Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making, while the Internet of Things (IoT) connects numerous devices through the internet for data collection and centralized analysis. Edge intelligence improves efficiency by minimizing reliance on cloud computing, enabling faster responses in critical applications such as autonomous vehicles and smart healthcare. Discover more about how these technologies transform connectivity and data processing.
Why it is important
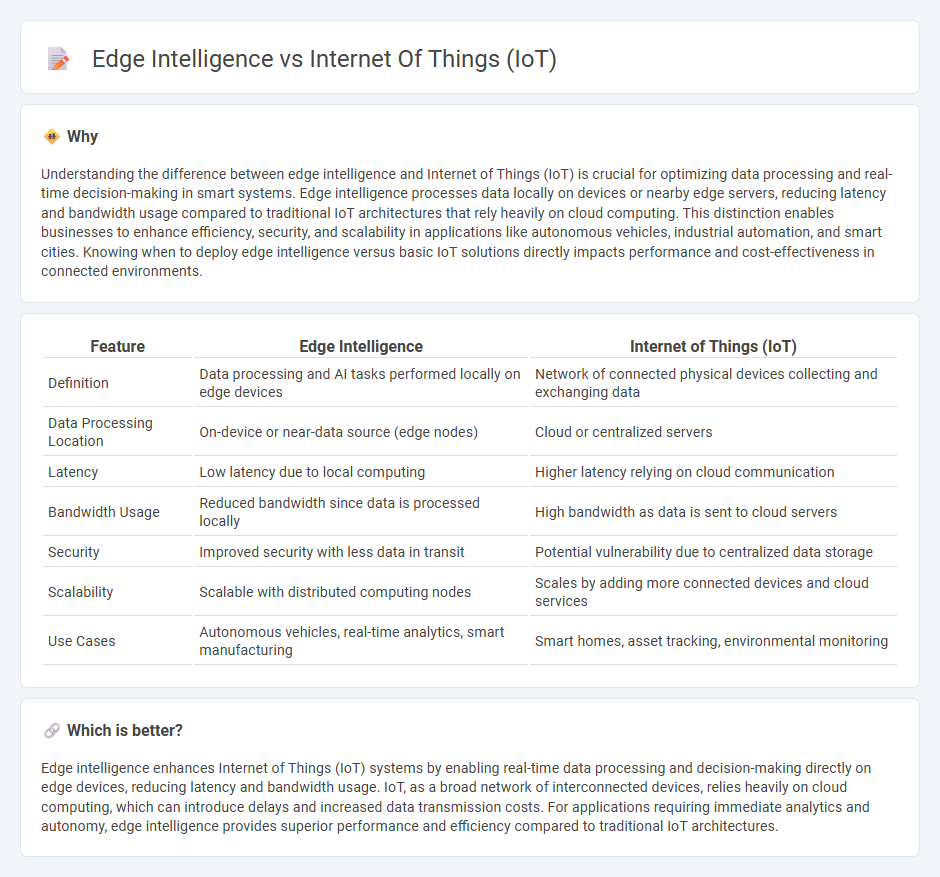
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT) is crucial for optimizing data processing and real-time decision-making in smart systems. Edge intelligence processes data locally on devices or nearby edge servers, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional IoT architectures that rely heavily on cloud computing. This distinction enables businesses to enhance efficiency, security, and scalability in applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart cities. Knowing when to deploy edge intelligence versus basic IoT solutions directly impacts performance and cost-effectiveness in connected environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Intelligence | Internet of Things (IoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data processing and AI tasks performed locally on edge devices | Network of connected physical devices collecting and exchanging data |
| Data Processing Location | On-device or near-data source (edge nodes) | Cloud or centralized servers |
| Latency | Low latency due to local computing | Higher latency relying on cloud communication |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced bandwidth since data is processed locally | High bandwidth as data is sent to cloud servers |
| Security | Improved security with less data in transit | Potential vulnerability due to centralized data storage |
| Scalability | Scalable with distributed computing nodes | Scales by adding more connected devices and cloud services |
| Use Cases | Autonomous vehicles, real-time analytics, smart manufacturing | Smart homes, asset tracking, environmental monitoring |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence enhances Internet of Things (IoT) systems by enabling real-time data processing and decision-making directly on edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. IoT, as a broad network of interconnected devices, relies heavily on cloud computing, which can introduce delays and increased data transmission costs. For applications requiring immediate analytics and autonomy, edge intelligence provides superior performance and efficiency compared to traditional IoT architectures.
Connection
Edge intelligence processes data locally on IoT devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by analyzing information near the data source. This synergy enhances real-time decision-making in applications such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. Integrating edge intelligence with IoT networks improves efficiency, security, and scalability in distributed computing environments.
Key Terms
Connectivity
The Internet of Things (IoT) relies on extensive network connectivity to link billions of devices, enabling data collection and remote monitoring across diverse applications such as smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare. Edge intelligence enhances this framework by processing data locally on edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while improving real-time decision-making capabilities. Explore how combining IoT with edge intelligence transforms connectivity and operational efficiency in modern networks.
Data Processing Location
Internet of Things (IoT) primarily relies on centralized cloud servers to process and analyze data collected from connected devices, enabling comprehensive insights but often introducing latency and bandwidth constraints. Edge intelligence shifts data processing closer to the source, leveraging edge devices and local servers to perform real-time analytics and reduce dependency on cloud infrastructures, enhancing responsiveness and security. Explore the evolving roles of IoT and edge intelligence to optimize data processing strategies for advanced applications.
Real-time Analytics
Internet of Things (IoT) enables data collection from interconnected devices, while edge intelligence processes this data locally for real-time analytics, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Edge intelligence enhances IoT by providing immediate insights and faster decision-making at the source without relying on centralized cloud servers. Discover how real-time analytics transform operational efficiency through the synergy of IoT and edge intelligence.
Source and External Links
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity to collect and share data, enabling communication between devices for a wide range of applications across industries.
What Is the Internet of Things? - IoT describes a network of physical objects equipped with sensors and software to exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet, allowing for seamless interaction between people, processes, and things, with minimal human intervention.
What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - IoT is a collective network of connected devices and technology that enables communication between devices and the cloud, using sensors and processors to allow everyday objects to collect data and respond intelligently to user needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com