Alternative data lending leverages non-traditional information such as social media activity, utility payments, and rental history to assess creditworthiness, providing access to credit for unbanked or thin-file consumers. Open banking enables secure data sharing between financial institutions and third-party providers through APIs, enhancing transparency and facilitating personalized financial products. Explore how these innovative approaches are transforming credit evaluation and customer experience in modern banking.
Why it is important
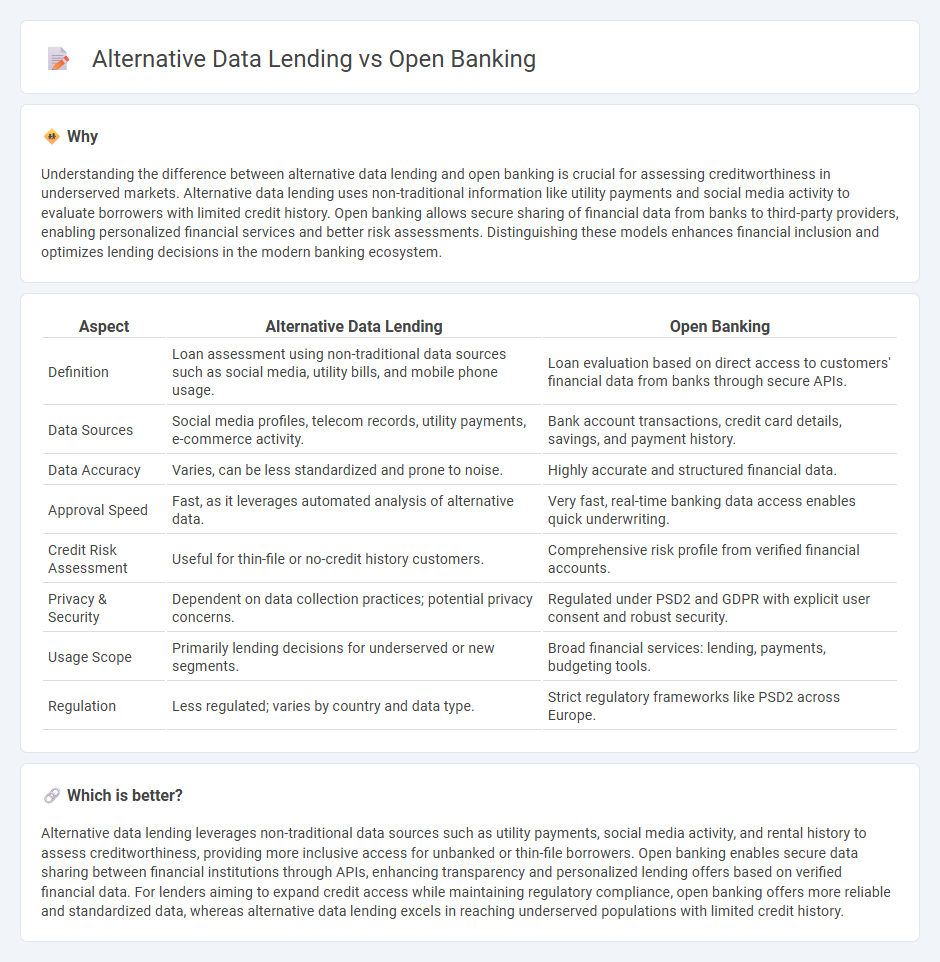
Understanding the difference between alternative data lending and open banking is crucial for assessing creditworthiness in underserved markets. Alternative data lending uses non-traditional information like utility payments and social media activity to evaluate borrowers with limited credit history. Open banking allows secure sharing of financial data from banks to third-party providers, enabling personalized financial services and better risk assessments. Distinguishing these models enhances financial inclusion and optimizes lending decisions in the modern banking ecosystem.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Data Lending | Open Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loan assessment using non-traditional data sources such as social media, utility bills, and mobile phone usage. | Loan evaluation based on direct access to customers' financial data from banks through secure APIs. |
| Data Sources | Social media profiles, telecom records, utility payments, e-commerce activity. | Bank account transactions, credit card details, savings, and payment history. |
| Data Accuracy | Varies, can be less standardized and prone to noise. | Highly accurate and structured financial data. |
| Approval Speed | Fast, as it leverages automated analysis of alternative data. | Very fast, real-time banking data access enables quick underwriting. |
| Credit Risk Assessment | Useful for thin-file or no-credit history customers. | Comprehensive risk profile from verified financial accounts. |
| Privacy & Security | Dependent on data collection practices; potential privacy concerns. | Regulated under PSD2 and GDPR with explicit user consent and robust security. |
| Usage Scope | Primarily lending decisions for underserved or new segments. | Broad financial services: lending, payments, budgeting tools. |
| Regulation | Less regulated; varies by country and data type. | Strict regulatory frameworks like PSD2 across Europe. |
Which is better?
Alternative data lending leverages non-traditional data sources such as utility payments, social media activity, and rental history to assess creditworthiness, providing more inclusive access for unbanked or thin-file borrowers. Open banking enables secure data sharing between financial institutions through APIs, enhancing transparency and personalized lending offers based on verified financial data. For lenders aiming to expand credit access while maintaining regulatory compliance, open banking offers more reliable and standardized data, whereas alternative data lending excels in reaching underserved populations with limited credit history.
Connection
Alternative data lending relies on non-traditional financial information such as utility payments, social media behavior, and mobile phone usage to assess creditworthiness. Open banking facilitates this process by providing secure access to customers' transactional data through APIs, enabling lenders to analyze real-time financial activity beyond credit scores. The integration of open banking with alternative data enhances risk assessment accuracy and broadens credit access for underserved consumers.
Key Terms
API Integration
Open banking leverages standardized APIs to securely share financial data from banks with third-party lenders, enabling real-time credit assessments and personalized loan offers. Alternative data lending integrates varied non-traditional data sources, such as utility payments, rental history, and social behavior, through APIs to augment creditworthiness evaluation beyond conventional banking records. Discover how API integration is revolutionizing lending models by balancing open banking frameworks with alternative data insights.
Consumer Consent
Open banking leverages consumer consent to securely share financial data via APIs, enabling lenders to access real-time transaction histories and account information. Alternative data lending relies on non-traditional data sources, such as utility payments and social media activity, often requiring explicit consent for data collection and usage. Explore how consumer consent frameworks shape transparency and trust in these innovative lending models.
Non-Traditional Data Sources
Open banking leverages secure API connections to access detailed financial transaction data directly from bank accounts, enabling precise credit risk assessment through real-time income and spending patterns. Alternative data lending taps into non-traditional sources such as utility payments, mobile phone usage, social media behavior, and e-commerce history to evaluate creditworthiness for individuals lacking comprehensive banking data. Explore the evolving landscape of non-traditional data sources in lending to understand how these innovations redefine credit access and financial inclusion.
Source and External Links
Open Banking - Wikipedia - Open banking is a system allowing customers to securely share financial data with authorized third parties through standardized APIs.
What is Open Banking? A Guide to the Future of Finance - Plaid - Open banking enables consumers to share financial data with third-party providers, enhancing the financial ecosystem through increased transparency and innovation.
Open Banking 101 - Mastercard - Open banking empowers consumers to securely share financial data, providing access to innovative financial experiences and more convenient financial management options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com