Neobanking offers fully digital banking experiences with streamlined services primarily for tech-savvy customers, emphasizing convenience and low fees. Offshore banking involves holding accounts outside one's home country, often used for asset protection, tax benefits, and privacy. Explore the key differences to determine which banking solution aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neobanking and offshore banking is crucial because neobanks provide digital-first, user-friendly financial services primarily within domestic jurisdictions, while offshore banks offer international banking services often used for asset protection and tax optimization. Neobanks focus on convenience, low fees, and technological innovation, catering to everyday banking needs. Offshore banking involves regulatory complexities and legal considerations important for global wealth management. Awareness of these distinctions helps individuals and businesses make informed decisions aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
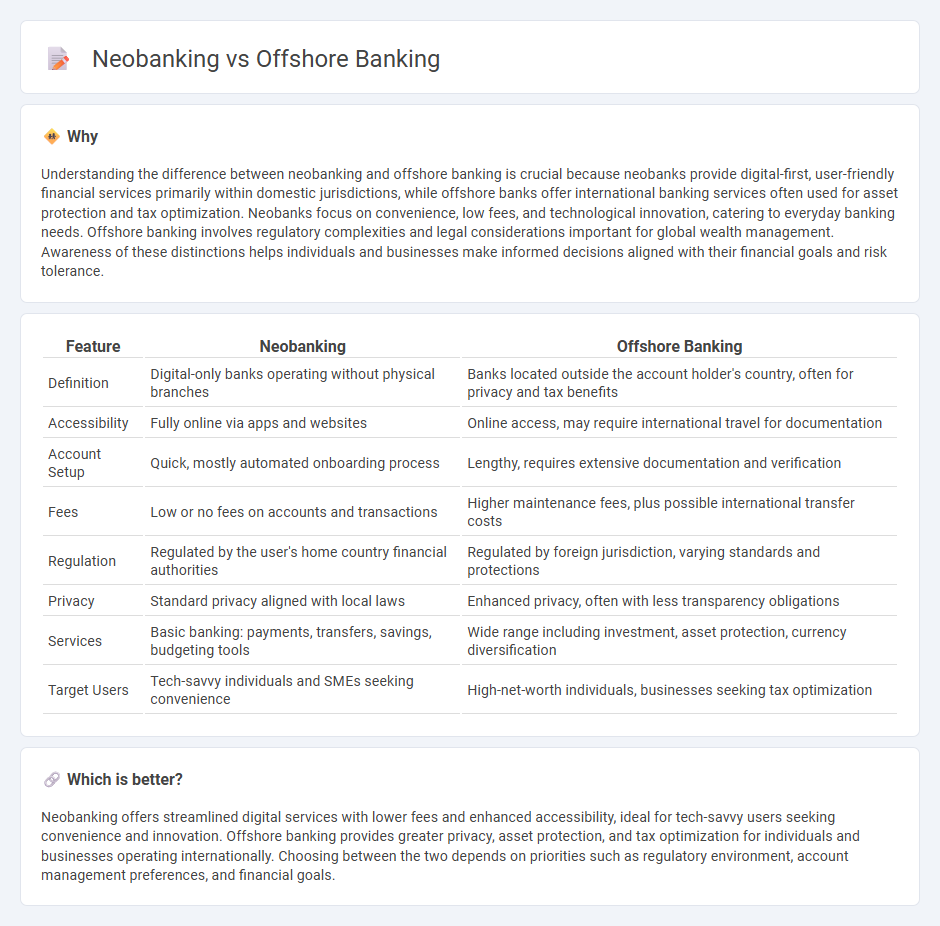
| Feature | Neobanking | Offshore Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks operating without physical branches | Banks located outside the account holder's country, often for privacy and tax benefits |
| Accessibility | Fully online via apps and websites | Online access, may require international travel for documentation |
| Account Setup | Quick, mostly automated onboarding process | Lengthy, requires extensive documentation and verification |
| Fees | Low or no fees on accounts and transactions | Higher maintenance fees, plus possible international transfer costs |
| Regulation | Regulated by the user's home country financial authorities | Regulated by foreign jurisdiction, varying standards and protections |
| Privacy | Standard privacy aligned with local laws | Enhanced privacy, often with less transparency obligations |
| Services | Basic banking: payments, transfers, savings, budgeting tools | Wide range including investment, asset protection, currency diversification |
| Target Users | Tech-savvy individuals and SMEs seeking convenience | High-net-worth individuals, businesses seeking tax optimization |
Which is better?
Neobanking offers streamlined digital services with lower fees and enhanced accessibility, ideal for tech-savvy users seeking convenience and innovation. Offshore banking provides greater privacy, asset protection, and tax optimization for individuals and businesses operating internationally. Choosing between the two depends on priorities such as regulatory environment, account management preferences, and financial goals.
Connection
Neobanking and offshore banking are connected through their shared emphasis on digital-first financial services and global accessibility. Neobanks often leverage offshore banking structures to offer clients enhanced privacy, tax benefits, and diversified investment opportunities beyond traditional banking jurisdictions. This synergy allows users to manage cross-border transactions seamlessly while benefiting from innovative, technology-driven banking solutions.
Key Terms
Regulatory Framework
Offshore banking operates under international regulatory frameworks that often emphasize privacy, asset protection, and tax efficiency, while neobanking is governed by domestic financial regulations focusing on consumer protection, digital security, and transparency. Offshore banks are typically subject to the laws of their offshore jurisdiction, which can vary widely in terms of compliance requirements and reporting standards. Explore the key regulatory differences to understand how these banking models impact security and legal obligations.
Digital-Only Services
Offshore banking offers international financial services with advantages like tax benefits, asset protection, and privacy, primarily through traditional bank infrastructures. Neobanking focuses on digital-only services, providing user-friendly mobile apps, real-time transactions, and lower fees without physical branches. Explore the differences further to decide which banking solution aligns best with your financial goals.
Cross-Border Transactions
Offshore banking offers enhanced privacy, tax advantages, and global asset diversification, making it ideal for high-net-worth individuals managing cross-border transactions. Neobanking emphasizes convenience and technology-driven services, providing seamless multi-currency accounts and low-cost international money transfers for everyday users conducting cross-border payments. Explore the detailed differences to choose the best financial solution for your international banking needs.
Source and External Links
Offshore bank - An offshore bank is a financial institution operated under an international banking license, often in tax haven jurisdictions, offering advantages such as strong privacy, low or no taxation, and protection from local instability, though it requires legal compliance with tax laws of the account holder's home country.
3 Key Benefits of Offshore Banking - Offshore banking provides key benefits including enhanced financial privacy and confidentiality due to strict secrecy laws in offshore jurisdictions, asset protection, and potential tax efficiency for individuals and companies.
Pros and Cons of Offshore Bank Accounts - Offshore bank accounts can offer stronger asset protection than domestic accounts, especially when combined with offshore trusts, and are legal if properly reported to tax authorities, but they are not tax evasion tools and must comply with applicable foreign and domestic laws.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com