Tiny machine learning enables efficient AI model deployment on low-power devices, optimizing sensor data processing directly on edge hardware. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth usage by performing real-time analysis close to the data source, contrasting with traditional centralized methods. Explore how integrating tiny machine learning with sensor data processing transforms smart systems and IoT applications.
Why it is important
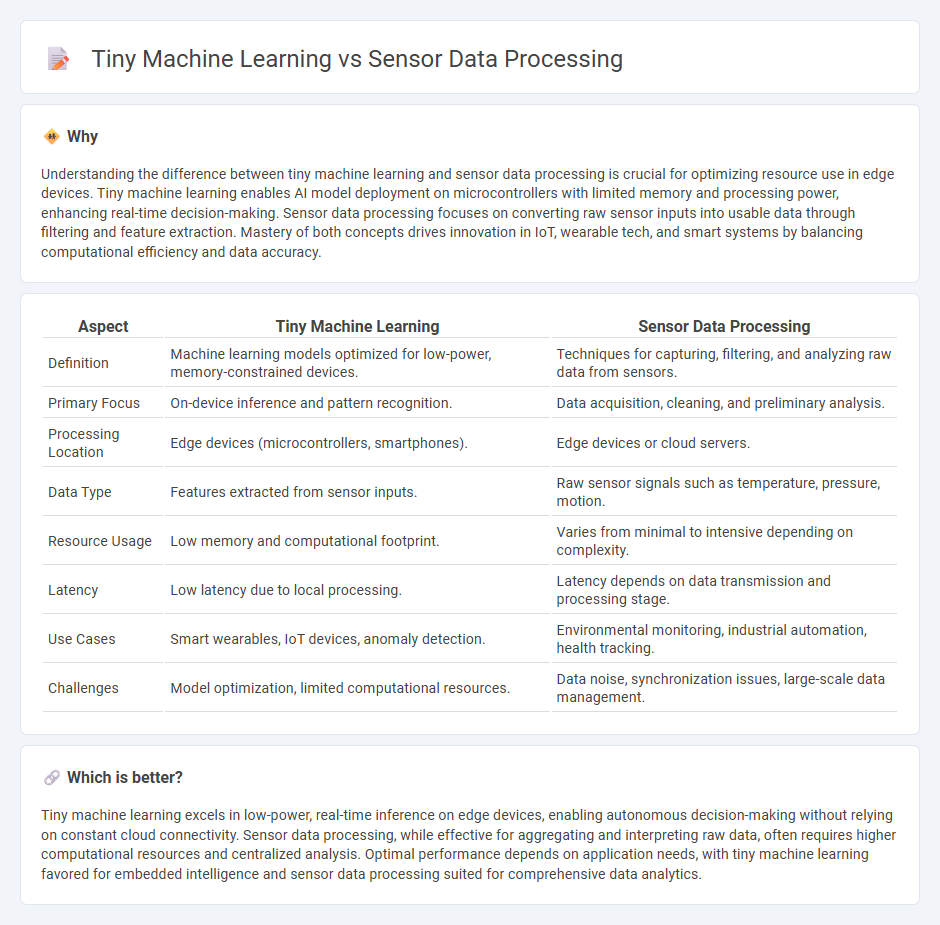
Understanding the difference between tiny machine learning and sensor data processing is crucial for optimizing resource use in edge devices. Tiny machine learning enables AI model deployment on microcontrollers with limited memory and processing power, enhancing real-time decision-making. Sensor data processing focuses on converting raw sensor inputs into usable data through filtering and feature extraction. Mastery of both concepts drives innovation in IoT, wearable tech, and smart systems by balancing computational efficiency and data accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tiny Machine Learning | Sensor Data Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Machine learning models optimized for low-power, memory-constrained devices. | Techniques for capturing, filtering, and analyzing raw data from sensors. |
| Primary Focus | On-device inference and pattern recognition. | Data acquisition, cleaning, and preliminary analysis. |
| Processing Location | Edge devices (microcontrollers, smartphones). | Edge devices or cloud servers. |
| Data Type | Features extracted from sensor inputs. | Raw sensor signals such as temperature, pressure, motion. |
| Resource Usage | Low memory and computational footprint. | Varies from minimal to intensive depending on complexity. |
| Latency | Low latency due to local processing. | Latency depends on data transmission and processing stage. |
| Use Cases | Smart wearables, IoT devices, anomaly detection. | Environmental monitoring, industrial automation, health tracking. |
| Challenges | Model optimization, limited computational resources. | Data noise, synchronization issues, large-scale data management. |
Which is better?
Tiny machine learning excels in low-power, real-time inference on edge devices, enabling autonomous decision-making without relying on constant cloud connectivity. Sensor data processing, while effective for aggregating and interpreting raw data, often requires higher computational resources and centralized analysis. Optimal performance depends on application needs, with tiny machine learning favored for embedded intelligence and sensor data processing suited for comprehensive data analytics.
Connection
Tiny machine learning enables real-time analysis and interpretation of sensor data by embedding efficient algorithms directly on low-power devices, enhancing responsiveness and reducing reliance on cloud processing. Sensor data processing extracts meaningful insights from raw data streams, which tiny machine learning models utilize to detect patterns, anomalies, and perform predictive tasks locally. This synergy optimizes edge computing applications in industries such as healthcare, environmental monitoring, and smart manufacturing by improving accuracy and minimizing latency.
Key Terms
**Sensor Data Processing:**
Sensor data processing involves capturing, filtering, and analyzing raw data from various sensors to extract meaningful insights, enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making in applications such as IoT, healthcare, and industrial automation. It emphasizes accuracy, noise reduction, data fusion, and efficient computation to handle high volumes of sensory inputs for precise outcomes. Explore how advanced sensor data processing techniques enhance smart systems for cutting-edge innovation.
Signal Filtering
Signal filtering in sensor data processing involves techniques such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters to remove noise and enhance signal quality for accurate measurement interpretation. Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) integrates lightweight algorithms directly on microcontrollers, enabling real-time adaptive filtering and feature extraction with minimal power consumption. Discover how combining advanced signal filtering with TinyML can revolutionize edge computing in IoT applications.
Data Fusion
Sensor data processing involves collecting, cleaning, and interpreting raw sensor inputs to extract meaningful information, while tiny machine learning (TinyML) applies lightweight algorithms on edge devices for real-time inference with minimal power consumption. Data fusion integrates multiple sensor data streams to enhance accuracy and reduce uncertainty, making it essential in both fields for improving decision-making processes. Explore how advanced data fusion techniques elevate the performance of TinyML models in constrained environments.
Source and External Links
Navigating Sensor Data Analytics | Expert Guide - Sensor data processing involves collecting data from sensors, cleaning and normalizing it, exploring it through visualization and statistics, and applying predictive modeling to extract actionable insights for real-time operational use.
Sensor Data Analytics: the 'Why', the 'When' and the 'How' - Advanced architectures for sensor data processing include real-time streaming data processors, control applications for actuation, centralized data lakes and warehouses for storage and contextual analysis, and modules for analytics and machine learning to generate insights and automate responses.
IoT Sensor Data Processing for Smart Cities - Kontur Inc. - Sensor data processing systematically cleans, transforms, and analyzes raw environmental data collected via IoT sensors, enabling real-time analysis and timely decision-making through cloud or local infrastructures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com