ESG reporting focuses on disclosing environmental, social, and governance metrics that reflect a company's sustainable practices and ethical impact, often guided by frameworks like SASB and GRI. Regulatory reporting mandates financial disclosures to comply with legal standards imposed by authorities such as the SEC or IASB, ensuring transparency and accountability in financial performance. Explore how integrating ESG and regulatory reporting can enhance corporate accountability and investor trust.
Why it is important
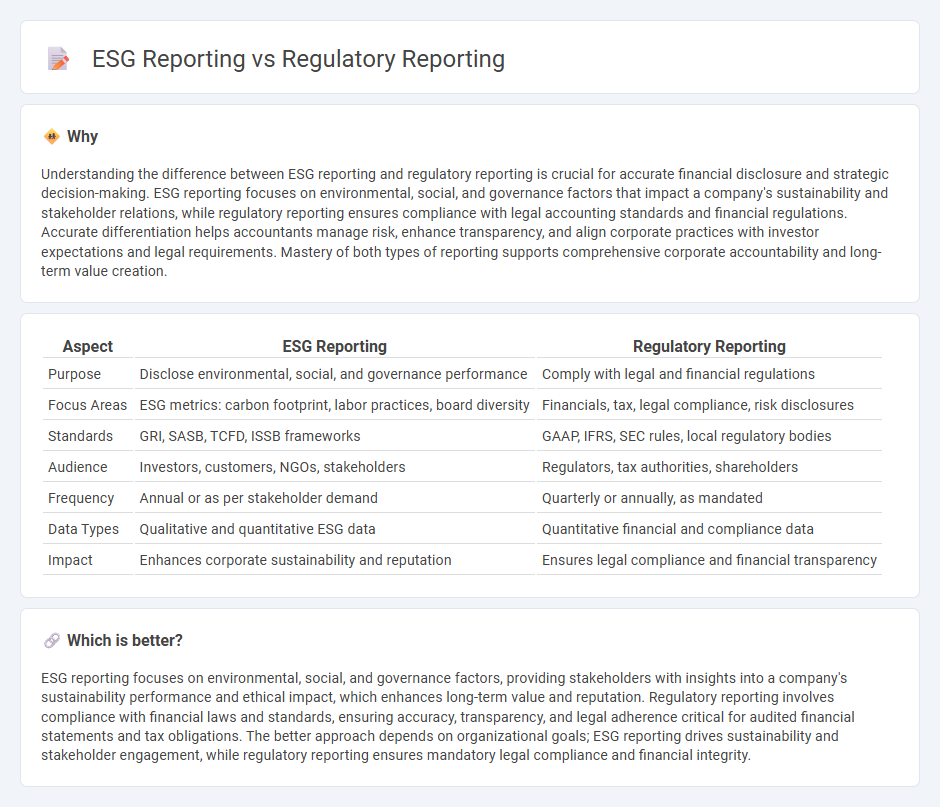
Understanding the difference between ESG reporting and regulatory reporting is crucial for accurate financial disclosure and strategic decision-making. ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors that impact a company's sustainability and stakeholder relations, while regulatory reporting ensures compliance with legal accounting standards and financial regulations. Accurate differentiation helps accountants manage risk, enhance transparency, and align corporate practices with investor expectations and legal requirements. Mastery of both types of reporting supports comprehensive corporate accountability and long-term value creation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Reporting | Regulatory Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Disclose environmental, social, and governance performance | Comply with legal and financial regulations |
| Focus Areas | ESG metrics: carbon footprint, labor practices, board diversity | Financials, tax, legal compliance, risk disclosures |
| Standards | GRI, SASB, TCFD, ISSB frameworks | GAAP, IFRS, SEC rules, local regulatory bodies |
| Audience | Investors, customers, NGOs, stakeholders | Regulators, tax authorities, shareholders |
| Frequency | Annual or as per stakeholder demand | Quarterly or annually, as mandated |
| Data Types | Qualitative and quantitative ESG data | Quantitative financial and compliance data |
| Impact | Enhances corporate sustainability and reputation | Ensures legal compliance and financial transparency |
Which is better?
ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors, providing stakeholders with insights into a company's sustainability performance and ethical impact, which enhances long-term value and reputation. Regulatory reporting involves compliance with financial laws and standards, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and legal adherence critical for audited financial statements and tax obligations. The better approach depends on organizational goals; ESG reporting drives sustainability and stakeholder engagement, while regulatory reporting ensures mandatory legal compliance and financial integrity.
Connection
ESG reporting and regulatory reporting are interconnected through compliance frameworks that require transparent disclosure of environmental, social, and governance factors alongside financial data. Both reporting types rely on standardized accounting principles to ensure accuracy, consistency, and accountability for stakeholders including investors, regulators, and analysts. Integrating ESG metrics into regulatory reports enhances risk assessment and supports sustainable business practices aligned with evolving regulations.
Key Terms
Compliance
Regulatory reporting mandates accurate submission of financial, operational, and risk data to government authorities, ensuring adherence to legal standards and avoiding penalties. ESG reporting, while also focused on compliance, emphasizes transparency around environmental, social, and governance metrics to meet investor and stakeholder expectations. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the evolving compliance landscape in corporate reporting.
Disclosure
Regulatory reporting mandates the disclosure of financial and operational data to comply with legal standards set by authorities like the SEC and IFRS, ensuring transparency and accountability. ESG reporting focuses on the voluntary disclosure of environmental, social, and governance metrics to demonstrate corporate sustainability and ethical impact to stakeholders. Explore how combining regulatory and ESG disclosures can enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust.
Sustainability
Regulatory reporting mandates organizations to comply with legal standards by disclosing financial and operational data, while ESG reporting emphasizes environmental, social, and governance metrics to showcase sustainability performance. ESG reporting drives transparency on carbon emissions, resource usage, social responsibility, and governance practices, aligning with global sustainability goals such as the UN SDGs. Explore how integrating ESG insights into regulatory frameworks strengthens long-term sustainability strategies and corporate accountability.
Source and External Links
What is Regulatory Reporting? - SolveXia - Regulatory reporting is the process through which financial institutions submit data and information to regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements, promoting transparency, risk management, and trust in financial markets.
What is Regulatory Reporting: A Beginner's Guide - Finreg-E - Regulatory reporting is the systematic process of collecting and submitting information about an organisation's financial and operational compliance to authorities, involving various report types such as financial statements, risk exposure reports, and transaction reports.
What Is Regulatory Reporting? A Complete Guide - HighGear - Regulatory reporting is the submission of data to regulatory authorities to show compliance with regulations, with reporting frequency varying by report type and penalties for non-compliance including fines, legal fees, and reputational damage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com