Circular electronics emphasize sustainability by focusing on reuse, repair, and recycling of electronic components, reducing electronic waste and conserving natural resources. Traditional electronics often follow a linear model, where devices are manufactured, used, and discarded, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Explore the benefits and challenges of circular electronics to understand how this innovative approach is transforming the tech industry.
Why it is important
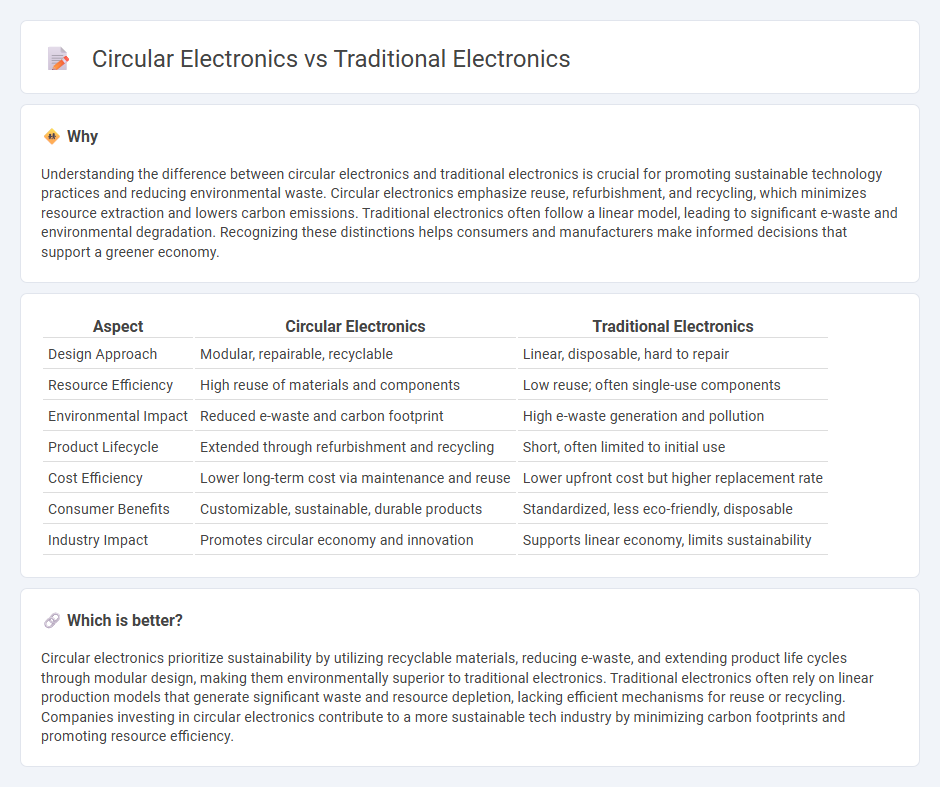
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and traditional electronics is crucial for promoting sustainable technology practices and reducing environmental waste. Circular electronics emphasize reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, which minimizes resource extraction and lowers carbon emissions. Traditional electronics often follow a linear model, leading to significant e-waste and environmental degradation. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers and manufacturers make informed decisions that support a greener economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Traditional Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Design Approach | Modular, repairable, recyclable | Linear, disposable, hard to repair |
| Resource Efficiency | High reuse of materials and components | Low reuse; often single-use components |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced e-waste and carbon footprint | High e-waste generation and pollution |
| Product Lifecycle | Extended through refurbishment and recycling | Short, often limited to initial use |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term cost via maintenance and reuse | Lower upfront cost but higher replacement rate |
| Consumer Benefits | Customizable, sustainable, durable products | Standardized, less eco-friendly, disposable |
| Industry Impact | Promotes circular economy and innovation | Supports linear economy, limits sustainability |
Which is better?
Circular electronics prioritize sustainability by utilizing recyclable materials, reducing e-waste, and extending product life cycles through modular design, making them environmentally superior to traditional electronics. Traditional electronics often rely on linear production models that generate significant waste and resource depletion, lacking efficient mechanisms for reuse or recycling. Companies investing in circular electronics contribute to a more sustainable tech industry by minimizing carbon footprints and promoting resource efficiency.
Connection
Circular electronics and traditional electronics are connected through the lifecycle management of electronic products, where traditional electronics serve as the starting point for circular processes such as refurbishing, recycling, and material recovery. Innovations in circular electronics focus on designing products with modularity, durability, and recyclability to minimize electronic waste generated by conventional manufacturing and disposal methods. This interconnected approach enhances resource efficiency, reduces environmental impact, and promotes sustainable consumption within the electronics industry.
Key Terms
Linear Economy
Traditional electronics operate predominantly within a Linear Economy framework, characterized by a 'take-make-dispose' model that results in significant resource depletion and e-waste generation. Circular electronics challenge this paradigm by emphasizing product longevity, reparability, and material recycling to minimize environmental impact and foster sustainable consumption. Discover how adopting circular economy principles revolutionizes electronic design and waste management for a greener future.
E-Waste
Traditional electronics produce substantial e-waste due to limited recycling and short product lifespans, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Circular electronics emphasize design for durability, reuse, and recyclability, significantly reducing e-waste and promoting sustainable resource management. Discover how circular electronics can transform e-waste challenges into opportunities for a greener future.
Product Lifecycle Extension
Traditional electronics often have limited product lifecycles due to planned obsolescence and non-repairable designs, leading to increased e-waste and resource depletion. Circular electronics prioritize product lifecycle extension through modular components, easy repairability, and upgradeability, significantly reducing environmental impact and fostering resource efficiency. Explore how circular electronics are transforming sustainability by extending device usability and minimizing waste.
Source and External Links
Electronics | Devices, Facts, & History - Traditional electronics refers to the branch of physics and electrical engineering focused on the emission, behavior, and effects of electrons, with historical roots in devices like vacuum tubes and early electronic computers such as ENIAC, which enabled advancements in radio, telephony, television, and computing.
Comparison of Power Electronics with Traditional Electronics - Traditional electronics primarily deals with the manipulation and regulation of low-level signals and small currents, differing from power electronics which manage higher power and voltage levels through efficient conversion techniques.
Electronics for beginners: A simple introduction - In traditional electronics, components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors are arranged in circuits--ranging from simple analog systems to complex digital devices--to control and process electrical signals for various applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com