Taxonomy alignment involves organizing financial data according to standardized frameworks like IFRS or GAAP, ensuring consistency and comparability in reporting. Chart of accounts mapping translates an organization's unique account codes into these standardized taxonomies to facilitate accurate financial consolidation and regulatory compliance. Explore how integrating taxonomy alignment with chart of accounts mapping optimizes accounting processes and enhances financial transparency.
Why it is important
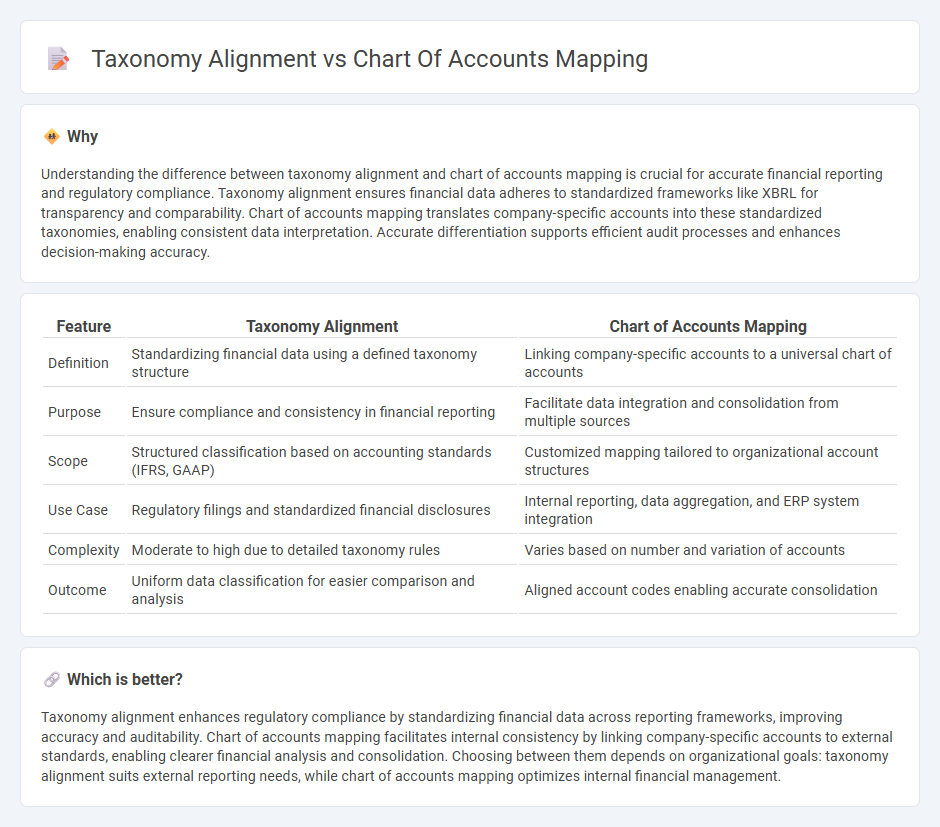
Understanding the difference between taxonomy alignment and chart of accounts mapping is crucial for accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance. Taxonomy alignment ensures financial data adheres to standardized frameworks like XBRL for transparency and comparability. Chart of accounts mapping translates company-specific accounts into these standardized taxonomies, enabling consistent data interpretation. Accurate differentiation supports efficient audit processes and enhances decision-making accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Taxonomy Alignment | Chart of Accounts Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardizing financial data using a defined taxonomy structure | Linking company-specific accounts to a universal chart of accounts |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance and consistency in financial reporting | Facilitate data integration and consolidation from multiple sources |
| Scope | Structured classification based on accounting standards (IFRS, GAAP) | Customized mapping tailored to organizational account structures |
| Use Case | Regulatory filings and standardized financial disclosures | Internal reporting, data aggregation, and ERP system integration |
| Complexity | Moderate to high due to detailed taxonomy rules | Varies based on number and variation of accounts |
| Outcome | Uniform data classification for easier comparison and analysis | Aligned account codes enabling accurate consolidation |
Which is better?
Taxonomy alignment enhances regulatory compliance by standardizing financial data across reporting frameworks, improving accuracy and auditability. Chart of accounts mapping facilitates internal consistency by linking company-specific accounts to external standards, enabling clearer financial analysis and consolidation. Choosing between them depends on organizational goals: taxonomy alignment suits external reporting needs, while chart of accounts mapping optimizes internal financial management.
Connection
Taxonomy alignment streamlines financial reporting by ensuring consistency between regulatory frameworks and organizational data. Chart of accounts mapping translates diverse account structures into standardized taxonomy elements, facilitating accurate and comparable financial disclosures. This connection enhances data integration, reduces errors, and supports compliance with accounting standards such as IFRS and GAAP.
Key Terms
General Ledger Codes
Chart of accounts mapping organizes General Ledger codes into structured categories reflecting an organization's financial transactions, enabling accurate reporting and analysis. Taxonomy alignment standardizes these codes to comply with regulatory frameworks like IFRS or US GAAP, facilitating consistent financial disclosures across entities. Explore further to understand best practices for integrating chart of accounts with accounting taxonomies.
Account Classification
Chart of accounts mapping involves categorizing financial transactions into predefined accounts to facilitate accurate bookkeeping and reporting. Taxonomy alignment ensures these accounts conform to standardized frameworks like IFRS or GAAP for consistent external reporting and regulatory compliance. Explore how precise account classification enhances financial clarity and regulatory adherence.
Standardized Labels
Chart of accounts mapping organizes financial data by linking account codes to standardized labels, ensuring consistency across multiple reporting systems. Taxonomy alignment further refines this by categorizing financial information according to regulatory frameworks and industry standards like IFRS or GAAP. Explore more to understand how standardized labels enhance accuracy in financial reporting and compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com