Crypto asset valuation relies on market prices and blockchain data to determine fair value, while replacement cost measures the expense of acquiring equivalent assets or services. Valuation methods for cryptocurrencies must account for high volatility, liquidity, and unique market dynamics, contrasting with traditional replacement cost calculations rooted in tangible asset acquisition. Explore further to understand the nuances and best practices in crypto asset valuation and replacement cost analysis.
Why it is important
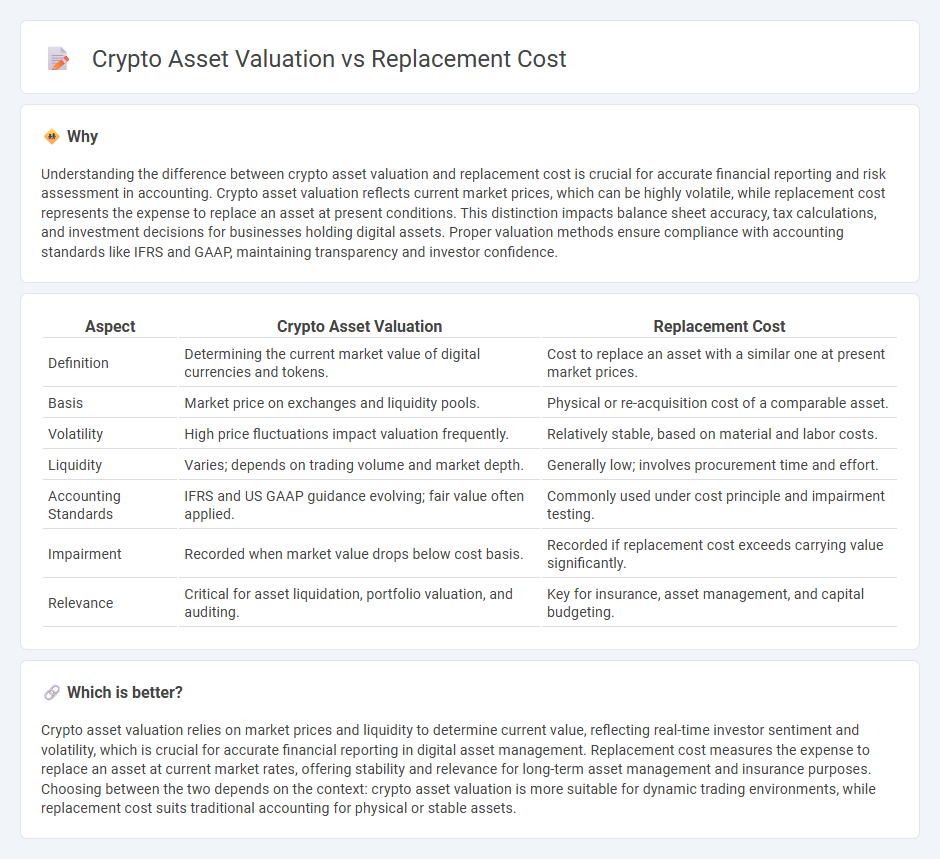
Understanding the difference between crypto asset valuation and replacement cost is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk assessment in accounting. Crypto asset valuation reflects current market prices, which can be highly volatile, while replacement cost represents the expense to replace an asset at present conditions. This distinction impacts balance sheet accuracy, tax calculations, and investment decisions for businesses holding digital assets. Proper valuation methods ensure compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP, maintaining transparency and investor confidence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crypto Asset Valuation | Replacement Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Determining the current market value of digital currencies and tokens. | Cost to replace an asset with a similar one at present market prices. |
| Basis | Market price on exchanges and liquidity pools. | Physical or re-acquisition cost of a comparable asset. |
| Volatility | High price fluctuations impact valuation frequently. | Relatively stable, based on material and labor costs. |
| Liquidity | Varies; depends on trading volume and market depth. | Generally low; involves procurement time and effort. |
| Accounting Standards | IFRS and US GAAP guidance evolving; fair value often applied. | Commonly used under cost principle and impairment testing. |
| Impairment | Recorded when market value drops below cost basis. | Recorded if replacement cost exceeds carrying value significantly. |
| Relevance | Critical for asset liquidation, portfolio valuation, and auditing. | Key for insurance, asset management, and capital budgeting. |
Which is better?
Crypto asset valuation relies on market prices and liquidity to determine current value, reflecting real-time investor sentiment and volatility, which is crucial for accurate financial reporting in digital asset management. Replacement cost measures the expense to replace an asset at current market rates, offering stability and relevance for long-term asset management and insurance purposes. Choosing between the two depends on the context: crypto asset valuation is more suitable for dynamic trading environments, while replacement cost suits traditional accounting for physical or stable assets.
Connection
Crypto asset valuation often incorporates replacement cost as a key metric, reflecting the expense to reacquire an identical asset under current market conditions. This approach provides a tangible estimate for accounting purposes, aligning book value with market realities amid crypto volatility. Replacement cost offers a realistic benchmark, supporting accurate financial reporting and risk assessment in the dynamic digital asset landscape.
Key Terms
Fair Value
Replacement cost reflects the expense required to acquire or replicate an asset, providing a tangible benchmark for valuation, while crypto asset valuation depends heavily on market dynamics, liquidity, and user demand, making Fair Value assessments more complex. Fair Value for crypto assets is often derived from real-time price discovery on exchanges, adjusted for volatility and underlying technology risks. Explore the nuances of Fair Value methodologies in crypto to understand how market participants gauge asset worth beyond traditional cost measures.
Historical Cost
Historical cost accounting records crypto assets at their original acquisition price, offering a stable and objective valuation method compared to fluctuating market prices. Replacement cost considers the current expense to acquire a similar crypto asset, reflecting real-time market conditions and potential investment risks. Explore how these valuation methods impact portfolio assessment and financial reporting for a deeper understanding.
Market Price
Market price in crypto asset valuation reflects the current trading value derived from supply and demand on exchanges. Replacement cost, typically used in traditional asset valuation, estimates the expense to recreate or replace the asset, but is less applicable in the volatile crypto market. Explore deeper insights into how market price drives crypto valuations and investment decisions.
Source and External Links
What Is Replacement Cost? - Replacement cost is the amount it would take to replace a damaged or stolen item with a similar one of the same make, model, and condition at current market prices, without accounting for depreciation.
Replacement Cost (Real Estate) - Definition, Calculate - In real estate, replacement cost is the estimated expense to construct a building of similar utility and quality to the one being evaluated, using current materials, labor, and building standards, but excluding costs like demolition or site accessibility.
Replacement cost definition - Replacement cost is the price an entity would pay to replace an existing asset with a similar one at current market prices, which may differ from the asset's market value and is used in insurance, acquisitions, and capital budgeting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com