Supercore inflation measures persistent price changes by excluding volatile sectors like food and energy, offering a clearer view of underlying inflation trends. Trimmed mean inflation calculates the average price changes after removing extreme price movements, providing a more stable indicator of core inflation. Explore the nuances between these inflation metrics to better understand their impact on economic policy.
Why it is important
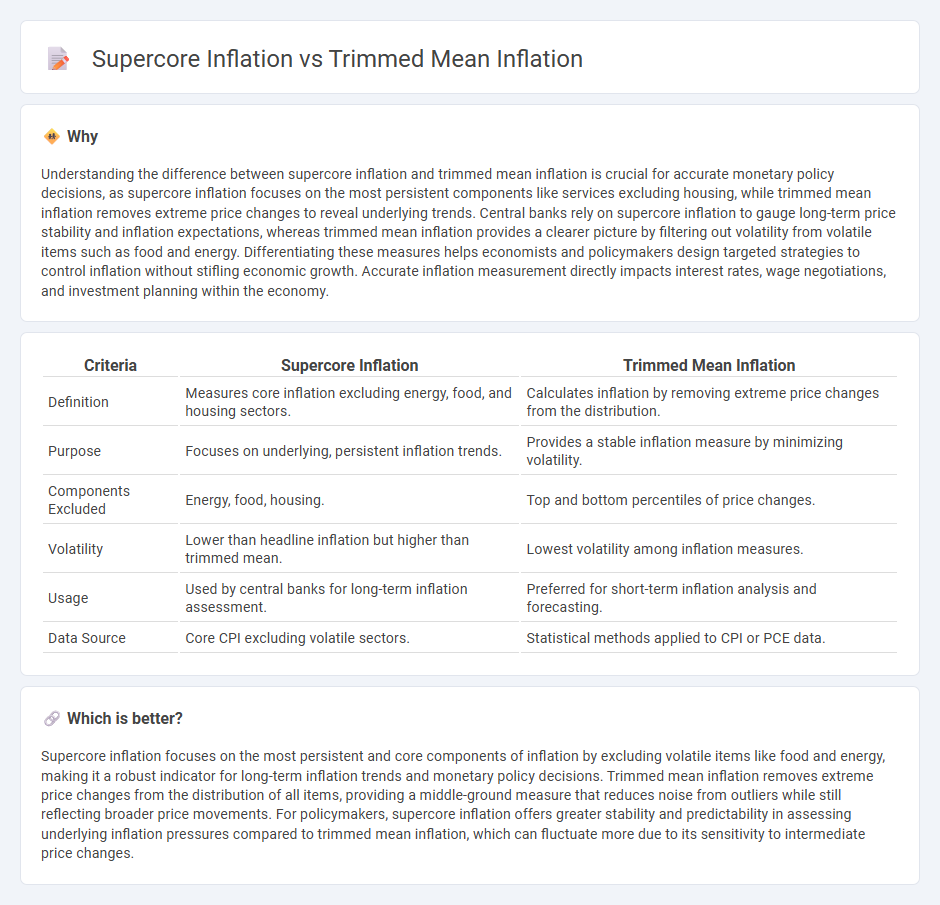
Understanding the difference between supercore inflation and trimmed mean inflation is crucial for accurate monetary policy decisions, as supercore inflation focuses on the most persistent components like services excluding housing, while trimmed mean inflation removes extreme price changes to reveal underlying trends. Central banks rely on supercore inflation to gauge long-term price stability and inflation expectations, whereas trimmed mean inflation provides a clearer picture by filtering out volatility from volatile items such as food and energy. Differentiating these measures helps economists and policymakers design targeted strategies to control inflation without stifling economic growth. Accurate inflation measurement directly impacts interest rates, wage negotiations, and investment planning within the economy.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Supercore Inflation | Trimmed Mean Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures core inflation excluding energy, food, and housing sectors. | Calculates inflation by removing extreme price changes from the distribution. |
| Purpose | Focuses on underlying, persistent inflation trends. | Provides a stable inflation measure by minimizing volatility. |
| Components Excluded | Energy, food, housing. | Top and bottom percentiles of price changes. |
| Volatility | Lower than headline inflation but higher than trimmed mean. | Lowest volatility among inflation measures. |
| Usage | Used by central banks for long-term inflation assessment. | Preferred for short-term inflation analysis and forecasting. |
| Data Source | Core CPI excluding volatile sectors. | Statistical methods applied to CPI or PCE data. |
Which is better?
Supercore inflation focuses on the most persistent and core components of inflation by excluding volatile items like food and energy, making it a robust indicator for long-term inflation trends and monetary policy decisions. Trimmed mean inflation removes extreme price changes from the distribution of all items, providing a middle-ground measure that reduces noise from outliers while still reflecting broader price movements. For policymakers, supercore inflation offers greater stability and predictability in assessing underlying inflation pressures compared to trimmed mean inflation, which can fluctuate more due to its sensitivity to intermediate price changes.
Connection
Supercore inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, closely aligns with trimmed mean inflation by focusing on the persistent underlying price trends within the economy. Both measures filter out extreme price movements to provide a clearer signal of inflationary pressures affecting monetary policy decisions. This connection helps central banks evaluate core inflation dynamics more accurately for effective economic planning.
Key Terms
Outliers
Trimmed mean inflation measures core price changes by excluding extreme outliers in the data set, offering a more stable reflection of underlying inflation trends. Supercore inflation narrows this focus further by analyzing only the most persistent and widespread price movements, filtering out temporary shocks and volatility. Explore deeper insights into how these metrics differentiate to better understand inflation dynamics.
Core Services
Trimmed mean inflation excludes extreme price changes by removing the highest and lowest inflation rates to provide a more stable measure of underlying price trends, while supercore inflation specifically targets core services prices, which tend to be more persistent and less volatile. Core services inflation captures sustained inflationary pressures driven by wages and rent, offering crucial insight into long-term inflation dynamics beyond goods and energy price fluctuations. Explore detailed analyses to understand how core services inflation shapes monetary policy and economic forecasting.
Volatility
Trimmed mean inflation excludes extreme price changes by removing the most volatile components, offering a smoother and more stable measure of underlying inflation trends. Supercore inflation narrows the focus further to highly persistent price changes in sectors like rents and services, providing insight into core inflation pressures less impacted by short-term volatility. Explore the differences and applications of these inflation metrics to better understand economic stability and monetary policy decisions.
Source and External Links
Consumer Price Data and Measures Explained - The trimmed mean inflation measure ranks individual price changes from lowest to highest, removes a specified percentage of the highest and lowest changes to reduce noise, and then averages the remaining prices weighted by expenditure shares, with examples like the 16% trimmed-mean CPI by the Cleveland Fed and a differently trimmed mean PCE by the Dallas Fed.
Background on Trimmed Mean Measures of Underlying Inflation - Trimmed mean inflation is calculated by ordering price changes and symmetrically excluding extreme values at both ends before averaging the middle portion, providing a core inflation gauge that excludes volatile price components on a period-by-period basis rather than excluding fixed items.
Dallas Trimmed Mean - Definition, How To Calculate, Advantages - The Dallas Trimmed Mean PCE Inflation Rate is a monthly core inflation measure that sorts price changes in the Personal Consumption Expenditures index, trims extreme changes, and averages the remainder to give a more stable indicator used by policymakers including the Federal Reserve for long-term economic planning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com