Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data within corporate sustainability reports to enhance transparency and stakeholder trust. Integrated report assurance combines financial and non-financial information assurance, providing a holistic validation of an organization's overall performance and value creation strategy. Explore how these assurance types differ and their impact on corporate accountability and reporting.
Why it is important
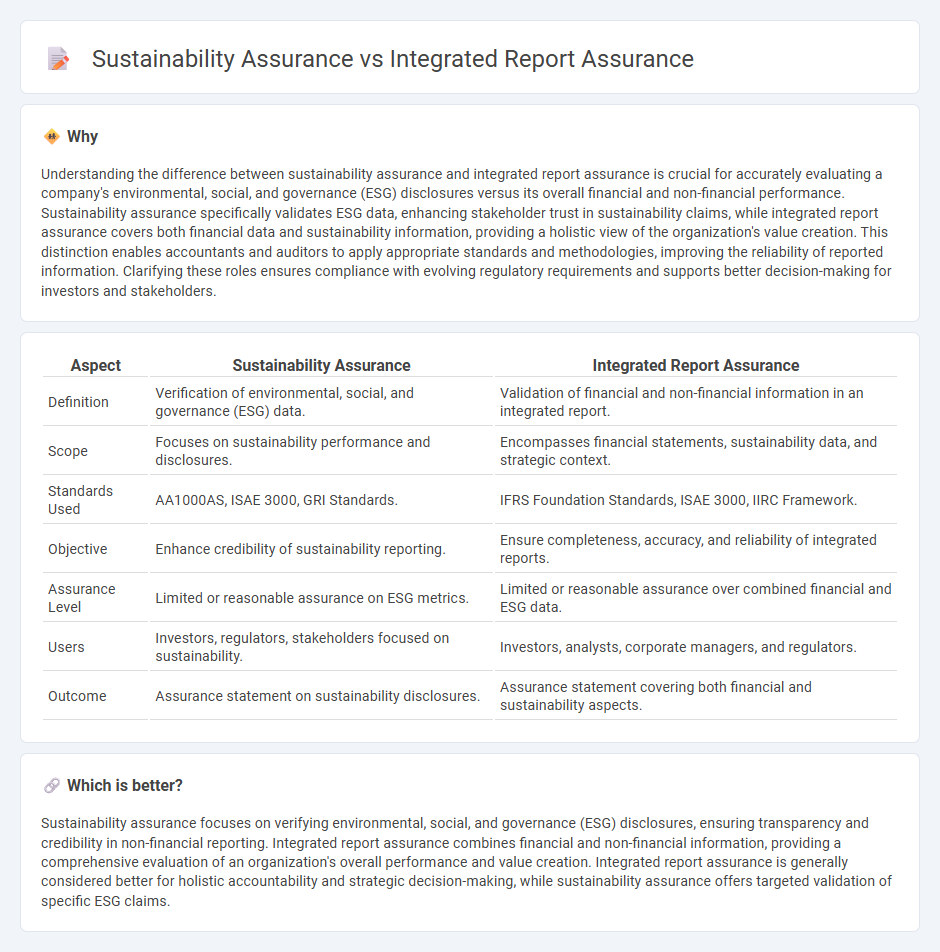
Understanding the difference between sustainability assurance and integrated report assurance is crucial for accurately evaluating a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures versus its overall financial and non-financial performance. Sustainability assurance specifically validates ESG data, enhancing stakeholder trust in sustainability claims, while integrated report assurance covers both financial data and sustainability information, providing a holistic view of the organization's value creation. This distinction enables accountants and auditors to apply appropriate standards and methodologies, improving the reliability of reported information. Clarifying these roles ensures compliance with evolving regulatory requirements and supports better decision-making for investors and stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Assurance | Integrated Report Assurance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verification of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data. | Validation of financial and non-financial information in an integrated report. |
| Scope | Focuses on sustainability performance and disclosures. | Encompasses financial statements, sustainability data, and strategic context. |
| Standards Used | AA1000AS, ISAE 3000, GRI Standards. | IFRS Foundation Standards, ISAE 3000, IIRC Framework. |
| Objective | Enhance credibility of sustainability reporting. | Ensure completeness, accuracy, and reliability of integrated reports. |
| Assurance Level | Limited or reasonable assurance on ESG metrics. | Limited or reasonable assurance over combined financial and ESG data. |
| Users | Investors, regulators, stakeholders focused on sustainability. | Investors, analysts, corporate managers, and regulators. |
| Outcome | Assurance statement on sustainability disclosures. | Assurance statement covering both financial and sustainability aspects. |
Which is better?
Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, ensuring transparency and credibility in non-financial reporting. Integrated report assurance combines financial and non-financial information, providing a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's overall performance and value creation. Integrated report assurance is generally considered better for holistic accountability and strategic decision-making, while sustainability assurance offers targeted validation of specific ESG claims.
Connection
Sustainability assurance and integrated report assurance are connected through their focus on enhancing the reliability and credibility of corporate disclosures. Both assurance processes evaluate non-financial information, such as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, alongside financial performance metrics to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive view of organizational impact. Firms increasingly integrate these assurance services to support transparent reporting frameworks and strengthen stakeholder trust in sustainability commitments.
Key Terms
Materiality
Integrated report assurance emphasizes the accuracy and completeness of material information that reflects an organization's strategy, governance, and performance, ensuring stakeholders receive a holistic view. Sustainability assurance specifically targets the verification of material environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, validating their relevance and reliability in line with stakeholder expectations. Explore further to understand the nuanced differences and implications of assurance practices focused on materiality.
Assurance Standards
Integrated report assurance primarily follows the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB) guidelines, emphasizing accuracy and reliability of financial and non-financial disclosures combined in a single document. Sustainability assurance aligns with standards such as the AccountAbility AA1000 Assurance Standard (AA1000AS) and ISAE 3000, focusing on the credibility and completeness of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information. Explore detailed distinctions and practical applications of both assurance types to enhance corporate reporting integrity.
Stakeholder Engagement
Integrated report assurance prioritizes verifying the accuracy of financial and non-financial information to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive view of organizational value creation over time. Sustainability assurance specifically evaluates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, ensuring transparency and credibility in sustainability performance to meet stakeholder expectations. Explore how these assurance types enhance stakeholder engagement and trust by diving deeper into their methodologies and impact.
Source and External Links
Executing the Board's Governance Responsibility for Integrated Reporting - This document highlights the importance of integrated reporting assurance in enhancing business resilience and sustainability by connecting all relevant business information.
Accelerating Integrated Reporting Assurance in the Public Interest - This report emphasizes the need for a global pathway to integrated reporting assurance to enhance confidence and credibility in integrated reporting.
A Roadmap for Accelerating Integrated Reporting Assurance - This resource outlines the importance and nature of integrated reporting assurance, utilizing ISAE 3000 as a foundational standard for assurance engagements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com