Circular electronics prioritize reuse, repair, and recycling of electronic components to minimize resource waste and reduce environmental impact. Resource efficiency in this context means maximizing the usage of raw materials by extending product lifecycles and minimizing e-waste. Explore how circular electronics are transforming sustainability in the tech industry.
Why it is important
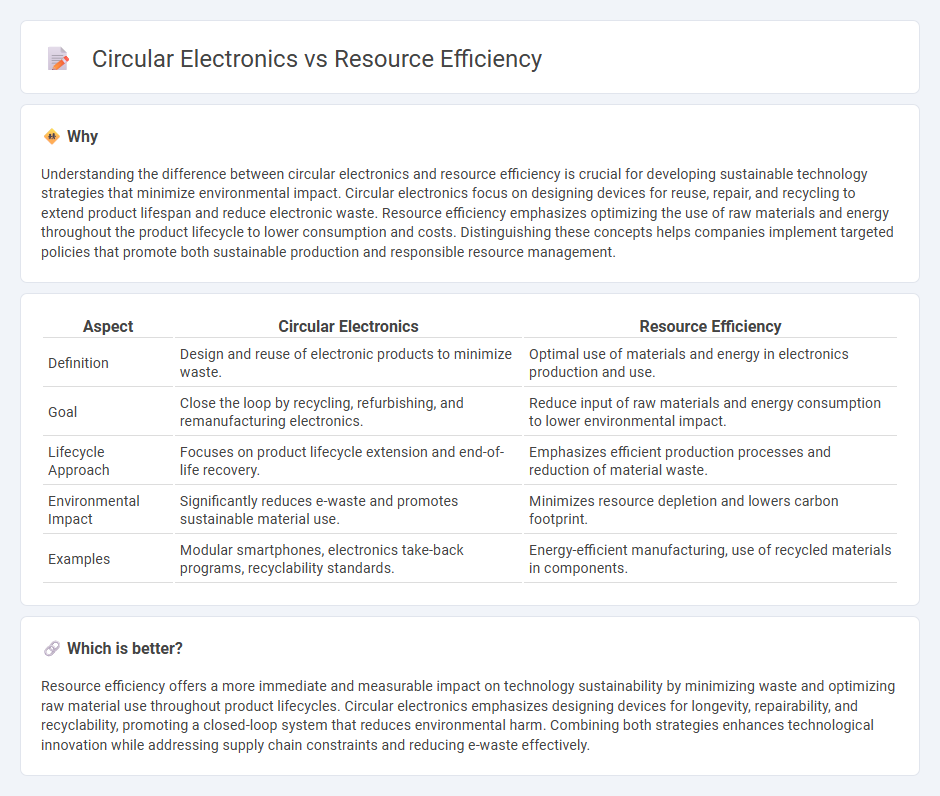
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and resource efficiency is crucial for developing sustainable technology strategies that minimize environmental impact. Circular electronics focus on designing devices for reuse, repair, and recycling to extend product lifespan and reduce electronic waste. Resource efficiency emphasizes optimizing the use of raw materials and energy throughout the product lifecycle to lower consumption and costs. Distinguishing these concepts helps companies implement targeted policies that promote both sustainable production and responsible resource management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Resource Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design and reuse of electronic products to minimize waste. | Optimal use of materials and energy in electronics production and use. |
| Goal | Close the loop by recycling, refurbishing, and remanufacturing electronics. | Reduce input of raw materials and energy consumption to lower environmental impact. |
| Lifecycle Approach | Focuses on product lifecycle extension and end-of-life recovery. | Emphasizes efficient production processes and reduction of material waste. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduces e-waste and promotes sustainable material use. | Minimizes resource depletion and lowers carbon footprint. |
| Examples | Modular smartphones, electronics take-back programs, recyclability standards. | Energy-efficient manufacturing, use of recycled materials in components. |
Which is better?
Resource efficiency offers a more immediate and measurable impact on technology sustainability by minimizing waste and optimizing raw material use throughout product lifecycles. Circular electronics emphasizes designing devices for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, promoting a closed-loop system that reduces environmental harm. Combining both strategies enhances technological innovation while addressing supply chain constraints and reducing e-waste effectively.
Connection
Circular electronics promote resource efficiency by designing devices for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, which reduces e-waste and conserves raw materials like rare earth metals. Implementing circular principles in electronics manufacturing minimizes environmental impact by enabling material recovery and reuse throughout the product lifecycle. This approach aligns with sustainable technology goals by enhancing material circularity and reducing dependence on finite resources.
Key Terms
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Resource efficiency in electronics emphasizes minimizing raw material use and energy consumption throughout production, aiming for cost-effective sustainability. Circular electronics integrate repairability, reuse, and recycling to extend product life and reduce waste, with Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) quantifying environmental impacts from cradle to grave. Explore detailed LCA methodologies to fully understand the synergy between resource efficiency and circular electronics for sustainable innovation.
E-waste Management
Resource efficiency in E-waste management emphasizes minimizing raw material extraction and maximizing product lifespan through repair and recycling. Circular electronics advances this approach by designing devices for easier disassembly, refurbishing, and closed-loop material recovery, thereby reducing environmental impact. Explore strategies and innovations driving sustainable E-waste management in the circular economy.
Design for Disassembly
Resource efficiency in circular electronics emphasizes minimizing waste and maximizing reuse through strategic Design for Disassembly (DfD), enabling easier separation of components and materials at end-of-life. This approach enhances recycling rates and supports sustainable manufacturing by allowing parts to be replaced or upgraded without damaging the device, thereby extending product lifespan. Explore how advancing DfD principles can transform electronic product sustainability.
Source and External Links
Resource Efficiency: The Importance Of Making The Most Of Available Resources - This article discusses optimizing data center resources to minimize waste and energy consumption while maximizing performance.
What is resource efficiency? - Resource efficiency involves using Earth's resources sustainably by minimizing environmental impacts, particularly focusing on energy efficiency.
Resource efficiency - Resource efficiency is about maximizing the use of resources such as money, materials, and staff while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com