Slowbalization reshapes global trade by emphasizing regional supply chains over long-distance dependencies, reducing risks associated with geopolitical tensions and transportation delays. Nearshoring accelerates this trend by moving production closer to consumer markets, enhancing responsiveness and cost efficiency. Explore how these shifts impact economic strategies and global competitiveness.
Why it is important
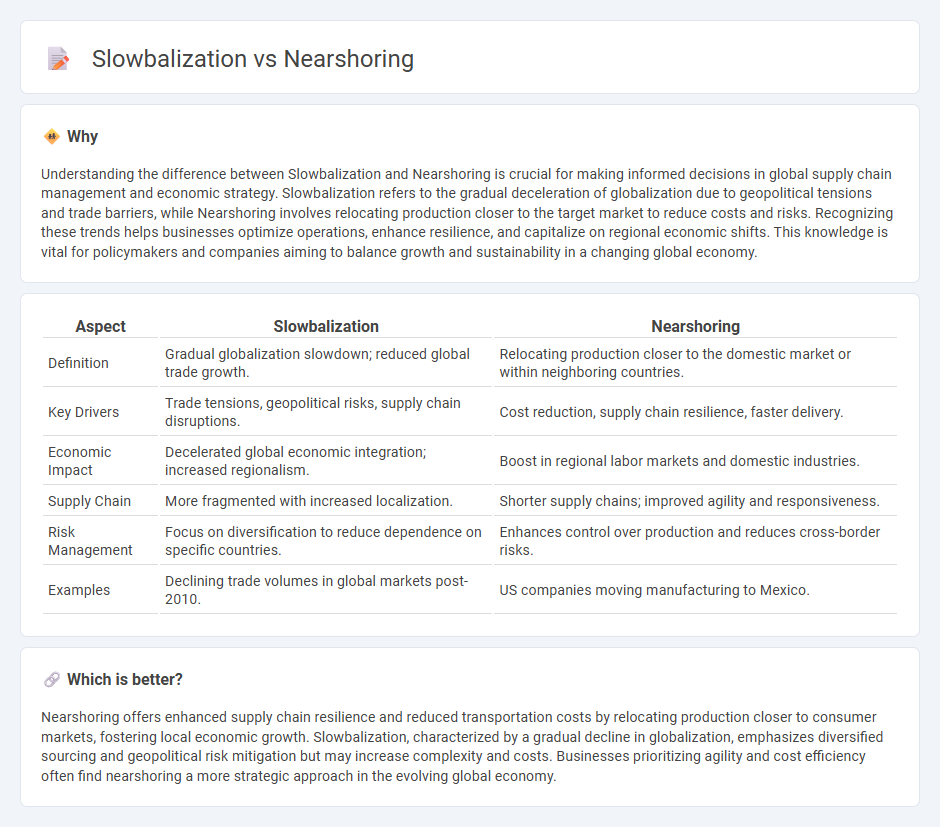
Understanding the difference between Slowbalization and Nearshoring is crucial for making informed decisions in global supply chain management and economic strategy. Slowbalization refers to the gradual deceleration of globalization due to geopolitical tensions and trade barriers, while Nearshoring involves relocating production closer to the target market to reduce costs and risks. Recognizing these trends helps businesses optimize operations, enhance resilience, and capitalize on regional economic shifts. This knowledge is vital for policymakers and companies aiming to balance growth and sustainability in a changing global economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Nearshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual globalization slowdown; reduced global trade growth. | Relocating production closer to the domestic market or within neighboring countries. |
| Key Drivers | Trade tensions, geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions. | Cost reduction, supply chain resilience, faster delivery. |
| Economic Impact | Decelerated global economic integration; increased regionalism. | Boost in regional labor markets and domestic industries. |
| Supply Chain | More fragmented with increased localization. | Shorter supply chains; improved agility and responsiveness. |
| Risk Management | Focus on diversification to reduce dependence on specific countries. | Enhances control over production and reduces cross-border risks. |
| Examples | Declining trade volumes in global markets post-2010. | US companies moving manufacturing to Mexico. |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers enhanced supply chain resilience and reduced transportation costs by relocating production closer to consumer markets, fostering local economic growth. Slowbalization, characterized by a gradual decline in globalization, emphasizes diversified sourcing and geopolitical risk mitigation but may increase complexity and costs. Businesses prioritizing agility and cost efficiency often find nearshoring a more strategic approach in the evolving global economy.
Connection
Slowbalization, characterized by a deceleration in global trade growth and supply chain integration, drives companies to adopt nearshoring strategies to reduce dependence on distant suppliers and mitigate geopolitical risks. Nearshoring enhances economic resilience by localizing production closer to end markets, improving supply chain agility in an era of slower globalization. This synergy between slowbalization and nearshoring reshapes global economic dynamics, emphasizing regional economic clusters and shorter cross-border trade routes.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Nearshoring reduces supply chain risks by relocating manufacturing closer to end markets, enhancing responsiveness and cost-efficiency compared to traditional offshore outsourcing. Slowbalization emphasizes regional supply chain resilience, diversification, and sustainability amid global trade uncertainties and geopolitical tensions. Explore how these strategies reshape global supply chains and impact business competitiveness.
Trade Flows
Nearshoring accelerates trade flows by relocating production closer to consumer markets, enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing transportation costs. Slowbalization reflects a gradual deceleration of global trade growth, driven by geopolitical tensions, rising protectionism, and shifting economic policies, causing more localized trade patterns. Explore detailed analyses of nearshoring and slowbalization impacts on global trade to better understand evolving market dynamics.
Regionalization
Nearshoring emphasizes relocating business processes closer to a company's home country to reduce costs and enhance supply chain efficiency, while slowbalization reflects a gradual slowdown in global trade growth driven by trade tensions and shifting geopolitical dynamics. Regionalization prioritizes strengthening local and regional supply networks to mitigate risks associated with global dependencies and to support economic resilience. Discover how adopting regionalization strategies can transform your business operations and supply chain stability.
Source and External Links
Nearshoring - Nearshoring is outsourcing business processes, often IT, to companies in a nearby country, frequently one sharing a border, to benefit from proximity and related advantages.
Nearshoring in Mexico - Nearshoring moves production closer to consumers to reduce costs and supply chain disruptions, heavily driven by US tariffs, trade agreements, COVID-19, transport cost rises, and geopolitical factors, offering Mexico significant economic growth potential.
What is Nearshoring? Definition, Benefits & Strategies - Anvyl - Nearshoring emphasizes working with suppliers in nearby countries to benefit from geographical closeness, shared culture, time zones, risk diversification, enhanced supply chain flexibility, and reduced environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com