Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access resources, minimizing risks in modern network environments. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) acts as a gatekeeper, providing visibility, real-time monitoring, and policy enforcement between cloud service users and cloud applications. Explore the nuances and benefits of these complementary security models to enhance organizational protection.
Why it is important
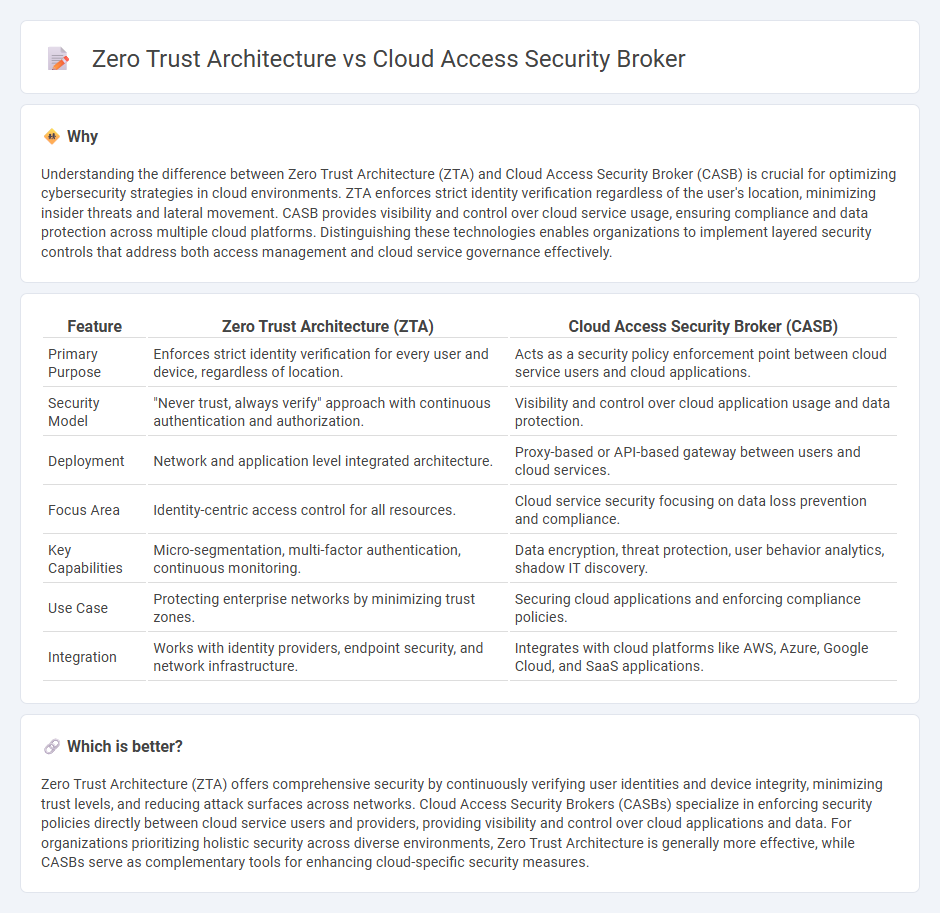
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) is crucial for optimizing cybersecurity strategies in cloud environments. ZTA enforces strict identity verification regardless of the user's location, minimizing insider threats and lateral movement. CASB provides visibility and control over cloud service usage, ensuring compliance and data protection across multiple cloud platforms. Distinguishing these technologies enables organizations to implement layered security controls that address both access management and cloud service governance effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) | Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Enforces strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of location. | Acts as a security policy enforcement point between cloud service users and cloud applications. |
| Security Model | "Never trust, always verify" approach with continuous authentication and authorization. | Visibility and control over cloud application usage and data protection. |
| Deployment | Network and application level integrated architecture. | Proxy-based or API-based gateway between users and cloud services. |
| Focus Area | Identity-centric access control for all resources. | Cloud service security focusing on data loss prevention and compliance. |
| Key Capabilities | Micro-segmentation, multi-factor authentication, continuous monitoring. | Data encryption, threat protection, user behavior analytics, shadow IT discovery. |
| Use Case | Protecting enterprise networks by minimizing trust zones. | Securing cloud applications and enforcing compliance policies. |
| Integration | Works with identity providers, endpoint security, and network infrastructure. | Integrates with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and SaaS applications. |
Which is better?
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) offers comprehensive security by continuously verifying user identities and device integrity, minimizing trust levels, and reducing attack surfaces across networks. Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) specialize in enforcing security policies directly between cloud service users and providers, providing visibility and control over cloud applications and data. For organizations prioritizing holistic security across diverse environments, Zero Trust Architecture is generally more effective, while CASBs serve as complementary tools for enhancing cloud-specific security measures.
Connection
Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification for every device and user attempting to access resources, minimizing risks in cloud environments. Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) act as security policy enforcement points between cloud service consumers and providers, ensuring data protection and compliance. Together, they enhance cloud security by integrating continuous verification with real-time monitoring and control over cloud access.
Key Terms
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) enhance Identity and Access Management (IAM) by providing real-time visibility, policy enforcement, and threat protection across cloud services, ensuring secure access control. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) fundamentally redefines IAM by continuously verifying user identities and device health without assuming trust, implementing strict least-privilege access and micro-segmentation. Explore detailed comparisons and implementation strategies to strengthen your organization's IAM posture.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide centralized visibility and control over cloud applications, enforcing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies to monitor and prevent sensitive data exposure in real-time. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) emphasizes strict identity verification and least-privilege access, reducing data loss risks by continuously validating users and devices before granting resource access. Explore how integrating CASB with Zero Trust frameworks enhances comprehensive DLP strategies.
Network Segmentation
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) provide visibility and control over cloud service usage by enforcing security policies, whereas Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) emphasizes strict identity verification and minimal trust, implementing granular Network Segmentation to isolate resources and reduce attack surfaces. Network Segmentation in Zero Trust divides networks into smaller zones to control traffic flow, limiting lateral movement and enhancing security compared to traditional perimeter-based CASB approaches. Explore how integrating CASB with Zero Trust's Network Segmentation can strengthen your cloud security strategy.
Source and External Links
What Is a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)? - This page explains how CASBs provide visibility, data control, and analytics to identify and combat threats in cloud environments.
Cloud access security broker - A cloud access security broker (CASB) is software that sits between users and cloud services, enforcing security policies and monitoring activity.
What is a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)? - This resource defines CASB as a security enforcement point that combines enterprise policies with cloud services to address security risks and compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com