Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to ensure transparent, immutable financial records, reducing errors and fraud compared to traditional manual accounting methods, which rely heavily on manual data entry and reconciliation. This shift enhances real-time data accuracy and streamlines auditing processes, offering businesses increased efficiency and security. Explore the benefits and practical applications of decentralized ledger accounting to revolutionize your financial management.
Why it is important
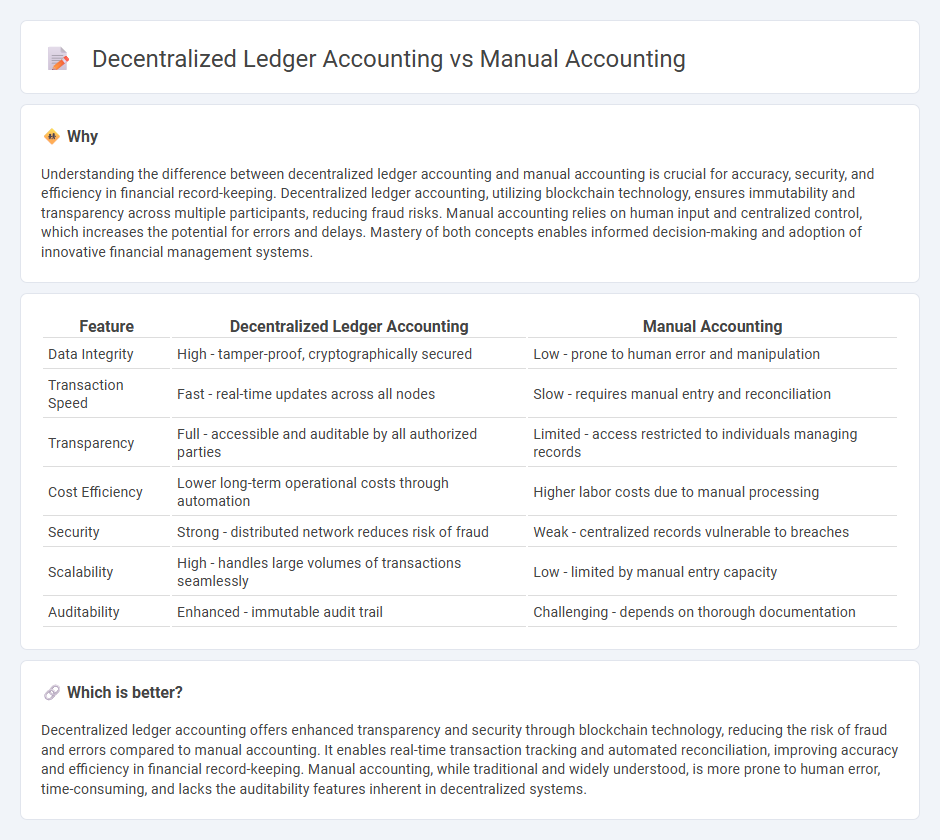
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and manual accounting is crucial for accuracy, security, and efficiency in financial record-keeping. Decentralized ledger accounting, utilizing blockchain technology, ensures immutability and transparency across multiple participants, reducing fraud risks. Manual accounting relies on human input and centralized control, which increases the potential for errors and delays. Mastery of both concepts enables informed decision-making and adoption of innovative financial management systems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Manual Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | High - tamper-proof, cryptographically secured | Low - prone to human error and manipulation |
| Transaction Speed | Fast - real-time updates across all nodes | Slow - requires manual entry and reconciliation |
| Transparency | Full - accessible and auditable by all authorized parties | Limited - access restricted to individuals managing records |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term operational costs through automation | Higher labor costs due to manual processing |
| Security | Strong - distributed network reduces risk of fraud | Weak - centralized records vulnerable to breaches |
| Scalability | High - handles large volumes of transactions seamlessly | Low - limited by manual entry capacity |
| Auditability | Enhanced - immutable audit trail | Challenging - depends on thorough documentation |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency and security through blockchain technology, reducing the risk of fraud and errors compared to manual accounting. It enables real-time transaction tracking and automated reconciliation, improving accuracy and efficiency in financial record-keeping. Manual accounting, while traditional and widely understood, is more prone to human error, time-consuming, and lacks the auditability features inherent in decentralized systems.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting and manual accounting both serve the fundamental purpose of recording financial transactions, but decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to provide a tamper-proof, transparent, and real-time record of entries. Manual accounting relies on traditional bookkeeping methods, often prone to human error and delayed updates, whereas decentralized ledgers enhance accuracy and trust through distributed consensus mechanisms. Integration of these systems can improve audit trails by combining trusted, immutable records with detailed, manual documentation practices.
Key Terms
Double-entry bookkeeping
Manual accounting relies on traditional double-entry bookkeeping, recording debits and credits in physical ledgers to maintain accurate financial records. Decentralized ledger accounting, exemplified by blockchain technology, automates these entries across distributed nodes, ensuring transparency and immutability without centralized control. Explore how integrating these accounting methods transforms financial management and auditing.
Centralized records
Manual accounting relies on centralized records maintained by a single authority, increasing the risk of errors, fraud, and data manipulation. In contrast, decentralized ledger accounting distributes record-keeping across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and reducing the potential for unauthorized alterations. Explore how adopting decentralized ledgers can revolutionize financial integrity and operational efficiency.
Blockchain
Manual accounting relies on traditional record-keeping methods prone to human error and limited transparency, while decentralized ledger accounting harnesses blockchain technology to offer immutable, transparent, and real-time financial records. Blockchain-enabled accounting eliminates the need for intermediaries by using cryptographic consensus to ensure data integrity and auditability across distributed networks. Explore the transformative potential of decentralized ledger accounting in revolutionizing financial transparency and security.
Source and External Links
manual accounting system | Wex - Law.Cornell.Edu - A manual accounting system records business transactions by hand in physical ledgers and books without using computer software, commonly used by small businesses to reduce costs and handle low transaction volumes.
Manual accounting system | EBSCO Research Starters - Manual accounting is a traditional, paper-based method of financial record-keeping that emphasizes careful, detailed work and is still favored by small businesses for its simplicity and low cost.
Manual Vs. Automated Accounting: What Are the Key Differences - Manual accounting requires recording each transaction by hand in journals and ledgers, which involves careful attention but is prone to human error and is less efficient than automated systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com