Quantum dots display technology offers superior color accuracy and brightness compared to traditional screens by utilizing semiconductor nanocrystals that emit precise light wavelengths. OLED displays provide deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios through self-emissive organic layers, enhancing the overall viewing experience. Explore the key differences and advantages of Quantum dots displays versus OLED technology to understand which suits your needs best.
Why it is important
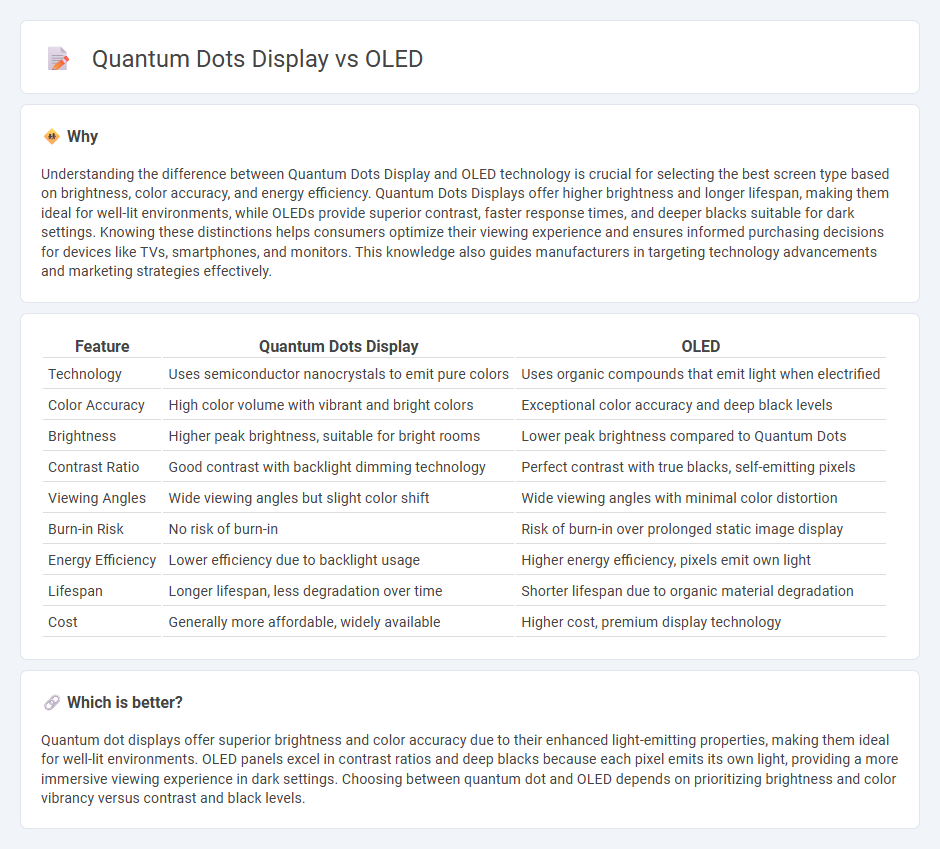
Understanding the difference between Quantum Dots Display and OLED technology is crucial for selecting the best screen type based on brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency. Quantum Dots Displays offer higher brightness and longer lifespan, making them ideal for well-lit environments, while OLEDs provide superior contrast, faster response times, and deeper blacks suitable for dark settings. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers optimize their viewing experience and ensures informed purchasing decisions for devices like TVs, smartphones, and monitors. This knowledge also guides manufacturers in targeting technology advancements and marketing strategies effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Dots Display | OLED |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses semiconductor nanocrystals to emit pure colors | Uses organic compounds that emit light when electrified |
| Color Accuracy | High color volume with vibrant and bright colors | Exceptional color accuracy and deep black levels |
| Brightness | Higher peak brightness, suitable for bright rooms | Lower peak brightness compared to Quantum Dots |
| Contrast Ratio | Good contrast with backlight dimming technology | Perfect contrast with true blacks, self-emitting pixels |
| Viewing Angles | Wide viewing angles but slight color shift | Wide viewing angles with minimal color distortion |
| Burn-in Risk | No risk of burn-in | Risk of burn-in over prolonged static image display |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to backlight usage | Higher energy efficiency, pixels emit own light |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan, less degradation over time | Shorter lifespan due to organic material degradation |
| Cost | Generally more affordable, widely available | Higher cost, premium display technology |
Which is better?
Quantum dot displays offer superior brightness and color accuracy due to their enhanced light-emitting properties, making them ideal for well-lit environments. OLED panels excel in contrast ratios and deep blacks because each pixel emits its own light, providing a more immersive viewing experience in dark settings. Choosing between quantum dot and OLED depends on prioritizing brightness and color vibrancy versus contrast and black levels.
Connection
Quantum dots display technology enhances OLED screens by integrating semiconductor nanocrystals that emit precise colors when exposed to electric current or light. This synergy results in OLED displays with improved color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency. Consequently, quantum dot OLED panels offer superior visual performance for televisions, smartphones, and other digital devices.
Key Terms
Emissive Technology
OLED displays use organic compounds that emit light directly when an electric current passes through, enabling true black levels and high contrast ratios due to pixel-level illumination. Quantum dot displays rely on inorganic semiconductor nanocrystals that enhance color accuracy and brightness when combined with a backlight, improving energy efficiency and color volume but lacking self-emissive properties. Explore the detailed differences in emissive technology to understand which display better suits your viewing needs.
Color Gamut
OLED displays achieve a wider and more vibrant color gamut by emitting light through organic compounds that produce pure, intense colors. Quantum dot displays enhance color reproduction by utilizing semiconductor nanocrystals that precisely emit specific wavelengths, resulting in more accurate and saturated colors compared to traditional LCDs. Discover how these advanced technologies impact your visual experience in detail.
Backlighting
OLED displays use self-emissive pixels that eliminate the need for backlighting, resulting in deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to Quantum Dot LCDs that rely on LED backlighting enhanced by quantum dot technology for improved color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots serve as a precise light conversion layer, enabling LCDs to achieve wider color gamuts and higher luminance, but they cannot match the true black levels produced by OLEDs due to their backlighting dependency. Learn more about how backlighting technology impacts display performance and viewing experience.
Source and External Links
OLED - Wikipedia - OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a type of LED with an organic electroluminescent layer that emits light when an electric current passes through it; commonly used in digital displays like TVs, smartphones, and monitors, with two main types based on small molecules or polymers and control schemes including PMOLED and AMOLED.
What is an OLED? - Ossila - OLEDs are organic LED displays with a simple layered structure, leading to innovations like foldable and rollable screens, produced mainly by vacuum evaporation but moving towards ink-jet printing for efficiency and lower material waste.
An introduction to OLED displays - OLEDs consist of organic thin films between two conductors that emit bright light under current; they dominate smartphone displays and are used in TVs and other electronics, with major manufacturers like LG Display and Samsung Display producing OLED panels for top-tier market products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com