Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority, leveraging cryptographic proofs to ensure data integrity and user privacy. Permissionless systems allow open participation in decentralized networks where anyone can join, validate, and interact without prior approval, fostering transparency and inclusivity. Explore the key differences and benefits of trustless computing and permissionless systems to understand their impact on the future of decentralized technology.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between trustless computing and permissionless systems is crucial for developing secure blockchain applications and decentralized networks. Trustless computing ensures secure interactions without relying on any single entity, while permissionless systems allow anyone to participate without centralized approval. Distinguishing these concepts helps optimize system design for transparency, security, and scalability in technologies such as cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. This knowledge enables developers to select appropriate frameworks that align with the desired level of decentralization and access control.
Comparison Table
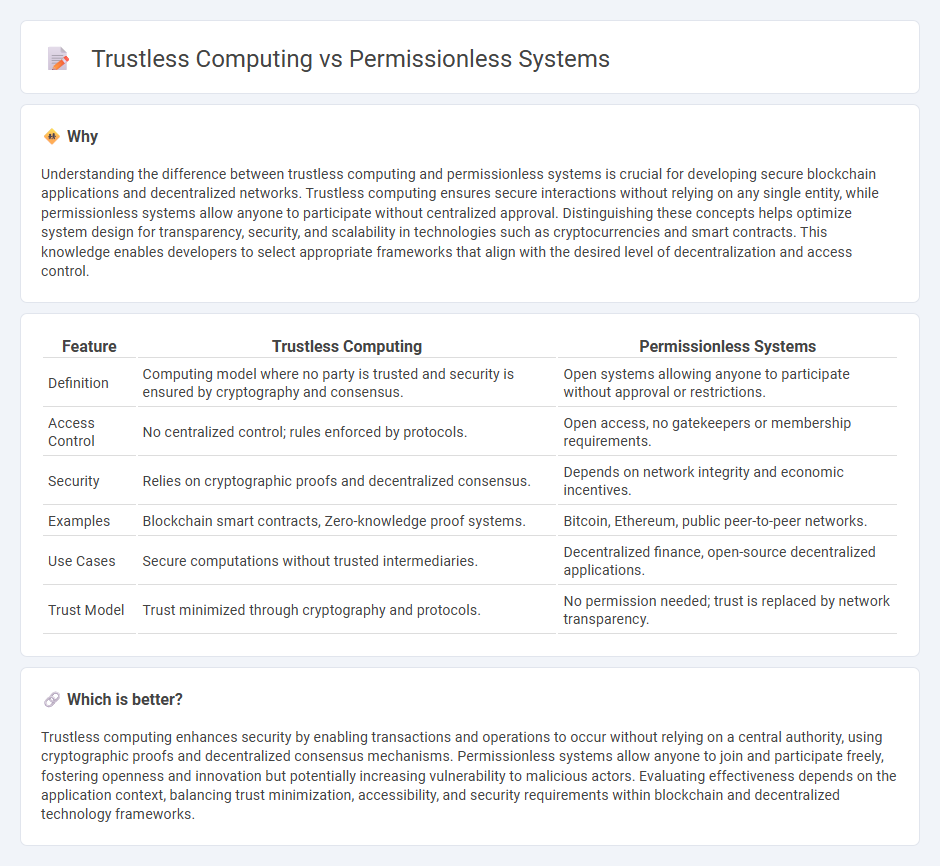
| Feature | Trustless Computing | Permissionless Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing model where no party is trusted and security is ensured by cryptography and consensus. | Open systems allowing anyone to participate without approval or restrictions. |
| Access Control | No centralized control; rules enforced by protocols. | Open access, no gatekeepers or membership requirements. |
| Security | Relies on cryptographic proofs and decentralized consensus. | Depends on network integrity and economic incentives. |
| Examples | Blockchain smart contracts, Zero-knowledge proof systems. | Bitcoin, Ethereum, public peer-to-peer networks. |
| Use Cases | Secure computations without trusted intermediaries. | Decentralized finance, open-source decentralized applications. |
| Trust Model | Trust minimized through cryptography and protocols. | No permission needed; trust is replaced by network transparency. |
Which is better?
Trustless computing enhances security by enabling transactions and operations to occur without relying on a central authority, using cryptographic proofs and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Permissionless systems allow anyone to join and participate freely, fostering openness and innovation but potentially increasing vulnerability to malicious actors. Evaluating effectiveness depends on the application context, balancing trust minimization, accessibility, and security requirements within blockchain and decentralized technology frameworks.
Connection
Trustless computing enables secure transactions by eliminating the need for a central authority, ensuring data integrity through cryptographic proofs and decentralized consensus mechanisms. Permissionless systems allow anyone to participate in the network, fostering open access and innovation without gatekeepers. Together, they create a decentralized ecosystem where trust is embedded in the technology rather than relying on intermediaries.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Permissionless systems enable users to participate without prior approval, fostering open access and broad decentralization by removing gatekeepers. Trustless computing relies on cryptographic algorithms and decentralized consensus mechanisms to operate without needing participants to trust a central authority, enhancing security and reducing reliance on intermediaries. Explore the fundamental differences and benefits of these approaches to decentralization in blockchain technology to deepen your understanding.
Consensus Mechanisms
Permissionless systems operate without centralized authority, enabling open participation and requiring robust consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions securely. Trustless computing ensures that participants can interact and execute code without needing to trust each other, relying on cryptographic proofs and decentralized consensus algorithms to maintain integrity and prevent fraud. Explore deeper into consensus mechanisms and their impact on decentralization and security to understand their evolving role in blockchain technologies.
Cryptographic Proofs
Permissionless systems enable open participation without centralized control, leveraging cryptographic proofs like zero-knowledge proofs and digital signatures to validate transactions securely. Trustless computing minimizes reliance on trusted intermediaries by employing cryptographic mechanisms such as multi-party computation and blockchains that ensure data integrity and consensus. Explore how advanced cryptographic proofs underpin these paradigms and their impact on decentralized technology innovation.
Source and External Links
Permissionless - Crypto.com - Permissionless systems, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, have no gatekeepers, allowing anyone to use or participate without needing approval from a central authority.
Permissionless vs. Permissioned Blockchains: Pros & Cons - 1Kosmos - Permissionless blockchains are radically decentralized, fully transparent, and operate without central control, enabling open participation and resilient, peer-to-peer networks.
Permissionless - Blockworks - Permissionlessness accelerates progress by removing the need for approval to exchange, build, communicate, or govern, but also brings challenges like increased risk of scams and the need for new forms of collective governance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com