularly in strategic sectors, aiming for greater autonomy but often at the cost of efficiency and increased costs. Economists generally favor de-risking for sustainable growth, as it balances risk management with global integration, whereas decoupling risks fragmenting markets and disrupting trade flows.
Connection
De-risking and decoupling are interconnected strategies aimed at minimizing economic vulnerabilities by reducing dependence on high-risk markets or geopolitical adversaries. De-risking involves diversifying supply chains and investment portfolios to avoid concentrated exposure, while decoupling goes further by intentionally separating economic ties, particularly between major powers like the U.S. and China. Both trends contribute to reshaping global trade networks, impacting international investment flows and economic growth patterns.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Diversification
Decoupling emphasizes separating supply chains to reduce dependency on specific regions or suppliers, aiming to enhance resilience against geopolitical and economic disruptions. De-risking focuses on identifying vulnerabilities within the supply chain and implementing strategies such as diversification, multi-sourcing, and inventory buffers to minimize potential losses. Explore more to understand how these approaches optimize supply chain diversification and ensure operational stability.
Economic Interdependence
Decoupling refers to the process of reducing economic interdependence between countries by separating supply chains and minimizing reliance on foreign partners, often driven by geopolitical tensions. De-risking involves identifying and mitigating specific vulnerabilities within economic partnerships to safeguard against disruptions without completely severing ties. Explore the differences between these strategies and their impact on global economic stability to better understand their roles in shaping international trade policies.
Strategic Autonomy
Strategic autonomy emphasizes reducing reliance on external entities to safeguard national interests, where decoupling involves actively separating from foreign dependencies, especially in technology and supply chains. De-risking focuses on mitigating vulnerabilities through diversification and risk management without complete separation. Explore deeper insights on how these approaches shape policy decisions and economic resilience.
Source and External Links
Decoupling (cosmology) - Wikipedia - In cosmology, decoupling refers to the period when different types of particles fall out of thermal equilibrium with each other due to the expansion of the universe, such as when photons and neutrinos became effectively independent, leading to phenomena like the cosmic microwave background.
DECOUPLING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Decoupling describes a situation in which two or more activities are separated or no longer develop in the same way, for example, when a company splits off part of its business from the rest of its operations.
China decoupling versus de-risking: What's the difference? - In economics, decoupling means the complete separation of trade and investment ties between economies, such as when companies move supply chains out of a country to reduce dependence, distinct from "de-risking," which seeks to manage rather than sever ties.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com