Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data bridges that connect decentralized smart contracts with real-world information, enabling secure, external data integration. Middleware acts as an intermediary software layer that facilitates communication and data management between different systems, enhancing interoperability and efficiency in blockchain ecosystems. Explore the distinct roles and benefits of blockchain oracles and middleware to deepen your understanding of their impact on technology.
Why it is important
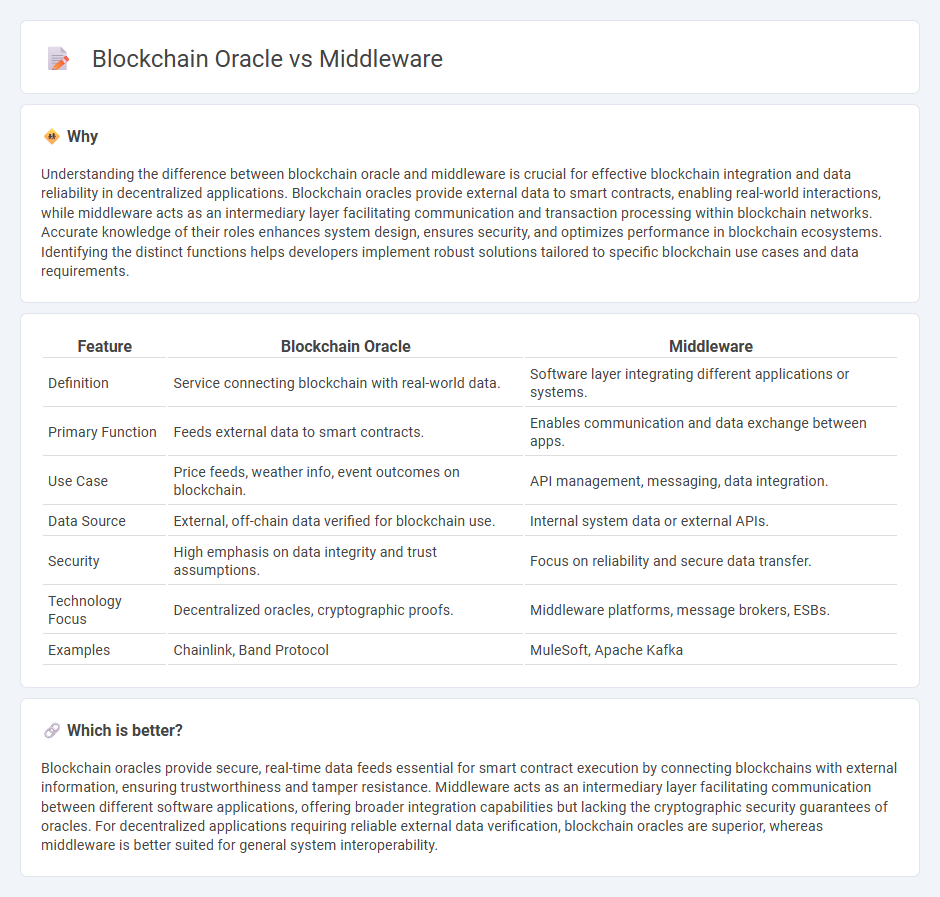
Understanding the difference between blockchain oracle and middleware is crucial for effective blockchain integration and data reliability in decentralized applications. Blockchain oracles provide external data to smart contracts, enabling real-world interactions, while middleware acts as an intermediary layer facilitating communication and transaction processing within blockchain networks. Accurate knowledge of their roles enhances system design, ensures security, and optimizes performance in blockchain ecosystems. Identifying the distinct functions helps developers implement robust solutions tailored to specific blockchain use cases and data requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Oracle | Middleware |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Service connecting blockchain with real-world data. | Software layer integrating different applications or systems. |
| Primary Function | Feeds external data to smart contracts. | Enables communication and data exchange between apps. |
| Use Case | Price feeds, weather info, event outcomes on blockchain. | API management, messaging, data integration. |
| Data Source | External, off-chain data verified for blockchain use. | Internal system data or external APIs. |
| Security | High emphasis on data integrity and trust assumptions. | Focus on reliability and secure data transfer. |
| Technology Focus | Decentralized oracles, cryptographic proofs. | Middleware platforms, message brokers, ESBs. |
| Examples | Chainlink, Band Protocol | MuleSoft, Apache Kafka |
Which is better?
Blockchain oracles provide secure, real-time data feeds essential for smart contract execution by connecting blockchains with external information, ensuring trustworthiness and tamper resistance. Middleware acts as an intermediary layer facilitating communication between different software applications, offering broader integration capabilities but lacking the cryptographic security guarantees of oracles. For decentralized applications requiring reliable external data verification, blockchain oracles are superior, whereas middleware is better suited for general system interoperability.
Connection
Blockchain oracles serve as trusted data feeds that enable smart contracts to interact with external information, while middleware functions as the intermediary layer facilitating communication between blockchain networks and enterprise systems. Together, oracles provide real-world data inputs that middleware processes and integrates, ensuring seamless and secure interoperability for decentralized applications. This connection enhances the reliability and functionality of blockchain solutions by bridging on-chain contracts with off-chain data sources.
Key Terms
Interoperability
Middleware bridges disparate systems by enabling seamless data exchange and communication between applications, enhancing interoperability in traditional IT environments. Blockchain oracles provide trusted external data to smart contracts by securely linking off-chain information with on-chain processes, addressing interoperability challenges unique to decentralized ecosystems. Explore how these technologies redefine data integration across platforms to unlock new possibilities.
Data transmission
Middleware facilitates efficient data transmission by acting as an intermediary layer that enables seamless communication between disparate software applications and systems, ensuring data compatibility and smooth integration. Blockchain oracles transmit real-world data to smart contracts on the blockchain, securely bridging off-chain information with on-chain execution to maintain data integrity and trustworthiness. Explore deeper how middleware and blockchain oracles uniquely address data transmission challenges in decentralized ecosystems.
Trust mechanism
Middleware acts as an intermediary layer facilitating communication and data exchange between disparate systems, maintaining trust through centralized control and predefined protocols. Blockchain oracles provide a decentralized trust mechanism by securely bridging external data to smart contracts, ensuring data integrity and tamper-proof verification via consensus networks. Explore more to understand how these trust frameworks impact system reliability and security.
Source and External Links
What is Middleware? - AWS - Middleware is software that enables different applications to communicate intelligently, abstracting underlying processes and providing secure, standardized interfaces for data exchange between frontend and backend systems.
Middleware - Wikipedia - Middleware refers to software that provides services to applications beyond what's offered by the operating system, acting as a bridge for communication and data management in distributed systems.
What Is Middleware? | IBM - Middleware functions as "software glue," connecting applications or components across distributed networks to streamline integration, accelerate development, and support modern cloud-native environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com