Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, minimizing the attack surface by assuming no implicit trust. Microsegmentation divides a network into isolated segments to contain threats and limit lateral movement within the environment. Discover how these complementary security strategies enhance organizational defense against modern cyber threats.
Why it is important
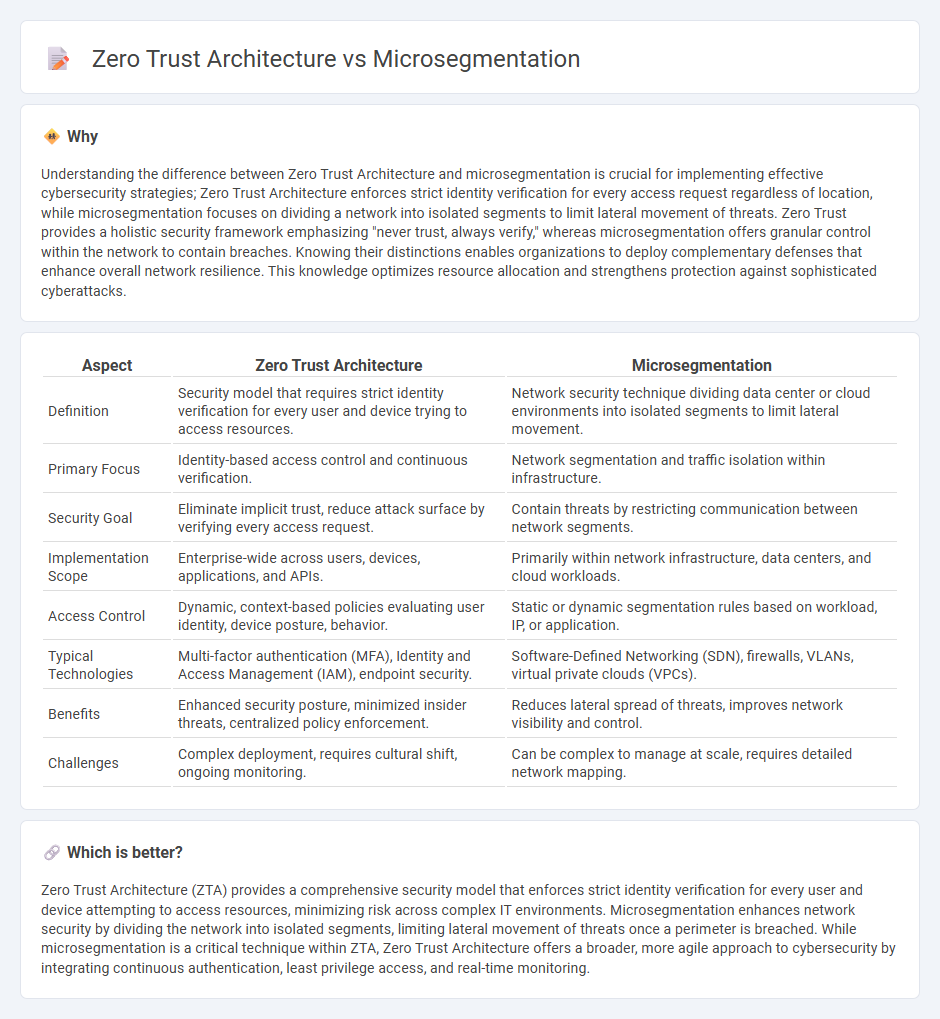
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Architecture and microsegmentation is crucial for implementing effective cybersecurity strategies; Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification for every access request regardless of location, while microsegmentation focuses on dividing a network into isolated segments to limit lateral movement of threats. Zero Trust provides a holistic security framework emphasizing "never trust, always verify," whereas microsegmentation offers granular control within the network to contain breaches. Knowing their distinctions enables organizations to deploy complementary defenses that enhance overall network resilience. This knowledge optimizes resource allocation and strengthens protection against sophisticated cyberattacks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Architecture | Microsegmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model that requires strict identity verification for every user and device trying to access resources. | Network security technique dividing data center or cloud environments into isolated segments to limit lateral movement. |
| Primary Focus | Identity-based access control and continuous verification. | Network segmentation and traffic isolation within infrastructure. |
| Security Goal | Eliminate implicit trust, reduce attack surface by verifying every access request. | Contain threats by restricting communication between network segments. |
| Implementation Scope | Enterprise-wide across users, devices, applications, and APIs. | Primarily within network infrastructure, data centers, and cloud workloads. |
| Access Control | Dynamic, context-based policies evaluating user identity, device posture, behavior. | Static or dynamic segmentation rules based on workload, IP, or application. |
| Typical Technologies | Multi-factor authentication (MFA), Identity and Access Management (IAM), endpoint security. | Software-Defined Networking (SDN), firewalls, VLANs, virtual private clouds (VPCs). |
| Benefits | Enhanced security posture, minimized insider threats, centralized policy enforcement. | Reduces lateral spread of threats, improves network visibility and control. |
| Challenges | Complex deployment, requires cultural shift, ongoing monitoring. | Can be complex to manage at scale, requires detailed network mapping. |
Which is better?
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) provides a comprehensive security model that enforces strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, minimizing risk across complex IT environments. Microsegmentation enhances network security by dividing the network into isolated segments, limiting lateral movement of threats once a perimeter is breached. While microsegmentation is a critical technique within ZTA, Zero Trust Architecture offers a broader, more agile approach to cybersecurity by integrating continuous authentication, least privilege access, and real-time monitoring.
Connection
Zero trust architecture relies on microsegmentation to enhance network security by dividing the IT environment into isolated segments, limiting lateral movement of threats. Microsegmentation enforces granular access controls within zero trust frameworks, ensuring each user or device verifies trust continuously before gaining access. This combination minimizes attack surfaces and reduces the risk of unauthorized access across enterprise networks.
Key Terms
Network Isolation
Microsegmentation enables granular network isolation by dividing data centers into secure segments, minimizing lateral movement of threats within IT environments. Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict access controls and continuous verification regardless of network location, ensuring that every connection is authenticated and authorized. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these approaches to enhance your network security strategy.
Least Privilege Access
Microsegmentation enhances network security by segmenting data centers into granular zones, enforcing Least Privilege Access at the workload level to minimize lateral movement of threats. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) adopts a broader security model, continuously verifying user identities and access permissions across all resources to uphold Least Privilege principles consistently. Explore detailed insights on combining microsegmentation and Zero Trust to maximize access control and threat reduction.
Identity-Based Security
Microsegmentation enhances network security by dividing data centers into isolated segments, restricting lateral movement of threats based on granular policies tied to user identities. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) enforces strict identity-based access controls by verifying every user and device request, regardless of network location, ensuring continuous authentication and least-privilege principles. Explore how integrating microsegmentation within a zero trust framework strengthens identity-based security for comprehensive threat mitigation.
Source and External Links
What is Microsegmentation? The Ultimate Guide to Zero Trust - Microsegmentation is a cybersecurity technique that divides a network into small, isolated segments, each with its own security perimeter, to reduce the attack surface and prevent lateral movement by attackers in the event of a breach.
Microsegmentation (network security) - Microsegmentation allows security architects to create network security zones per machine (or application) in data centers and cloud deployments, enabling granular isolation and protection of individual workloads.
Cybersecurity 101: Microsegmentation - Microsegmentation splits a network into smaller, separate, and isolated sections at the workload, application, or device level, enforcing strict security policies and supporting Zero Trust security models by restricting an attacker's ability to move freely if a segment is compromised.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com