Continuous audit employs automated tools to provide real-time monitoring and analysis of financial transactions, enhancing accuracy and compliance. Forensic audit focuses on investigating financial discrepancies, fraud, and legal violations through detailed examination of records and evidence. Explore further to understand the distinct methodologies and applications of these audit types.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between continuous audit and forensic audit is crucial for effective risk management and ensuring financial integrity. Continuous audit involves real-time monitoring of financial transactions to detect discrepancies early, while forensic audit focuses on investigating suspected fraud or financial misconduct after irregularities are identified. Knowing when to apply each audit type helps organizations optimize resource allocation and enhance fraud prevention strategies. Accurate audit classification ultimately supports compliance with regulatory standards and protects stakeholder interests.
Comparison Table
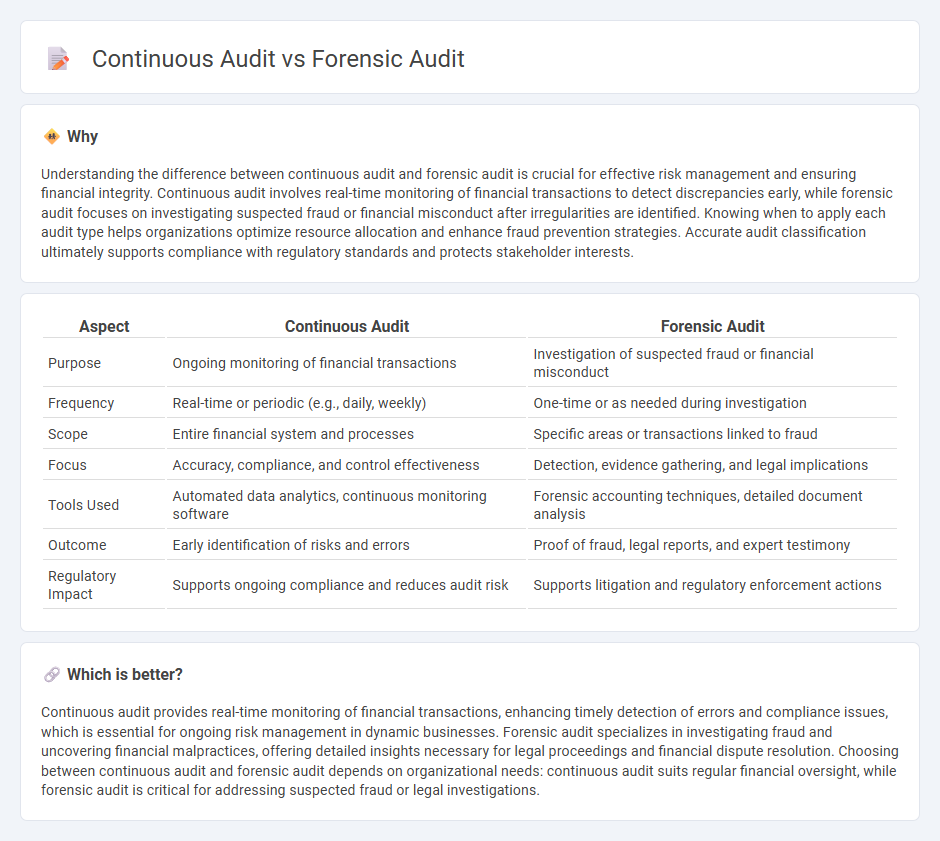
| Aspect | Continuous Audit | Forensic Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ongoing monitoring of financial transactions | Investigation of suspected fraud or financial misconduct |
| Frequency | Real-time or periodic (e.g., daily, weekly) | One-time or as needed during investigation |
| Scope | Entire financial system and processes | Specific areas or transactions linked to fraud |
| Focus | Accuracy, compliance, and control effectiveness | Detection, evidence gathering, and legal implications |
| Tools Used | Automated data analytics, continuous monitoring software | Forensic accounting techniques, detailed document analysis |
| Outcome | Early identification of risks and errors | Proof of fraud, legal reports, and expert testimony |
| Regulatory Impact | Supports ongoing compliance and reduces audit risk | Supports litigation and regulatory enforcement actions |
Which is better?
Continuous audit provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions, enhancing timely detection of errors and compliance issues, which is essential for ongoing risk management in dynamic businesses. Forensic audit specializes in investigating fraud and uncovering financial malpractices, offering detailed insights necessary for legal proceedings and financial dispute resolution. Choosing between continuous audit and forensic audit depends on organizational needs: continuous audit suits regular financial oversight, while forensic audit is critical for addressing suspected fraud or legal investigations.
Connection
Continuous audit and forensic audit are connected through their focus on enhancing financial accuracy and fraud detection within organizations. Continuous audits use automated tools to provide real-time monitoring and analysis of financial transactions, enabling early identification of irregularities. Forensic audits build on this foundation by investigating those irregularities in depth to uncover fraud, financial misconduct, and provide evidence for legal proceedings.
Key Terms
**Forensic Audit:**
Forensic audit involves detailed examination of financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, or legal violations, often conducted after suspicious activities are identified. It relies heavily on investigative techniques, evidence gathering, and expert analysis to support legal cases or regulatory compliance. Explore the differences and applications of forensic and continuous audits to enhance your organization's risk management approach.
Fraud Detection
Forensic audits focus on investigating specific instances of fraud through detailed examination of financial records and transactions, often triggered by suspicion or allegations. Continuous audits employ technology-driven monitoring systems to analyze data in real time, enabling early detection and prevention of fraudulent activities by identifying anomalies as they occur. Explore the differences in methodologies and benefits of forensic and continuous audits to enhance your fraud detection strategies.
Evidence Collection
Forensic audit emphasizes meticulous evidence collection to detect fraud and legal violations, ensuring data integrity for potential litigation. Continuous audit employs automated tools for real-time monitoring and evidence gathering, enhancing timely risk identification. Explore more to understand the distinct methodologies and benefits of each audit type.
Source and External Links
What is a Forensic Audit and Do I Need One? - This webpage provides an overview of forensic audits, including their purpose and process, especially in uncovering financial issues or fraud.
Forensic Audit Guide - This guide explains the definition, reasons, and steps involved in a forensic audit, highlighting its role in legal proceedings.
Forensic Accounting - This Wikipedia page discusses forensic accounting, focusing on its methodologies to detect financial misconduct and its role in legal trials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com