Neuromorphic chips mimic the architecture and functioning of the human brain, enabling efficient processing of complex sensory data and adaptive learning, while ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) offer highly specialized hardware optimized for specific tasks with superior performance and power efficiency. Neuromorphic technologies excel in tasks requiring real-time processing and low energy consumption, whereas ASICs dominate in applications needing fast, dedicated computation. Explore deeper to understand how these advanced technologies shape the future of computing.
Why it is important
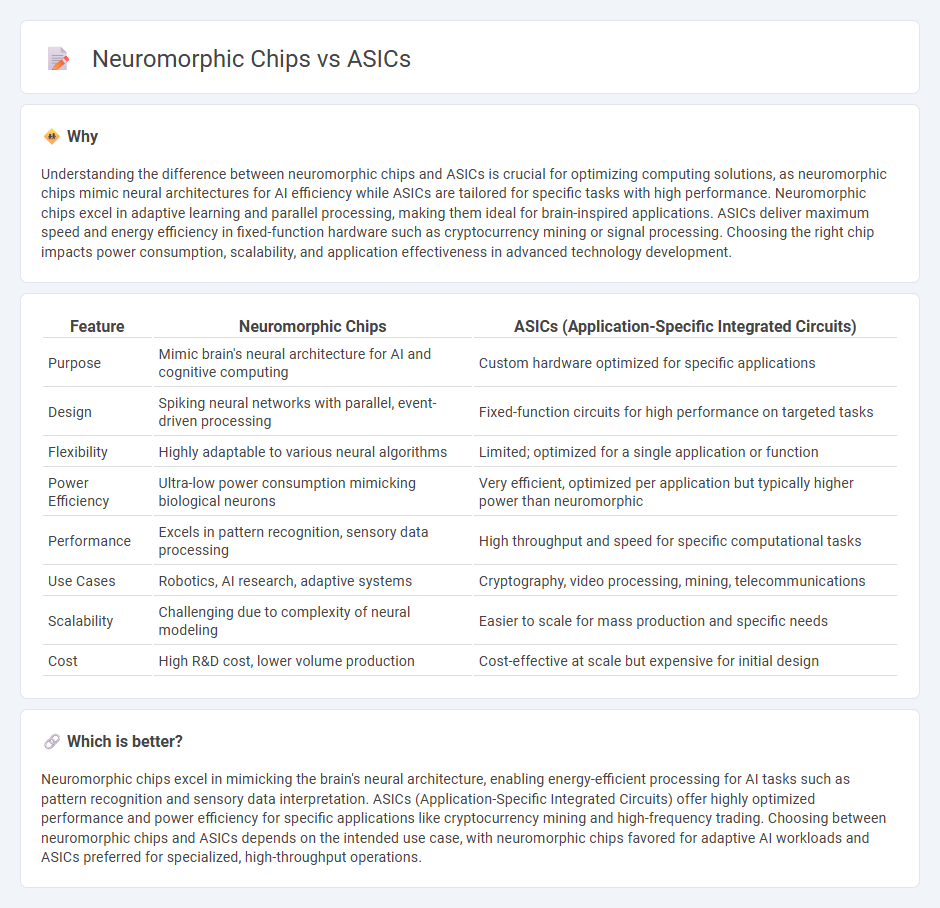
Understanding the difference between neuromorphic chips and ASICs is crucial for optimizing computing solutions, as neuromorphic chips mimic neural architectures for AI efficiency while ASICs are tailored for specific tasks with high performance. Neuromorphic chips excel in adaptive learning and parallel processing, making them ideal for brain-inspired applications. ASICs deliver maximum speed and energy efficiency in fixed-function hardware such as cryptocurrency mining or signal processing. Choosing the right chip impacts power consumption, scalability, and application effectiveness in advanced technology development.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neuromorphic Chips | ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Mimic brain's neural architecture for AI and cognitive computing | Custom hardware optimized for specific applications |
| Design | Spiking neural networks with parallel, event-driven processing | Fixed-function circuits for high performance on targeted tasks |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to various neural algorithms | Limited; optimized for a single application or function |
| Power Efficiency | Ultra-low power consumption mimicking biological neurons | Very efficient, optimized per application but typically higher power than neuromorphic |
| Performance | Excels in pattern recognition, sensory data processing | High throughput and speed for specific computational tasks |
| Use Cases | Robotics, AI research, adaptive systems | Cryptography, video processing, mining, telecommunications |
| Scalability | Challenging due to complexity of neural modeling | Easier to scale for mass production and specific needs |
| Cost | High R&D cost, lower volume production | Cost-effective at scale but expensive for initial design |
Which is better?
Neuromorphic chips excel in mimicking the brain's neural architecture, enabling energy-efficient processing for AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sensory data interpretation. ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) offer highly optimized performance and power efficiency for specific applications like cryptocurrency mining and high-frequency trading. Choosing between neuromorphic chips and ASICs depends on the intended use case, with neuromorphic chips favored for adaptive AI workloads and ASICs preferred for specialized, high-throughput operations.
Connection
Neuromorphic chips and ASICs both represent specialized hardware designed to optimize specific computing tasks, with neuromorphic chips mimicking neural architectures for brain-inspired processing while ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) focus on bespoke circuitry tailored to dedicated functions. These technologies converge by leveraging ASIC design principles to create highly efficient neuromorphic processors that enable low-power, high-speed computation ideal for artificial intelligence and cognitive applications. The synergy between neuromorphic engineering and ASIC fabrication techniques accelerates advancements in edge computing, robotics, and complex data analysis.
Key Terms
Architecture
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) feature a rigid architecture tailored for specific tasks, offering high performance and energy efficiency within predefined operations. Neuromorphic chips emulate the structure of biological neural networks, incorporating spiking neurons and synapses to enable adaptive, parallel processing suited for AI and cognitive computing. Explore deeper insights into how architectural differences impact efficiency and application potential.
Parallelism
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) deliver high parallelism by executing predefined tasks efficiently with dedicated hardware, enabling faster processing speeds for specific applications such as cryptocurrency mining and AI inference. Neuromorphic chips emulate the brain's neural networks, facilitating massive parallelism through event-driven architectures that enhance adaptability and energy efficiency in tasks like pattern recognition and sensory data processing. Explore the latest advancements in parallel computing to understand how these chip architectures continue to revolutionize computing power and efficiency.
Energy efficiency
ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) deliver high energy efficiency by tailoring hardware for specific tasks, minimizing power consumption during operation. Neuromorphic chips emulate neural networks with event-driven architectures, achieving significant energy savings in cognitive computing and pattern recognition. Explore more to understand how these technologies drive the future of low-power computing.
Source and External Links
Asics - Wikipedia - ASICS is a Japanese multinational corporation known primarily for producing sportswear and sneakers, with a name derived from the Latin phrase "anima sana in corpore sano" meaning a sound mind in a sound body.
ASICS Shoes & Clothing - Foot Locker - ASICS originated from Onitsuka Tiger, starting with basketball shoes in the 1950s and evolving through innovations such as suction cup-like outsole designs for better stopping power.
Asics Metaspeed Sky Tokyo | Full Review - YouTube - The ASICS Metaspeed Sky Tokyo is a race day shoe featuring FlyteFoam Turbo Plus midsole and AS6 grip rubber for excellent traction and cornering performance, even in wet conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com