Skiplagging exploits pricing inefficiencies in airline ticketing by intentionally booking multi-leg flights to take advantage of lower fares on shorter segments. Arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences between markets, such as purchasing goods or assets at a lower price in one market and selling them at a higher price in another. Explore the detailed mechanisms and economic implications of skiplagging and arbitrage to understand their impact on market efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between skiplagging and arbitrage is crucial for optimizing economic strategies in travel and finance sectors. Skiplagging involves booking multi-leg flights to exploit pricing inefficiencies, affecting airline revenue management. Arbitrage exploits price differences between markets to generate profit, ensuring market efficiency. Distinguishing these practices helps businesses and consumers make informed decisions while complying with legal and ethical standards.
Comparison Table
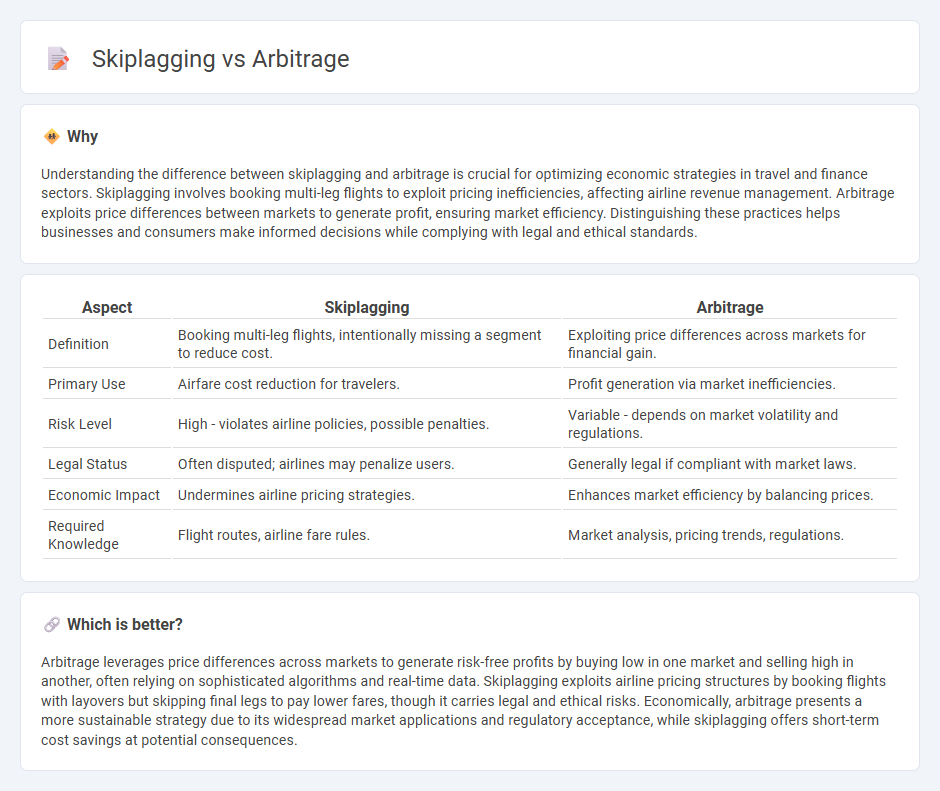
| Aspect | Skiplagging | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Booking multi-leg flights, intentionally missing a segment to reduce cost. | Exploiting price differences across markets for financial gain. |
| Primary Use | Airfare cost reduction for travelers. | Profit generation via market inefficiencies. |
| Risk Level | High - violates airline policies, possible penalties. | Variable - depends on market volatility and regulations. |
| Legal Status | Often disputed; airlines may penalize users. | Generally legal if compliant with market laws. |
| Economic Impact | Undermines airline pricing strategies. | Enhances market efficiency by balancing prices. |
| Required Knowledge | Flight routes, airline fare rules. | Market analysis, pricing trends, regulations. |
Which is better?
Arbitrage leverages price differences across markets to generate risk-free profits by buying low in one market and selling high in another, often relying on sophisticated algorithms and real-time data. Skiplagging exploits airline pricing structures by booking flights with layovers but skipping final legs to pay lower fares, though it carries legal and ethical risks. Economically, arbitrage presents a more sustainable strategy due to its widespread market applications and regulatory acceptance, while skiplagging offers short-term cost savings at potential consequences.
Connection
Skiplagging exploits pricing inefficiencies in airline ticketing by booking multi-leg flights with the intent to skip segments, creating arbitrage opportunities between different fare classes. Arbitrage involves capitalizing on price discrepancies in markets, and skiplagging acts as a form of consumer-driven arbitrage by leveraging airline pricing policies. Both practices reveal gaps in market efficiency, impacting revenue management strategies and influencing economic models of supply and demand.
Key Terms
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets by purchasing assets at a lower price and selling them at a higher price for profit. Skiplagging leverages hidden city ticketing in airfare, booking flights with a layover to capitalize on cheaper fares to intermediate destinations. Explore the nuances of these strategies to understand their applications and legal considerations.
Market Inefficiency
Arbitrage exploits market inefficiencies by simultaneously buying and selling assets in different markets to profit from price discrepancies. Skiplagging leverages airline pricing structures by booking multi-leg flights and intentionally missing the final segment to secure cheaper fares. Discover how these strategies capitalize on market inefficiencies and their impact on consumer behavior.
Hidden City Ticketing
Hidden city ticketing is a travel strategy where passengers book flights with layovers in their intended destination, effectively paying less than direct flight prices. Unlike arbitrage, which exploits price differences across markets, hidden city ticketing relies on airlines' pricing models and often involves risks like ticket cancellation or no checked baggage allowed. Explore more about how hidden city ticketing can save money on flights and the potential pitfalls associated with it.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of capitalizing on a price difference in two or more markets by simultaneously buying and selling an asset to lock in profit from the price discrepancy.
Arbitrage | Definition and Examples - A Common Trading Strategy - Arbitrage involves buying an asset in one market at a lower price and selling it in another market at a higher price to profit from the imbalance, with the expectation that prices will eventually converge.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Pure arbitrage is a risk-free strategy where an investor exploits temporary price differences for the same asset across different markets, though such opportunities have become rare due to advanced technology and market efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com