Blockchain audit trails provide immutable, transparent transaction records enhancing data integrity and security in accounting processes. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems logging offers comprehensive tracking of financial activities within integrated business functions but can be vulnerable to data manipulation. Explore the key differences between blockchain audit trails and ERP system logs to improve your organization's financial accountability.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between Blockchain audit trails and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems logging is crucial for ensuring accurate financial transparency and regulatory compliance in accounting. Blockchain audit trails provide immutable, time-stamped records that enhance security and traceability, whereas ERP system logs are typically centralized and susceptible to alterations. Accurate distinction supports effective risk management and fraud detection in accounting practices. Understanding these differences optimizes internal controls and audit reliability.
Comparison Table
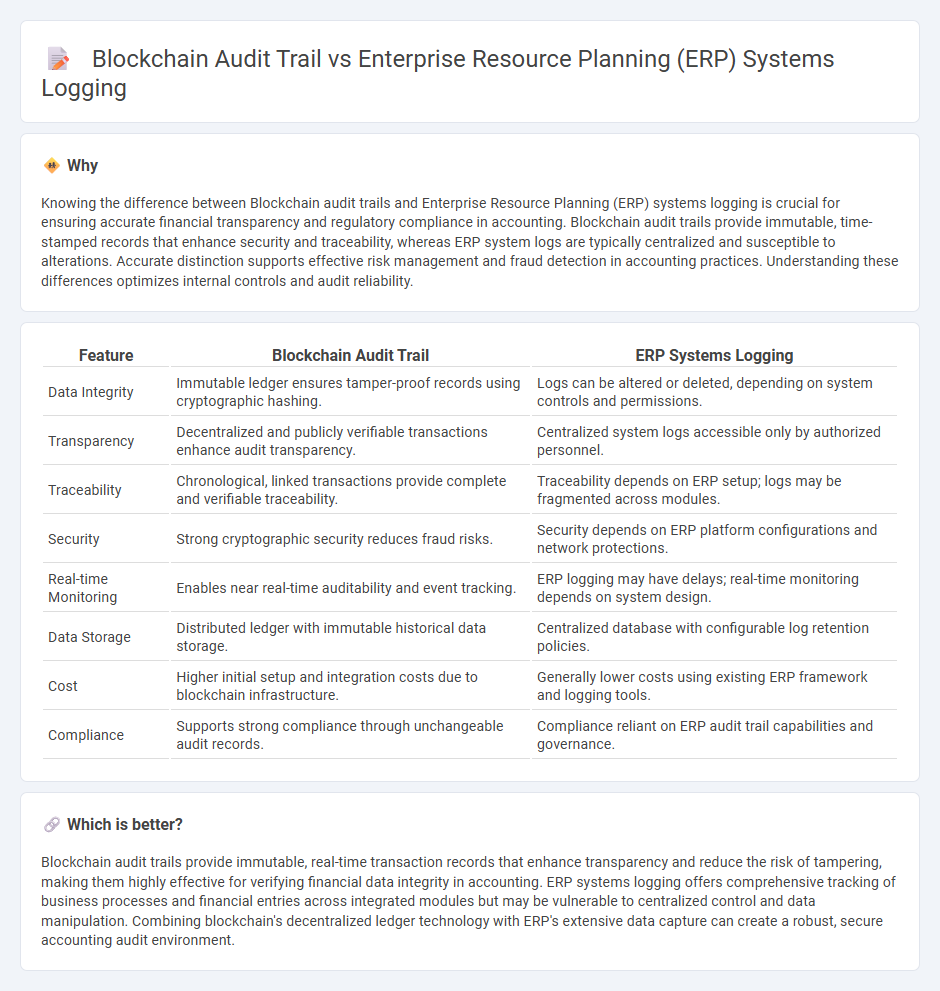
| Feature | Blockchain Audit Trail | ERP Systems Logging |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable ledger ensures tamper-proof records using cryptographic hashing. | Logs can be altered or deleted, depending on system controls and permissions. |
| Transparency | Decentralized and publicly verifiable transactions enhance audit transparency. | Centralized system logs accessible only by authorized personnel. |
| Traceability | Chronological, linked transactions provide complete and verifiable traceability. | Traceability depends on ERP setup; logs may be fragmented across modules. |
| Security | Strong cryptographic security reduces fraud risks. | Security depends on ERP platform configurations and network protections. |
| Real-time Monitoring | Enables near real-time auditability and event tracking. | ERP logging may have delays; real-time monitoring depends on system design. |
| Data Storage | Distributed ledger with immutable historical data storage. | Centralized database with configurable log retention policies. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup and integration costs due to blockchain infrastructure. | Generally lower costs using existing ERP framework and logging tools. |
| Compliance | Supports strong compliance through unchangeable audit records. | Compliance reliant on ERP audit trail capabilities and governance. |
Which is better?
Blockchain audit trails provide immutable, real-time transaction records that enhance transparency and reduce the risk of tampering, making them highly effective for verifying financial data integrity in accounting. ERP systems logging offers comprehensive tracking of business processes and financial entries across integrated modules but may be vulnerable to centralized control and data manipulation. Combining blockchain's decentralized ledger technology with ERP's extensive data capture can create a robust, secure accounting audit environment.
Connection
Blockchain audit trails and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems logging intersect by providing immutable, real-time transaction records that enhance the accuracy and transparency of financial data. ERP systems generate comprehensive logs of business processes, while blockchain secures these logs through cryptographic hashing, creating a tamper-proof audit trail. This integration strengthens internal controls and supports regulatory compliance by ensuring data integrity in accounting workflows.
Key Terms
Data Integrity
ERP systems logging provides comprehensive tracking of user activities and system changes, ensuring accountability within centralized databases. Blockchain audit trails offer immutable, decentralized records that enhance data integrity by preventing tampering and unauthorized modifications. Explore the advantages of each method to determine the best solution for your enterprise's data integrity needs.
Traceability
ERP systems logging provides centralized traceability by maintaining detailed records of transactions, user activities, and system changes within a single database, enabling efficient audit trails and compliance tracking. Blockchain audit trails offer decentralized, immutable records that enhance transparency and security, making it difficult to alter or tamper with transaction history while ensuring a reliable trace of all data entries. Explore the advantages and limitations of both technologies to understand their impact on operational traceability and audit integrity.
Immutability
ERP systems typically use centralized databases for logging, which can be vulnerable to tampering or unauthorized modifications, impacting the integrity of audit trails. Blockchain audit trails leverage decentralized ledger technology to ensure immutability, providing cryptographic proof that records cannot be altered retroactively without consensus from the network. Explore the fundamental differences in data security and audit reliability by delving deeper into ERP and blockchain-based audit solutions.
Source and External Links
What is ERP Security and Why Does it Matter? - Logpoint - ERP systems log user activities, transactions, and system events, which can be centrally monitored and audited, especially when integrated with SIEM tools for real-time security and compliance oversight.
Enterprise Resource Planning - ERP/MRP systems - MRPeasy - ERP systems automatically log and compile business-critical data--such as orders, shipments, invoices, and inventory changes--into centralized modules like accounts receivable, accounts payable, and general ledger for reporting and analysis.
What is an Enterprise Resource Planning System? | Workday - Modern ERP systems continuously document changes and transactions, providing an always-on audit trail that enables controllers to track, investigate, and resolve data issues in real time, while eliminating manual reconciliation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com