Quantum dots display technology offers superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens, which rely on color filters and backlighting. Unlike LCDs, quantum dots emit precise wavelengths of light, resulting in more vibrant visuals and enhanced viewing angles. Discover how quantum dots revolutionize display technology and improve your visual experience.
Why it is important
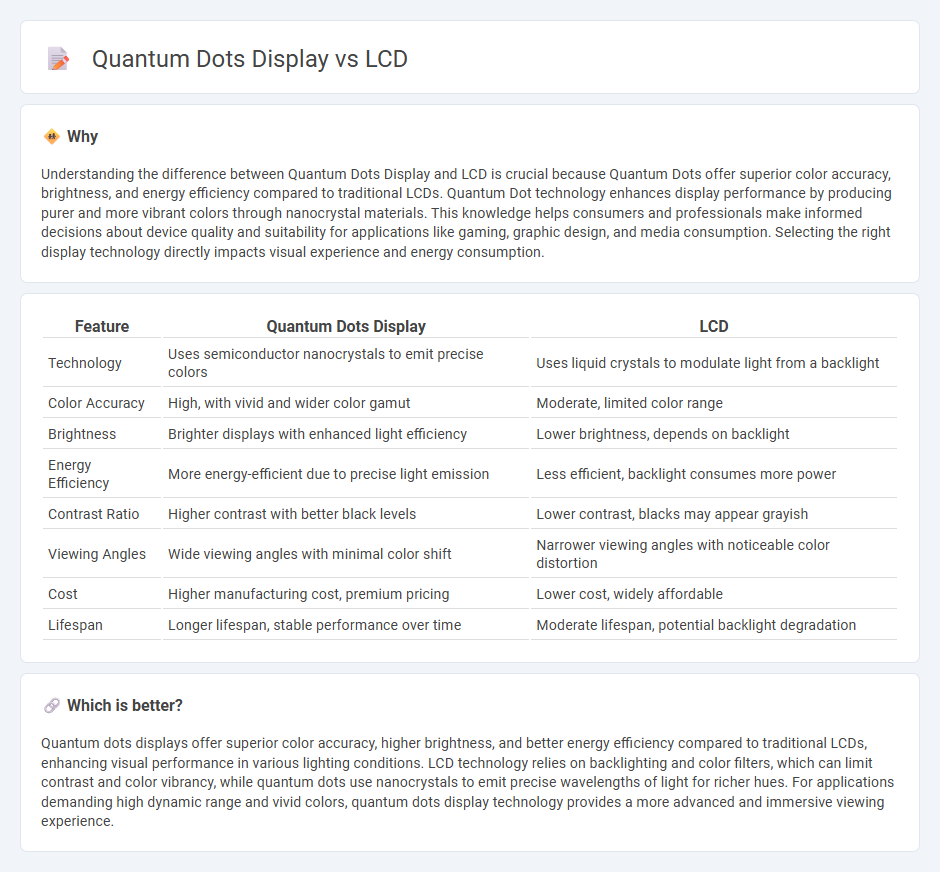
Understanding the difference between Quantum Dots Display and LCD is crucial because Quantum Dots offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCDs. Quantum Dot technology enhances display performance by producing purer and more vibrant colors through nanocrystal materials. This knowledge helps consumers and professionals make informed decisions about device quality and suitability for applications like gaming, graphic design, and media consumption. Selecting the right display technology directly impacts visual experience and energy consumption.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Dots Display | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses semiconductor nanocrystals to emit precise colors | Uses liquid crystals to modulate light from a backlight |
| Color Accuracy | High, with vivid and wider color gamut | Moderate, limited color range |
| Brightness | Brighter displays with enhanced light efficiency | Lower brightness, depends on backlight |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient due to precise light emission | Less efficient, backlight consumes more power |
| Contrast Ratio | Higher contrast with better black levels | Lower contrast, blacks may appear grayish |
| Viewing Angles | Wide viewing angles with minimal color shift | Narrower viewing angles with noticeable color distortion |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost, premium pricing | Lower cost, widely affordable |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan, stable performance over time | Moderate lifespan, potential backlight degradation |
Which is better?
Quantum dots displays offer superior color accuracy, higher brightness, and better energy efficiency compared to traditional LCDs, enhancing visual performance in various lighting conditions. LCD technology relies on backlighting and color filters, which can limit contrast and color vibrancy, while quantum dots use nanocrystals to emit precise wavelengths of light for richer hues. For applications demanding high dynamic range and vivid colors, quantum dots display technology provides a more advanced and immersive viewing experience.
Connection
Quantum dots enhance LCD technology by improving color accuracy and brightness through nanoscale semiconductor particles that emit precise wavelengths of light when energized. This integration allows LCD screens to produce broader color gamuts and higher dynamic range, offering more vivid and lifelike images. Manufacturers use quantum dot films as backlighting layers in LCD panels to achieve superior display performance while maintaining energy efficiency.
Key Terms
Backlighting
LCD displays rely on LED backlighting that emits white light passing through color filters, while Quantum Dot displays use a blue LED backlight combined with a quantum dot layer to enhance color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots convert blue light into precise primary colors, resulting in higher color gamut and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LCDs. Explore the technological differences and benefits of Quantum Dot backlighting to understand its impact on modern display quality.
Color Gamut
Quantum dot displays outperform traditional LCDs by offering a wider color gamut, covering up to 90-100% of the DCI-P3 color space compared to the 60-70% range typical for LCDs. This enhanced color accuracy and vibrancy result from quantum dots' ability to emit pure, narrow-spectrum colors when excited by a backlight. Discover how quantum dot technology revolutionizes visual experience by exploring its advantages beyond color gamut.
Nanocrystals
Quantum dot displays utilize nanocrystals composed of semiconductor materials that emit precise wavelengths of light when excited, resulting in superior color accuracy and brightness compared to traditional LCDs. These nanocrystals enhance the backlighting system by converting blue LED light into pure red and green hues, significantly expanding the color gamut and improving energy efficiency. Explore the science behind nanocrystals to understand how quantum dot technology revolutionizes modern displays.
Source and External Links
Liquid-crystal display - Wikipedia - An LCD is a flat-panel display that uses liquid crystals and polarizers to modulate light, relying on a backlight or reflector to produce images, and is used widely in TVs, monitors, smartphones, and other devices, replacing older bulkier display technologies like CRTs.
What is LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)? - TechTarget - LCD is a flat panel display technology using liquid crystals that block light to create images, consuming less power than older display types like LED and plasma, and now increasingly replaced by newer technologies such as OLED.
What is a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)? Advantages & Disadvantages - LCDs have liquid crystals between two electrodes that align when electric current is applied to control light passage, offering thin, lightweight, energy-efficient displays with sharp images, using backlights such as LED or CCFL for illumination.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com