Biodiversity credits represent quantifiable environmental benefits aimed at preserving ecosystems and species, while circular economy tokens incentivize sustainable resource use by promoting recycling and waste reduction. Both mechanisms drive economic models focused on environmental impact but differ in scope, with biodiversity credits targeting conservation and circular tokens enhancing material efficiency. Explore how these innovative economic tools reshape sustainability and investment strategies.
Why it is important
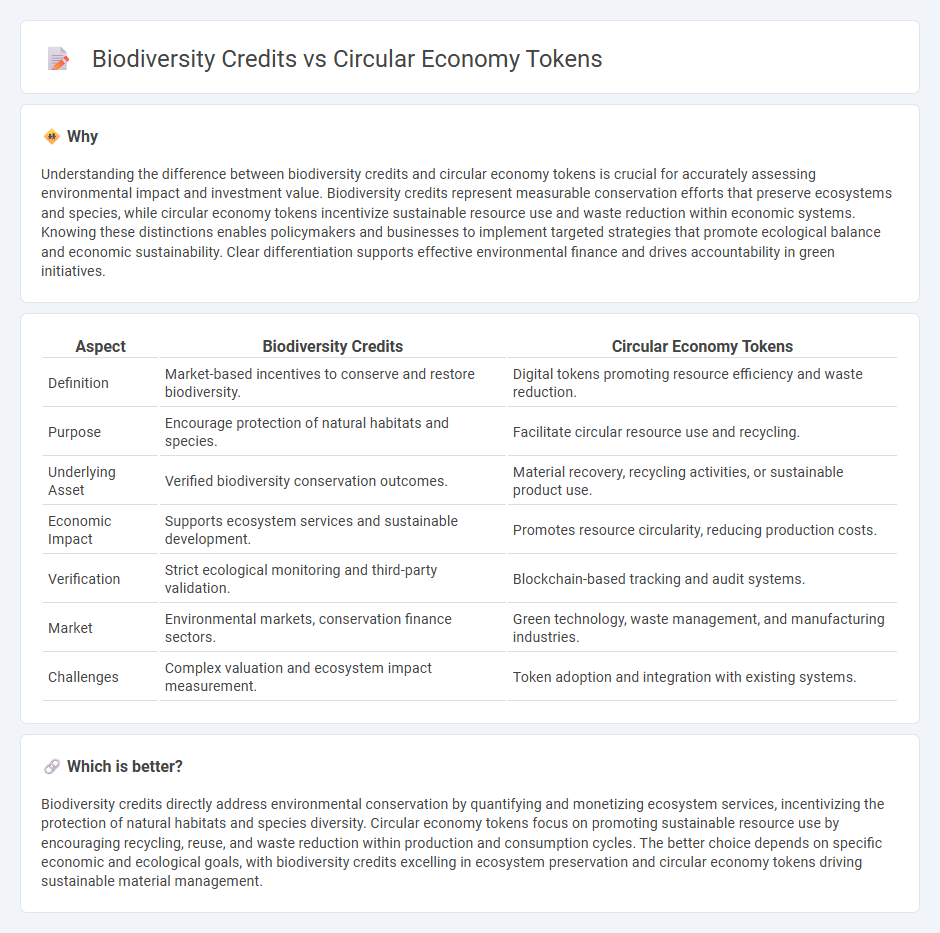
Understanding the difference between biodiversity credits and circular economy tokens is crucial for accurately assessing environmental impact and investment value. Biodiversity credits represent measurable conservation efforts that preserve ecosystems and species, while circular economy tokens incentivize sustainable resource use and waste reduction within economic systems. Knowing these distinctions enables policymakers and businesses to implement targeted strategies that promote ecological balance and economic sustainability. Clear differentiation supports effective environmental finance and drives accountability in green initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biodiversity Credits | Circular Economy Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-based incentives to conserve and restore biodiversity. | Digital tokens promoting resource efficiency and waste reduction. |
| Purpose | Encourage protection of natural habitats and species. | Facilitate circular resource use and recycling. |
| Underlying Asset | Verified biodiversity conservation outcomes. | Material recovery, recycling activities, or sustainable product use. |
| Economic Impact | Supports ecosystem services and sustainable development. | Promotes resource circularity, reducing production costs. |
| Verification | Strict ecological monitoring and third-party validation. | Blockchain-based tracking and audit systems. |
| Market | Environmental markets, conservation finance sectors. | Green technology, waste management, and manufacturing industries. |
| Challenges | Complex valuation and ecosystem impact measurement. | Token adoption and integration with existing systems. |
Which is better?
Biodiversity credits directly address environmental conservation by quantifying and monetizing ecosystem services, incentivizing the protection of natural habitats and species diversity. Circular economy tokens focus on promoting sustainable resource use by encouraging recycling, reuse, and waste reduction within production and consumption cycles. The better choice depends on specific economic and ecological goals, with biodiversity credits excelling in ecosystem preservation and circular economy tokens driving sustainable material management.
Connection
Biodiversity credits and circular economy tokens both serve as market-based instruments designed to incentivize sustainable practices and resource efficiency, linking environmental conservation with economic activity. Biodiversity credits quantify and monetize ecosystem services preservation, while circular economy tokens facilitate the tracking and exchange of materials within closed-loop systems to reduce waste. Their integration promotes a holistic approach, aligning financial incentives with ecological restoration and sustainable resource management.
Key Terms
Resource Regeneration
Circular economy tokens incentivize sustainable resource use by tracking material lifecycle and promoting recycling, thereby reducing waste and conserving natural capital. Biodiversity credits fund conservation projects aimed at restoring habitats and enhancing ecosystem services, directly supporting species preservation and ecological balance. Explore how both tools drive resource regeneration and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Tokenization
Circular economy tokens represent assets that promote resource efficiency and waste reduction through blockchain-based incentivization, enabling transparent tracking of sustainable production cycles. Biodiversity credits tokenize ecosystem conservation efforts by quantifying, verifying, and trading biodiversity preservation activities to support habitat protection and restoration. Explore the distinctions and potential of these digital assets further to understand their impact on sustainable development and environmental finance.
Ecosystem Services
Circular economy tokens represent tradable digital assets that incentivize sustainable resource use by tracking material flows and promoting waste reduction. Biodiversity credits specifically quantify ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, habitat preservation, and water filtration, enabling market-based conservation funding. Explore detailed mechanisms and impacts of both approaches to enhance ecosystem service valuation.
Source and External Links
Tokenized Circular Economy - Digital tokens on blockchain create verifiable lifecycle records and use smart contracts to automate incentives for circular economy behaviors like recycling and product take-back programs, enhancing transparency and participation.
Leveraging tokenization in blockchain-based circular economy - Systems like RecycleToCoin incentivize recycling single-use plastics by rewarding participants with blockchain tokens redeemable for rewards or cryptocurrency, promoting active public involvement in sustainability efforts.
Blockchain can drive the Circular Economy | PA Consulting - Blockchain tokenizes natural resources into tradable digital identities, making resource value visible and motivating circular behaviors through rewards, exemplified by solutions like Plastic Bank's digital tokens for recycled plastics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com