Payroll crypto taxation involves tracking and reporting cryptocurrency payments as taxable income according to IRS guidelines, ensuring compliance with digital currency regulations. Payroll auditing focuses on examining payroll records and processes to detect discrepancies, errors, or fraud, maintaining financial accuracy and regulatory adherence. Explore the nuances and best practices for mastering both payroll crypto taxation and payroll auditing to enhance your accounting expertise.
Why it is important
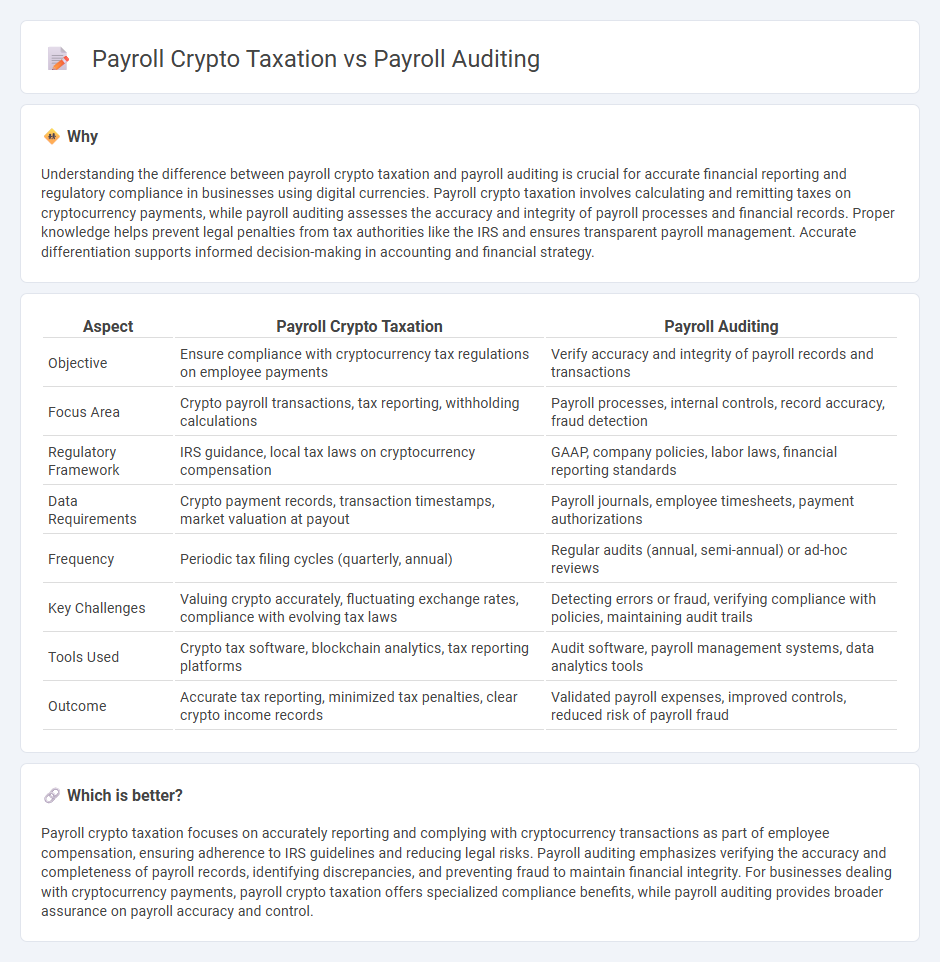
Understanding the difference between payroll crypto taxation and payroll auditing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance in businesses using digital currencies. Payroll crypto taxation involves calculating and remitting taxes on cryptocurrency payments, while payroll auditing assesses the accuracy and integrity of payroll processes and financial records. Proper knowledge helps prevent legal penalties from tax authorities like the IRS and ensures transparent payroll management. Accurate differentiation supports informed decision-making in accounting and financial strategy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Payroll Crypto Taxation | Payroll Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Ensure compliance with cryptocurrency tax regulations on employee payments | Verify accuracy and integrity of payroll records and transactions |
| Focus Area | Crypto payroll transactions, tax reporting, withholding calculations | Payroll processes, internal controls, record accuracy, fraud detection |
| Regulatory Framework | IRS guidance, local tax laws on cryptocurrency compensation | GAAP, company policies, labor laws, financial reporting standards |
| Data Requirements | Crypto payment records, transaction timestamps, market valuation at payout | Payroll journals, employee timesheets, payment authorizations |
| Frequency | Periodic tax filing cycles (quarterly, annual) | Regular audits (annual, semi-annual) or ad-hoc reviews |
| Key Challenges | Valuing crypto accurately, fluctuating exchange rates, compliance with evolving tax laws | Detecting errors or fraud, verifying compliance with policies, maintaining audit trails |
| Tools Used | Crypto tax software, blockchain analytics, tax reporting platforms | Audit software, payroll management systems, data analytics tools |
| Outcome | Accurate tax reporting, minimized tax penalties, clear crypto income records | Validated payroll expenses, improved controls, reduced risk of payroll fraud |
Which is better?
Payroll crypto taxation focuses on accurately reporting and complying with cryptocurrency transactions as part of employee compensation, ensuring adherence to IRS guidelines and reducing legal risks. Payroll auditing emphasizes verifying the accuracy and completeness of payroll records, identifying discrepancies, and preventing fraud to maintain financial integrity. For businesses dealing with cryptocurrency payments, payroll crypto taxation offers specialized compliance benefits, while payroll auditing provides broader assurance on payroll accuracy and control.
Connection
Payroll crypto taxation involves calculating and reporting tax liabilities for employee compensation paid in cryptocurrencies, intersecting directly with payroll auditing, which verifies the accuracy of these records and compliance with tax laws. Effective payroll auditing ensures that crypto payroll transactions are properly documented, preventing discrepancies and potential legal penalties. Both processes rely on detailed transaction tracking, regulatory knowledge, and adherence to financial reporting standards to maintain transparency and accountability in crypto payroll management.
Key Terms
**Payroll Auditing:**
Payroll auditing involves systematically reviewing payroll processes to ensure compliance with labor laws, tax regulations, and company policies, reducing the risk of financial discrepancies and penalties. This process verifies accurate employee compensation, tax withholding, and benefits distribution by cross-referencing payroll records with timesheets and tax filings. Explore the key benefits and best practices of payroll auditing to enhance financial accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Internal Controls
Payroll auditing centers on evaluating internal controls to ensure accuracy in employee compensation records, compliance with labor laws, and prevention of fraud or errors within payroll processes. Payroll crypto taxation requires robust internal controls to track, report, and comply with tax obligations related to cryptocurrency payments, addressing challenges such as valuation, transaction transparency, and regulatory compliance. Explore how integrating advanced internal controls can optimize both traditional payroll auditing and emerging crypto taxation frameworks.
Compliance
Payroll auditing ensures accuracy and compliance with labor laws and tax regulations by systematically reviewing payroll processes and documentation. Payroll crypto taxation deals with the complexities of reporting cryptocurrency payments as wages, requiring adherence to IRS guidelines and proper valuation of digital assets. Explore how businesses can maintain compliance in both traditional payroll audits and emerging crypto payroll challenges.
Source and External Links
See Payroll Audit Mistakes and Right Approaches - Payroll auditing involves risk assessment procedures, evaluating payroll-related internal controls, reconciling payroll to IRS forms like 941, reviewing payroll withholding accounts, and performing fraud-related payroll procedures if needed.
Payroll Audit: Checklist & How To Run It [Free Template] - A payroll audit is a regular review of payroll records to ensure correct payments, accurate deductions, and proper employee data; key steps include verifying employee data, hours worked versus paid, and all types of variable compensation such as overtime and bonuses.
How to Audit Payroll - Conducting a payroll audit entails verifying employee status and pay rates, cross-referencing hours worked with attendance data, checking variable payments, confirming tax and deduction accuracy, and ensuring compliance with changing employment regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com