Blockchain oracles bridge smart contracts with real-world data, enabling decentralized applications to access external information securely and reliably. Consensus mechanisms validate and agree upon transaction records across distributed networks, maintaining blockchain integrity and preventing fraud. Explore how these technologies interplay to enhance blockchain functionality and trust.
Why it is important
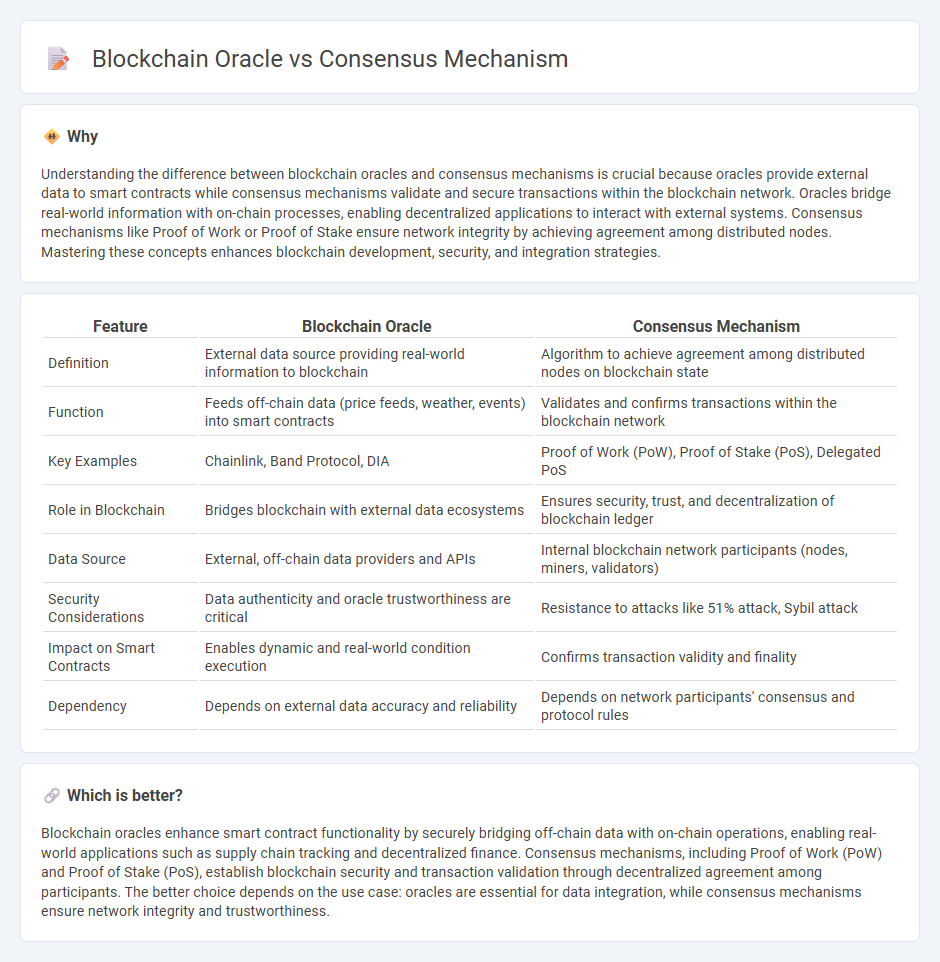
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracles and consensus mechanisms is crucial because oracles provide external data to smart contracts while consensus mechanisms validate and secure transactions within the blockchain network. Oracles bridge real-world information with on-chain processes, enabling decentralized applications to interact with external systems. Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake ensure network integrity by achieving agreement among distributed nodes. Mastering these concepts enhances blockchain development, security, and integration strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Consensus Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | External data source providing real-world information to blockchain | Algorithm to achieve agreement among distributed nodes on blockchain state |
| Function | Feeds off-chain data (price feeds, weather, events) into smart contracts | Validates and confirms transactions within the blockchain network |
| Key Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol, DIA | Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated PoS |
| Role in Blockchain | Bridges blockchain with external data ecosystems | Ensures security, trust, and decentralization of blockchain ledger |
| Data Source | External, off-chain data providers and APIs | Internal blockchain network participants (nodes, miners, validators) |
| Security Considerations | Data authenticity and oracle trustworthiness are critical | Resistance to attacks like 51% attack, Sybil attack |
| Impact on Smart Contracts | Enables dynamic and real-world condition execution | Confirms transaction validity and finality |
| Dependency | Depends on external data accuracy and reliability | Depends on network participants' consensus and protocol rules |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles enhance smart contract functionality by securely bridging off-chain data with on-chain operations, enabling real-world applications such as supply chain tracking and decentralized finance. Consensus mechanisms, including Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), establish blockchain security and transaction validation through decentralized agreement among participants. The better choice depends on the use case: oracles are essential for data integration, while consensus mechanisms ensure network integrity and trustworthiness.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data feeds that supply external information to smart contracts, enabling accurate execution based on real-world inputs. Consensus mechanisms validate and agree upon the state of the blockchain, ensuring data integrity and security among decentralized nodes. Together, oracles provide reliable external data while consensus mechanisms maintain the trustworthiness of on-chain decisions.
Key Terms
Validation (Consensus Mechanism)
Consensus mechanisms ensure decentralized validation by enabling network participants to agree on the legitimacy of transactions, safeguarding blockchain integrity. Blockchain oracles provide external data inputs but rely on consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake to validate that data within the blockchain context. Explore further to understand how these components collaborate for secure and trustworthy blockchain operations.
Data Feed (Blockchain Oracle)
Consensus mechanisms ensure agreement on valid transactions across blockchain nodes, maintaining network integrity and security through protocols like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Blockchain oracles, specifically data feeds, provide external real-world information such as price feeds, weather data, or sports scores, enabling smart contracts to execute based on off-chain events. Explore how integrating reliable blockchain oracles enhances decentralized applications and smart contract accuracy.
Trustlessness
Consensus mechanisms ensure trustlessness by enabling decentralized agreement on blockchain state without relying on a central authority, maintaining data integrity across nodes. Blockchain oracles enhance blockchain functionality by securely feeding external real-world data into smart contracts yet often require trust assumptions to verify data authenticity. Explore in-depth differences to understand how decentralization impacts trust in blockchain ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Consensus Mechanisms: How Blockchains Stay Secure - Ledger - A consensus mechanism is the method by which blockchain nodes agree on whether to add data to the chain, ensuring decentralized agreement, error avoidance, and protection from malicious transactions without the need for centralized authority.
What Is a Consensus Mechanism? | Built In - Consensus mechanisms are protocols that bring all nodes of a distributed blockchain network into agreement by verifying transactions collectively, preventing double-spending and ensuring that only valid data is permanently added to the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms In Blockchain: A Deep Dive Into ... - Hacken - Consensus mechanisms maintain blockchain security and operational integrity by requiring nodes to agree on the state of the ledger before updating it, enabling decentralized networks to function without centralized control and preventing attacks like double-spending and Sybil attacks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com