Self-healing networks leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data to automatically detect, isolate, and repair faults, ensuring continuous network performance without human intervention. Fault-tolerant networks, designed with redundant hardware and protocols, maintain functionality despite hardware failures through backup systems and failover mechanisms. Explore more about how these network technologies enhance reliability and efficiency in modern communication infrastructure.
Why it is important
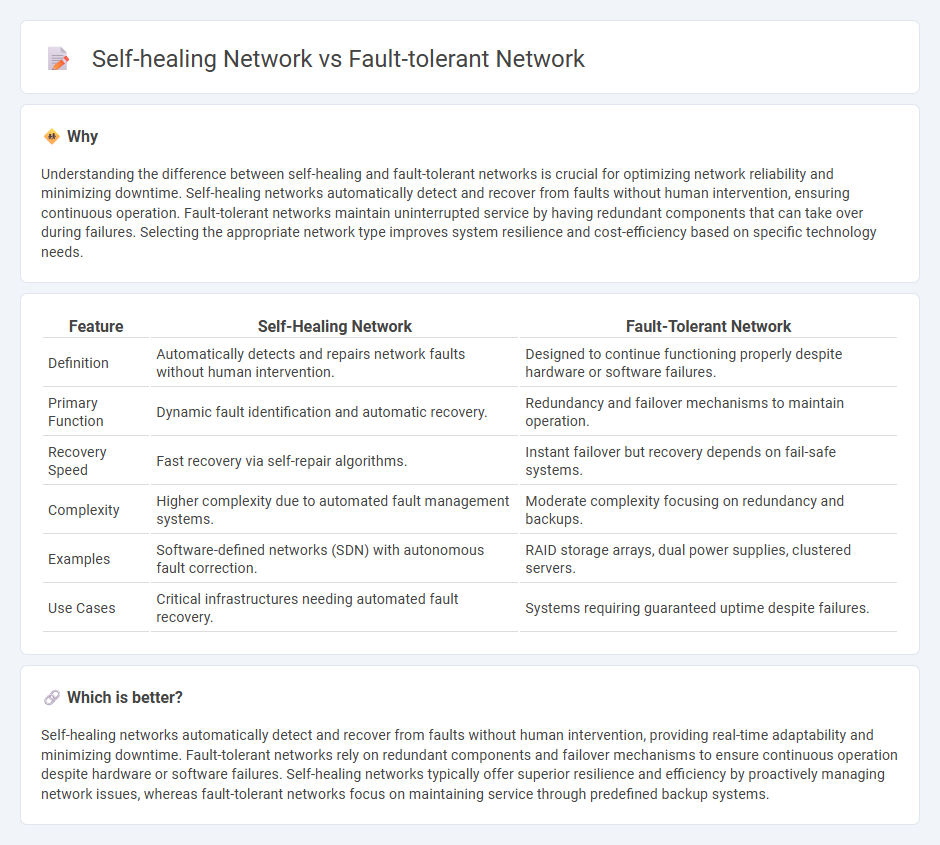
Understanding the difference between self-healing and fault-tolerant networks is crucial for optimizing network reliability and minimizing downtime. Self-healing networks automatically detect and recover from faults without human intervention, ensuring continuous operation. Fault-tolerant networks maintain uninterrupted service by having redundant components that can take over during failures. Selecting the appropriate network type improves system resilience and cost-efficiency based on specific technology needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Self-Healing Network | Fault-Tolerant Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatically detects and repairs network faults without human intervention. | Designed to continue functioning properly despite hardware or software failures. |
| Primary Function | Dynamic fault identification and automatic recovery. | Redundancy and failover mechanisms to maintain operation. |
| Recovery Speed | Fast recovery via self-repair algorithms. | Instant failover but recovery depends on fail-safe systems. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to automated fault management systems. | Moderate complexity focusing on redundancy and backups. |
| Examples | Software-defined networks (SDN) with autonomous fault correction. | RAID storage arrays, dual power supplies, clustered servers. |
| Use Cases | Critical infrastructures needing automated fault recovery. | Systems requiring guaranteed uptime despite failures. |
Which is better?
Self-healing networks automatically detect and recover from faults without human intervention, providing real-time adaptability and minimizing downtime. Fault-tolerant networks rely on redundant components and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operation despite hardware or software failures. Self-healing networks typically offer superior resilience and efficiency by proactively managing network issues, whereas fault-tolerant networks focus on maintaining service through predefined backup systems.
Connection
Self-healing networks enhance fault-tolerant networks by automatically detecting and recovering from failures to maintain continuous connectivity. Fault-tolerant networks use redundant pathways and systems to prevent service disruption, while self-healing mechanisms dynamically reroute traffic and isolate faults in real-time. Together, these technologies ensure robust network reliability and minimize downtime in critical infrastructures.
Key Terms
**Fault-tolerant network:**
Fault-tolerant networks are designed to maintain continuous operation despite hardware or software failures by incorporating redundant components, error detection, and recovery mechanisms. These networks minimize downtime and data loss through automatic failover and backup systems that ensure reliable communication in critical environments such as data centers and financial institutions. Explore the differences and applications of fault-tolerant and self-healing networks to optimize your network resilience strategy.
Redundancy
Fault-tolerant networks enhance reliability by incorporating redundancy, such as duplicate hardware or multiple communication paths, to ensure continuous operation despite component failures. Self-healing networks further improve resilience by automatically detecting faults and dynamically rerouting traffic without manual intervention, leveraging redundancy for rapid recovery. Explore the detailed mechanisms and advantages of these network types to understand their impact on modern communication systems.
Failover
Fault-tolerant networks employ failover mechanisms to seamlessly switch to backup systems or paths upon detecting a failure, ensuring continuous network availability with minimal disruption. Self-healing networks extend this concept by automatically identifying failures and dynamically rerouting traffic without manual intervention, promoting quicker recovery and enhanced resilience. Explore our detailed analysis to understand the key differences in failover strategies between fault-tolerant and self-healing networks.
Source and External Links
The Ultimate Guide On Designing a Fault Tolerant Network 101 - This guide explains the principles of designing fault-tolerant networks, focusing on Layer 2 methods and using protocols like VLAN and MSTP to enhance network reliability.
Fault Tolerant Ethernet - Fault Tolerant Ethernet is a proprietary protocol developed by Honeywell to provide rapid network redundancy, utilizing dual network paths for resilient communication.
What is Fault Tolerance? - This article discusses fault tolerance in networks, highlighting techniques such as redundancy, replication, failover, load balancing, and clustering to ensure continuous operation despite component failures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com