eBPF provides advanced kernel-level observability and security by enabling custom programs to run efficiently within the Linux kernel, offering real-time insights and minimal performance overhead. Auditd focuses on traditional system auditing by logging security-related events, primarily user actions and file accesses, which helps in compliance and forensic analysis. Explore the key differences between eBPF and Auditd to determine the best fit for your Linux system monitoring and security needs.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between eBPF and Auditd is crucial for effective system monitoring and security in modern Linux environments. eBPF offers high-performance, programmable tracing within the kernel, enabling detailed real-time observability with minimal overhead. Auditd provides traditional, rule-based auditing focused on security event logging and compliance reporting. Understanding their distinct capabilities helps optimize resource use, enhance security posture, and tailor monitoring strategies to specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
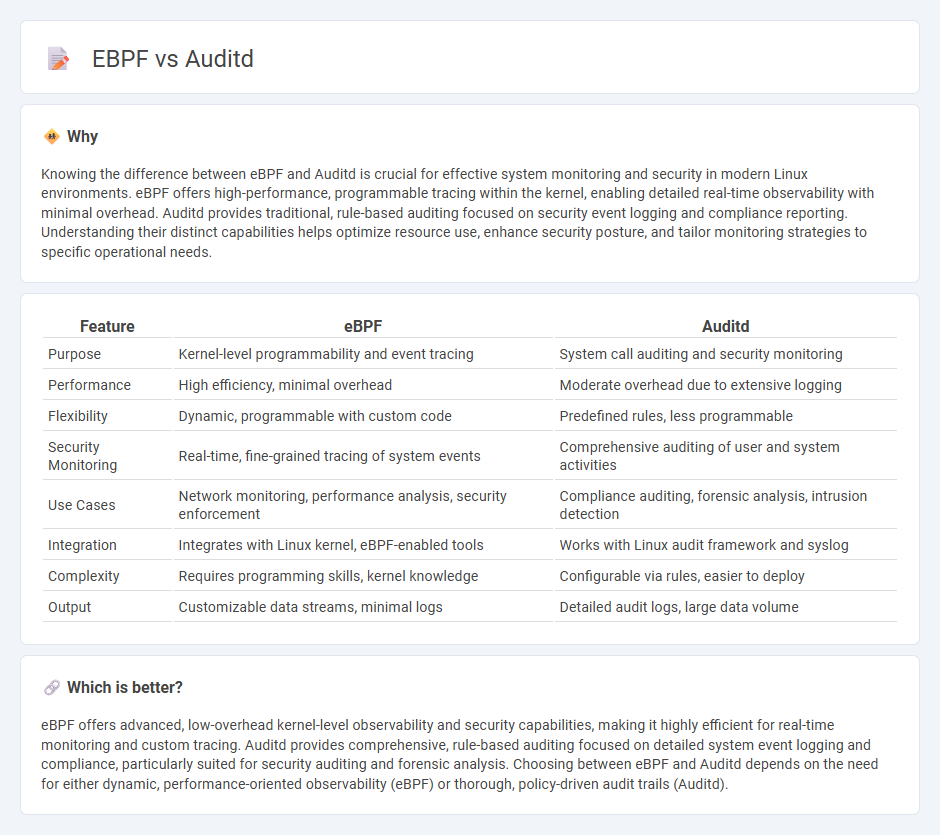
| Feature | eBPF | Auditd |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Kernel-level programmability and event tracing | System call auditing and security monitoring |
| Performance | High efficiency, minimal overhead | Moderate overhead due to extensive logging |
| Flexibility | Dynamic, programmable with custom code | Predefined rules, less programmable |
| Security Monitoring | Real-time, fine-grained tracing of system events | Comprehensive auditing of user and system activities |
| Use Cases | Network monitoring, performance analysis, security enforcement | Compliance auditing, forensic analysis, intrusion detection |
| Integration | Integrates with Linux kernel, eBPF-enabled tools | Works with Linux audit framework and syslog |
| Complexity | Requires programming skills, kernel knowledge | Configurable via rules, easier to deploy |
| Output | Customizable data streams, minimal logs | Detailed audit logs, large data volume |
Which is better?
eBPF offers advanced, low-overhead kernel-level observability and security capabilities, making it highly efficient for real-time monitoring and custom tracing. Auditd provides comprehensive, rule-based auditing focused on detailed system event logging and compliance, particularly suited for security auditing and forensic analysis. Choosing between eBPF and Auditd depends on the need for either dynamic, performance-oriented observability (eBPF) or thorough, policy-driven audit trails (Auditd).
Connection
eBPF (extended Berkeley Packet Filter) enhances Auditd by enabling dynamic tracing and monitoring of system calls with minimal overhead. Auditd utilizes eBPF programs to capture detailed security events and kernel-level telemetry in real time. This integration improves system audit capabilities, offering precise event filtering and performance-efficient logging within Linux environments.
Key Terms
System Monitoring
Auditd provides comprehensive system call auditing by capturing detailed logs of security-relevant events within the Linux kernel, enabling thorough compliance and forensic analysis. eBPF offers dynamic, programmable tracing for real-time system performance monitoring and security detection without the overhead of traditional tools, allowing users to customize probes efficiently. Explore deeper insights into how Auditd and eBPF enhance system monitoring capabilities tailored to your needs.
Kernel-level Tracing
Auditd provides comprehensive kernel-level tracing through Linux Audit Framework, capturing detailed security-relevant events with reliable event logging and compliance support. eBPF offers dynamic, programmable tracing capabilities that allow fine-grained monitoring and real-time data collection with minimal performance overhead. Explore the advantages and use cases of auditd and eBPF for advanced kernel tracing to enhance your system monitoring strategies.
Event Logging
Auditd provides traditional, kernel-based event logging by monitoring system calls and security-related activities with extensive predefined rules, ensuring compliance and granular audit trails. eBPF offers dynamic tracing and event logging capabilities directly within the Linux kernel, enabling efficient, customizable, and high-performance monitoring without the overhead of traditional logging methods. Explore the detailed comparison of Auditd and eBPF event logging to enhance your system security strategy.
Source and External Links
Linux auditd: What Is It and How Do You Use It? - Insentra - auditd is a core component of the Linux Auditing System that monitors and records system activities based on admin-defined rules, enabling security monitoring, compliance, intrusion detection, and forensic analysis.
Configure Linux system auditing with auditd - Red Hat - Sysadmins use auditd to log security-relevant events, define custom audit rules, search logs, and create reports to track violations and enhance system security policies.
auditd(8) - Linux manual page - auditd is the userspace daemon responsible for writing audit records to disk, with configuration via auditd.conf and rules managed through utilities like auditctl and augenrules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com