Generative audio leverages AI algorithms to create original sounds and music by synthesizing audio data, offering innovative possibilities beyond traditional sound design. Digital signal processing (DSP) focuses on manipulating existing audio signals to enhance, filter, or transform sound quality through mathematical techniques in real-time applications. Explore the transformative impact of generative audio and DSP on modern sound technology and creative production.
Why it is important
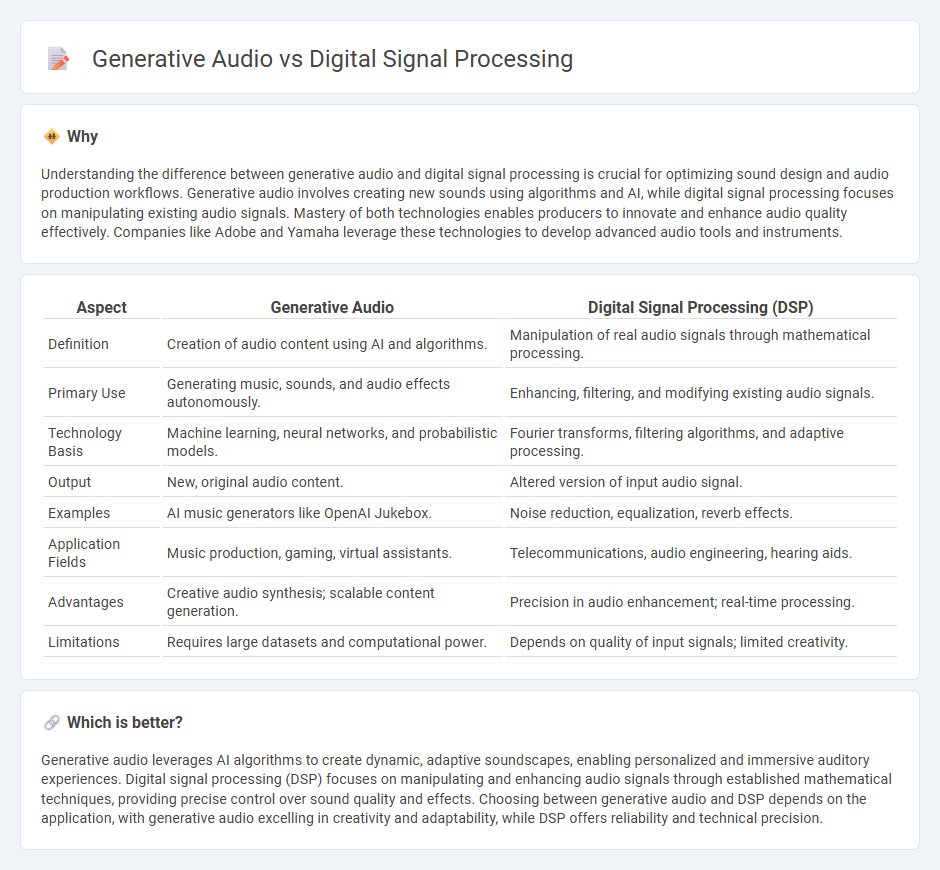
Understanding the difference between generative audio and digital signal processing is crucial for optimizing sound design and audio production workflows. Generative audio involves creating new sounds using algorithms and AI, while digital signal processing focuses on manipulating existing audio signals. Mastery of both technologies enables producers to innovate and enhance audio quality effectively. Companies like Adobe and Yamaha leverage these technologies to develop advanced audio tools and instruments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Generative Audio | Digital Signal Processing (DSP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of audio content using AI and algorithms. | Manipulation of real audio signals through mathematical processing. |
| Primary Use | Generating music, sounds, and audio effects autonomously. | Enhancing, filtering, and modifying existing audio signals. |
| Technology Basis | Machine learning, neural networks, and probabilistic models. | Fourier transforms, filtering algorithms, and adaptive processing. |
| Output | New, original audio content. | Altered version of input audio signal. |
| Examples | AI music generators like OpenAI Jukebox. | Noise reduction, equalization, reverb effects. |
| Application Fields | Music production, gaming, virtual assistants. | Telecommunications, audio engineering, hearing aids. |
| Advantages | Creative audio synthesis; scalable content generation. | Precision in audio enhancement; real-time processing. |
| Limitations | Requires large datasets and computational power. | Depends on quality of input signals; limited creativity. |
Which is better?
Generative audio leverages AI algorithms to create dynamic, adaptive soundscapes, enabling personalized and immersive auditory experiences. Digital signal processing (DSP) focuses on manipulating and enhancing audio signals through established mathematical techniques, providing precise control over sound quality and effects. Choosing between generative audio and DSP depends on the application, with generative audio excelling in creativity and adaptability, while DSP offers reliability and technical precision.
Connection
Generative audio leverages advanced digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to create complex soundscapes by manipulating audio signals algorithmically. DSP algorithms analyze, synthesize, and transform audio data, enabling generative models to produce dynamic and evolving sound patterns. This synergy enhances applications in music production, virtual reality, and interactive media by providing more immersive and adaptive auditory experiences.
Key Terms
Fourier Transform
Digital signal processing leverages the Fourier Transform to analyze frequency components within audio signals, enabling noise reduction, filtering, and spectral analysis. Generative audio uses the Fourier Transform to synthesize sounds by manipulating frequency data, creating complex audio textures and timbres from mathematical models. Explore deeper insights into how Fourier Transform bridges signal processing and generative audio techniques.
Neural Networks
Digital signal processing (DSP) employs deterministic algorithms to analyze, modify, and synthesize audio signals, focusing on filtering, compression, and noise reduction through mathematical operations. Generative audio leverages neural networks, particularly deep learning models such as convolutional and recurrent networks, to create novel sounds by learning complex audio representations and patterns from large datasets. Explore the transformative advancements of neural networks in audio generation and their impact on future sound design.
Signal Synthesis
Digital signal processing (DSP) involves manipulating audio signals using algorithms to enhance, filter, or transform sounds, while generative audio focuses on creating new soundscapes through automated or AI-driven synthesis techniques. Signal synthesis in DSP typically relies on deterministic methods such as additive, subtractive, and FM synthesis, enabling precise control over timbre and harmonic content. Explore further to understand how these approaches shape modern audio production and sound design.
Source and External Links
Digital signal processing - Wikipedia - Digital signal processing (DSP) uses digital computation to process signals represented as sequences of numbers, with applications in audio, telecommunications, radar, image processing, and more, providing advantages like error correction and data compression over analog processing.
What is Digital Signal Processing (DSP)? - GeeksforGeeks - DSP involves converting analog signals to digital, processing them to reduce noise and errors, and can be used in audio production to enhance recording quality and fix signal issues.
Digital Signal Processing Tutorial - Tutorialspoint - A DSP system consists of input/output interfaces, a compute engine, and memory units that enable fast processing of signals for applications including audio/video processing, medical signals analysis, and radar/sonar signal processing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com