Micro-dosing spending involves making small, frequent purchases to better manage cash flow and minimize waste, contrasting with bulk purchasing, which leverages volume discounts and inventory stockpiling to reduce unit costs. This approach affects consumer behavior, supply chain dynamics, and overall economic efficiency by balancing immediate affordability against long-term savings. Explore more to understand how these spending strategies impact market trends and financial planning.
Why it is important
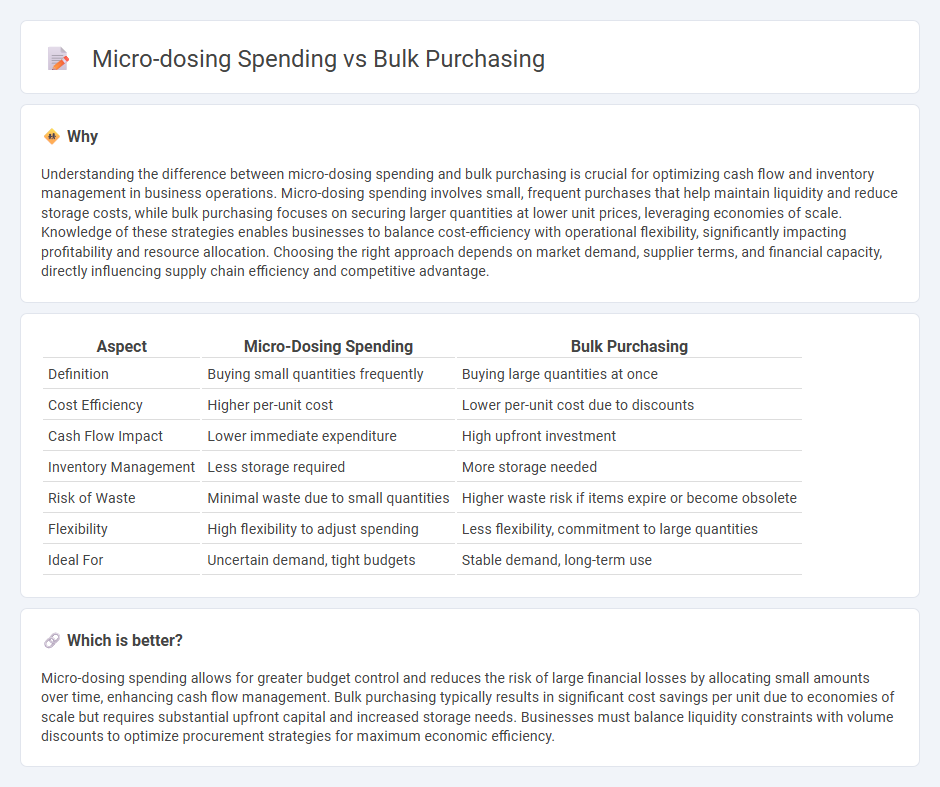
Understanding the difference between micro-dosing spending and bulk purchasing is crucial for optimizing cash flow and inventory management in business operations. Micro-dosing spending involves small, frequent purchases that help maintain liquidity and reduce storage costs, while bulk purchasing focuses on securing larger quantities at lower unit prices, leveraging economies of scale. Knowledge of these strategies enables businesses to balance cost-efficiency with operational flexibility, significantly impacting profitability and resource allocation. Choosing the right approach depends on market demand, supplier terms, and financial capacity, directly influencing supply chain efficiency and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-Dosing Spending | Bulk Purchasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying small quantities frequently | Buying large quantities at once |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher per-unit cost | Lower per-unit cost due to discounts |
| Cash Flow Impact | Lower immediate expenditure | High upfront investment |
| Inventory Management | Less storage required | More storage needed |
| Risk of Waste | Minimal waste due to small quantities | Higher waste risk if items expire or become obsolete |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to adjust spending | Less flexibility, commitment to large quantities |
| Ideal For | Uncertain demand, tight budgets | Stable demand, long-term use |
Which is better?
Micro-dosing spending allows for greater budget control and reduces the risk of large financial losses by allocating small amounts over time, enhancing cash flow management. Bulk purchasing typically results in significant cost savings per unit due to economies of scale but requires substantial upfront capital and increased storage needs. Businesses must balance liquidity constraints with volume discounts to optimize procurement strategies for maximum economic efficiency.
Connection
Micro-dosing spending involves making frequent, small purchases to manage cash flow and reduce immediate costs, while bulk purchasing focuses on acquiring large quantities at discounted rates to lower per-unit expenses. Both strategies optimize budget efficiency by balancing short-term liquidity with long-term cost savings. Companies and consumers leverage these methods to strategically control expenses and maximize economic value.
Key Terms
Economies of scale
Bulk purchasing leverages economies of scale by reducing per-unit costs through large volume acquisitions, making it cost-effective for high-demand products. In contrast, micro-dosing spending incurs higher per-unit costs but minimizes waste and allows for flexible, precise consumption tailored to specific needs. Explore how strategic balancing between these methods can optimize budget efficiency and inventory management.
Cash flow management
Bulk purchasing enhances cash flow management by reducing per-unit costs and minimizing frequent procurement expenses, leading to substantial upfront capital allocation. Micro-dosing spending allows for tighter cash control and flexibility, avoiding large inventory holding costs and mitigating risks of overstocking. Explore more ways to optimize cash flow strategies tailored to your purchasing patterns.
Price discrimination
Price discrimination strategies in bulk purchasing allow consumers to benefit from lower per-unit costs by buying larger quantities, effectively reducing average spending for high-volume buyers. Micro-dosing spending, in contrast, involves purchasing minimal quantities at higher per-unit prices, catering to consumers valuing flexibility or trial usage over cost savings. Explore deeper insights into pricing models and consumer behavior to optimize your purchasing strategy.
Source and External Links
Bulk Purchasing: Definition, Benefits, and More - Printful - Bulk purchasing is buying large quantities of a product at once to get a lower price per unit, saving money and allowing businesses to increase profit margins despite requiring more storage and planning.
Bulk Purchasing - ProcureDesk - Bulk purchasing is a procurement strategy to acquire goods in large quantities to leverage economies of scale and cut costs, though it requires careful demand forecasting, negotiation, and inventory management.
Guide to Bulk and Wholesale Buying - Amazon Business - Bulk buying means purchasing many units of a product for a discounted per-unit price, used by retailers, resellers, and consumers for cost savings and supply chain efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com