Synthetic media detection leverages advanced algorithms to identify manipulated or AI-generated content, distinguishing it from authentic digital creations. Image forensics focuses on analyzing metadata, compression artifacts, and pixel inconsistencies to verify the integrity of photographs and videos. Explore the latest methods and tools in synthetic media detection and image forensics to deepen your understanding of digital authenticity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and image forensics is crucial for accurately identifying manipulated content and preventing misinformation. Synthetic media detection focuses on recognizing AI-generated or deepfake content, while image forensics examines image authenticity through metadata and pixel-level analysis. This distinction enhances cybersecurity measures and supports digital forensics investigations in various sectors. Mastery of both fields ensures robust defense against evolving digital threats and protects the integrity of visual data.
Comparison Table
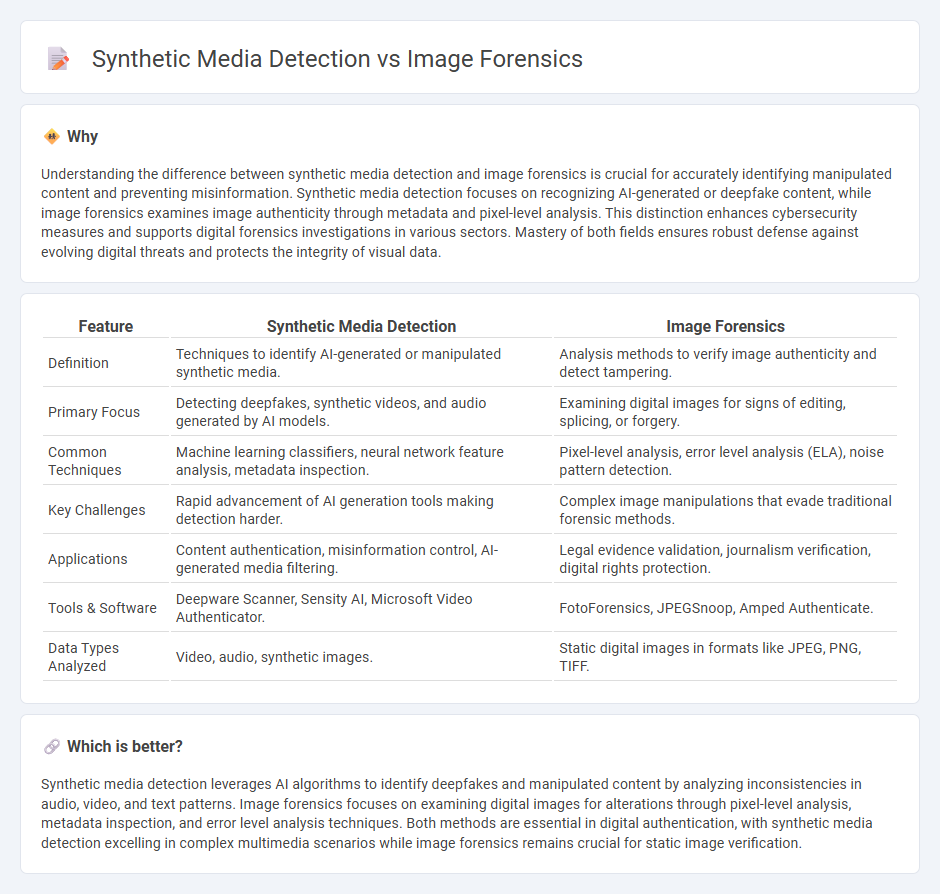
| Feature | Synthetic Media Detection | Image Forensics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques to identify AI-generated or manipulated synthetic media. | Analysis methods to verify image authenticity and detect tampering. |
| Primary Focus | Detecting deepfakes, synthetic videos, and audio generated by AI models. | Examining digital images for signs of editing, splicing, or forgery. |
| Common Techniques | Machine learning classifiers, neural network feature analysis, metadata inspection. | Pixel-level analysis, error level analysis (ELA), noise pattern detection. |
| Key Challenges | Rapid advancement of AI generation tools making detection harder. | Complex image manipulations that evade traditional forensic methods. |
| Applications | Content authentication, misinformation control, AI-generated media filtering. | Legal evidence validation, journalism verification, digital rights protection. |
| Tools & Software | Deepware Scanner, Sensity AI, Microsoft Video Authenticator. | FotoForensics, JPEGSnoop, Amped Authenticate. |
| Data Types Analyzed | Video, audio, synthetic images. | Static digital images in formats like JPEG, PNG, TIFF. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection leverages AI algorithms to identify deepfakes and manipulated content by analyzing inconsistencies in audio, video, and text patterns. Image forensics focuses on examining digital images for alterations through pixel-level analysis, metadata inspection, and error level analysis techniques. Both methods are essential in digital authentication, with synthetic media detection excelling in complex multimedia scenarios while image forensics remains crucial for static image verification.
Connection
Synthetic media detection and image forensics are closely connected through their shared goal of identifying manipulated or artificially generated visual content. Image forensics employs analytical techniques like pixel analysis, metadata examination, and source verification to detect alterations, while synthetic media detection focuses on recognizing computer-generated imagery and deepfakes using AI-based algorithms and neural network patterns. Together, they enhance digital trust by providing complementary methods to authenticate images and prevent misinformation.
Key Terms
Deepfake Detection
Deepfake detection is a critical subfield of image forensics that employs advanced algorithms to identify manipulated visual content generated by synthetic media technologies. Techniques such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) analyze inconsistencies in facial movements, lighting, and texture to distinguish genuine images from deepfakes. Explore the latest developments in deepfake detection to understand how cutting-edge tools combat synthetic media threats.
Digital Watermarking
Digital watermarking plays a crucial role in image forensics by embedding imperceptible data to verify authenticity and trace image provenance. In synthetic media detection, watermarking helps identify manipulated or AI-generated content by distinguishing genuine digital signatures from fabricated visuals. Explore advanced digital watermarking techniques to enhance both image fraud prevention and synthetic media verification capabilities.
Source Identification
Image forensics specializes in authenticating visual content by analyzing inconsistencies in metadata, pixel-level anomalies, and camera sensor patterns to trace the original source of images. Synthetic media detection leverages advanced AI algorithms and neural network models to differentiate between real and artificially generated images, focusing on unique generation artifacts left by GANs or deepfake techniques. Explore cutting-edge methodologies in source identification to enhance the reliability of digital content verification.
Source and External Links
Image Forensics - Hany Farid - Image forensics involves analyzing an image to determine if it has been manipulated since it was recorded, using techniques like clone detection, SIFT features, and algorithms such as RANSAC for finding image tampering evidence.
Forensically, free online photo forensics tools - Forensically is a free web-based toolkit offering magnification, clone detection, error level analysis, and metadata extraction to help uncover image manipulations.
What Is a Forensic Image? | Definition from TechTarget - A forensic image is a bit-by-bit sector copy of a storage device used for digital investigations, capturing active, unused, and deleted data intact for later analysis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com