Cryptocurrency valuation involves assessing digital assets based on market value fluctuations, emphasizing fair value accounting principles. The cost model records cryptocurrencies at their initial purchase price, less any impairment, providing a more stable but potentially less reflective financial position. Explore deeper insights into the comparative advantages and implications of these accounting methods for a comprehensive understanding.
Why it is important
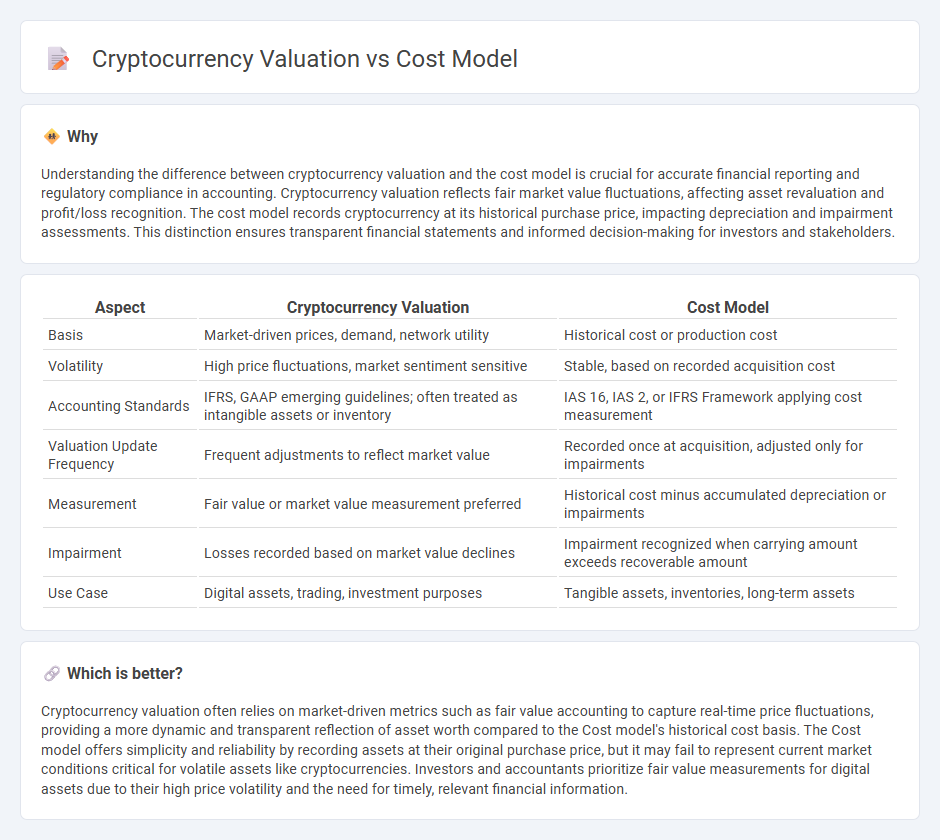
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency valuation and the cost model is crucial for accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance in accounting. Cryptocurrency valuation reflects fair market value fluctuations, affecting asset revaluation and profit/loss recognition. The cost model records cryptocurrency at its historical purchase price, impacting depreciation and impairment assessments. This distinction ensures transparent financial statements and informed decision-making for investors and stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Valuation | Cost Model |
|---|---|---|
| Basis | Market-driven prices, demand, network utility | Historical cost or production cost |
| Volatility | High price fluctuations, market sentiment sensitive | Stable, based on recorded acquisition cost |
| Accounting Standards | IFRS, GAAP emerging guidelines; often treated as intangible assets or inventory | IAS 16, IAS 2, or IFRS Framework applying cost measurement |
| Valuation Update Frequency | Frequent adjustments to reflect market value | Recorded once at acquisition, adjusted only for impairments |
| Measurement | Fair value or market value measurement preferred | Historical cost minus accumulated depreciation or impairments |
| Impairment | Losses recorded based on market value declines | Impairment recognized when carrying amount exceeds recoverable amount |
| Use Case | Digital assets, trading, investment purposes | Tangible assets, inventories, long-term assets |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency valuation often relies on market-driven metrics such as fair value accounting to capture real-time price fluctuations, providing a more dynamic and transparent reflection of asset worth compared to the Cost model's historical cost basis. The Cost model offers simplicity and reliability by recording assets at their original purchase price, but it may fail to represent current market conditions critical for volatile assets like cryptocurrencies. Investors and accountants prioritize fair value measurements for digital assets due to their high price volatility and the need for timely, relevant financial information.
Connection
Cryptocurrency valuation relies heavily on the cost model to determine the initial recognition and measurement of digital assets based on acquisition or production costs. The cost model provides a structured approach to record cryptocurrencies at historical cost less any impairment losses, ensuring consistent and transparent financial reporting. This connection enables accountants to track value fluctuations while maintaining compliance with accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP.
Key Terms
Historical Cost
Historical cost accounting records assets at their original purchase price, providing a stable and objective basis for evaluating investments compared to volatile cryptocurrency market prices. Cryptocurrency valuation often fluctuates due to market speculation, making historical cost a useful reference point for assessing long-term value and investment performance. Explore deeper insights into cost models and cryptocurrency valuation methods to optimize your financial strategy.
Fair Value
The cost model evaluates cryptocurrency valuation by considering the initial investment and production expenses, ignoring market fluctuations or speculative demand. Fair value in this context reflects an asset's true worth based on intrinsic factors, such as development costs and technological innovation, offering a more stable valuation framework. Explore comprehensive insights into how the cost model and fair value impact cryptocurrency assessment.
Volatility
Cost models provide a structured approach to assessing cryptocurrency value by analyzing production expenses and mining difficulty, whereas valuation models emphasize market sentiment and speculative demand, driving significant volatility. Bitcoin's price fluctuations reflect the tension between intrinsic cost factors and external market forces, resulting in rapid and unpredictable value changes. Explore the dynamics shaping cryptocurrency volatility to deepen your understanding.
Source and External Links
Cost Models: A Guide for Effective Budgeting - This webpage provides a comprehensive guide on building cost models, focusing on defining scope, gathering data, and segmenting costs to aid in decision-making and strategic planning.
Recommendations for Creating a Cost Model - This article offers insights into developing cost models in Azure, emphasizing aligning estimates with cost drivers and associating costs with business metrics for effective resource utilization.
Cost Models - This resource explains cost models as mathematical equations, typically represented as "Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost," and discusses their application in ecommerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com