Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices such as IoT sensors, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making, while cloud computing relies on centralized servers to handle large-scale data storage and complex analytics. The integration of AI at the network edge optimizes bandwidth use and improves responsiveness for critical applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities. Discover how combining edge intelligence with cloud computing transforms modern technology ecosystems.
Why it is important
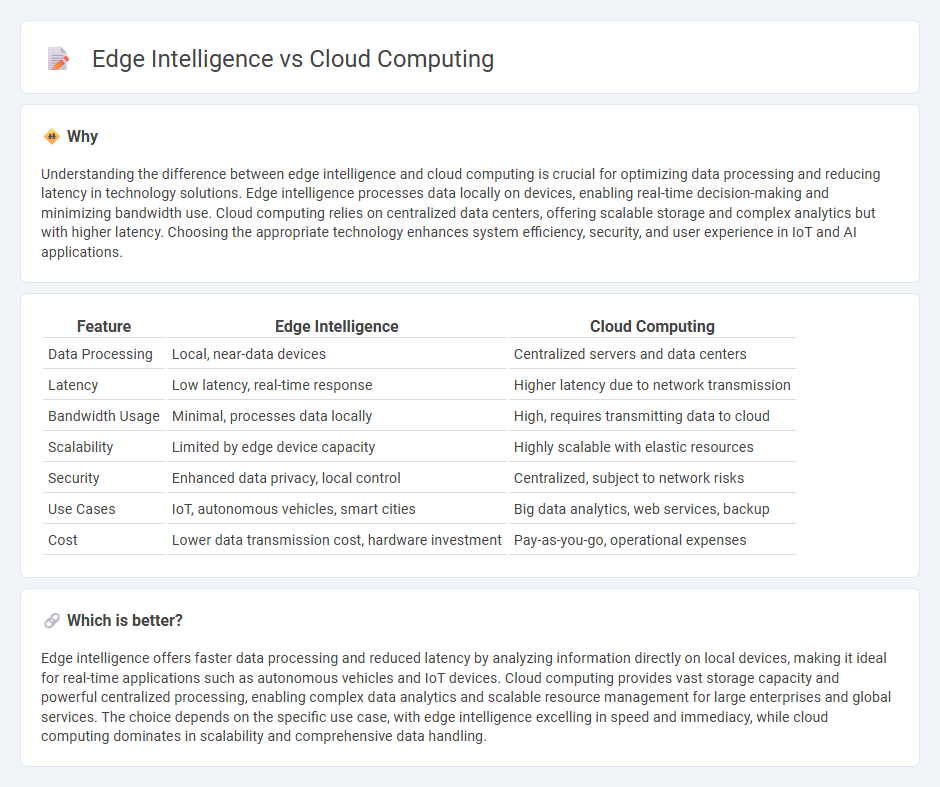
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and cloud computing is crucial for optimizing data processing and reducing latency in technology solutions. Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices, enabling real-time decision-making and minimizing bandwidth use. Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers, offering scalable storage and complex analytics but with higher latency. Choosing the appropriate technology enhances system efficiency, security, and user experience in IoT and AI applications.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Intelligence | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | Local, near-data devices | Centralized servers and data centers |
| Latency | Low latency, real-time response | Higher latency due to network transmission |
| Bandwidth Usage | Minimal, processes data locally | High, requires transmitting data to cloud |
| Scalability | Limited by edge device capacity | Highly scalable with elastic resources |
| Security | Enhanced data privacy, local control | Centralized, subject to network risks |
| Use Cases | IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities | Big data analytics, web services, backup |
| Cost | Lower data transmission cost, hardware investment | Pay-as-you-go, operational expenses |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence offers faster data processing and reduced latency by analyzing information directly on local devices, making it ideal for real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and IoT devices. Cloud computing provides vast storage capacity and powerful centralized processing, enabling complex data analytics and scalable resource management for large enterprises and global services. The choice depends on the specific use case, with edge intelligence excelling in speed and immediacy, while cloud computing dominates in scalability and comprehensive data handling.
Connection
Edge intelligence enhances cloud computing by processing data locally on edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while enabling real-time analytics. Cloud computing provides centralized storage, scalability, and advanced machine learning models that edge devices leverage for complex tasks. Together, they create a hybrid ecosystem where data is efficiently managed between edge nodes and cloud infrastructure, optimizing performance and resource allocation.
Key Terms
Data Latency
Cloud computing processes data in centralized data centers, often resulting in higher data latency due to the distance between devices and servers. Edge intelligence reduces data latency by processing information locally on edge devices, enabling real-time analytics and faster decision-making. Explore more to understand how minimizing data latency impacts efficiency and performance in modern networks.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation in cloud computing relies on centralized data centers, offering vast computational power but facing latency and bandwidth constraints when processing real-time data from distributed devices. Edge intelligence distributes processing closer to data sources, optimizing resource use by minimizing latency and reducing bandwidth usage, which enhances responsiveness for time-critical applications. Explore more to understand how combining cloud and edge computing can revolutionize resource allocation strategies.
Source and External Links
Cloud Computing - Cloud computing involves delivering hosted IT services over the internet with a pay-as-you-go model, utilizing remote data centers and servers.
Cloud Computing - Cloud computing is a model providing network access to a scalable pool of shareable resources, characterized by self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
Cloud Computing - Cloud computing offers on-demand access to computing resources like servers, storage, and software over the internet, with flexible pricing based on usage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com