Edge mesh computing enhances network efficiency by interconnecting multiple edge devices to share processing tasks, reducing latency and improving data distribution. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities closer to the data source through localized nodes, enabling real-time analytics and faster decision-making at the network's edge. Explore more to understand how these technologies redefine data processing for IoT and smart systems.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and fog computing is crucial for optimizing network architecture and improving data processing efficiency. Edge mesh decentralizes computing by connecting multiple edge devices to share resources, enhancing scalability and fault tolerance. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities closer to the data source, enabling real-time analytics and reduced latency. Choosing the right approach impacts system performance, security, and operational costs in IoT and smart device deployments.
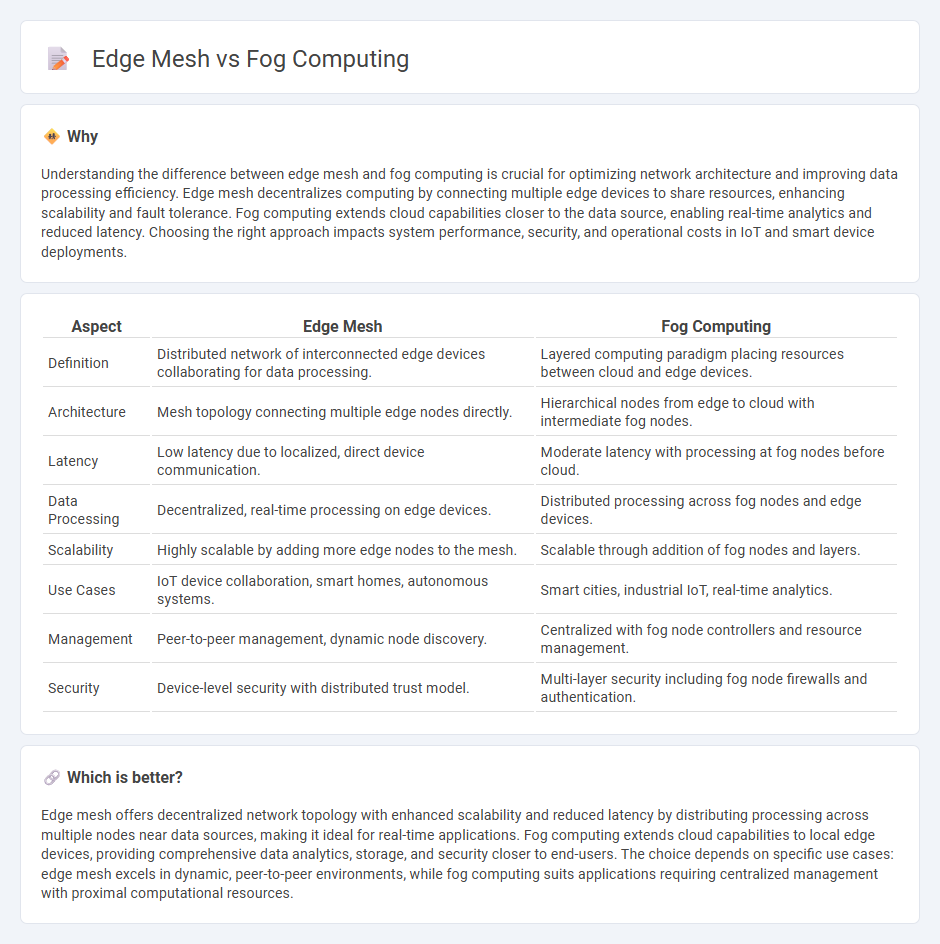
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Edge Mesh | Fog Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed network of interconnected edge devices collaborating for data processing. | Layered computing paradigm placing resources between cloud and edge devices. |
| Architecture | Mesh topology connecting multiple edge nodes directly. | Hierarchical nodes from edge to cloud with intermediate fog nodes. |
| Latency | Low latency due to localized, direct device communication. | Moderate latency with processing at fog nodes before cloud. |
| Data Processing | Decentralized, real-time processing on edge devices. | Distributed processing across fog nodes and edge devices. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable by adding more edge nodes to the mesh. | Scalable through addition of fog nodes and layers. |
| Use Cases | IoT device collaboration, smart homes, autonomous systems. | Smart cities, industrial IoT, real-time analytics. |
| Management | Peer-to-peer management, dynamic node discovery. | Centralized with fog node controllers and resource management. |
| Security | Device-level security with distributed trust model. | Multi-layer security including fog node firewalls and authentication. |
Which is better?
Edge mesh offers decentralized network topology with enhanced scalability and reduced latency by distributing processing across multiple nodes near data sources, making it ideal for real-time applications. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities to local edge devices, providing comprehensive data analytics, storage, and security closer to end-users. The choice depends on specific use cases: edge mesh excels in dynamic, peer-to-peer environments, while fog computing suits applications requiring centralized management with proximal computational resources.
Connection
Edge mesh and fog computing both enhance distributed computing by decentralizing data processing closer to IoT devices, reducing latency and bandwidth use. Edge mesh organizes interconnected edge nodes into a flexible, resilient network, while fog computing extends cloud capabilities to the network's edge, enabling real-time analytics and improved scalability. Together, they optimize resource allocation and support seamless data flow across edge devices and fog nodes.
Key Terms
Latency
Fog computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source through distributed nodes across the network, optimizing response times for time-sensitive applications. Edge mesh extends this by interconnecting multiple edge devices and nodes, enabling localized data sharing and computation that further minimizes latency and enhances real-time performance. Explore the differences in architecture and latency benefits to understand which solution best suits your application needs.
Decentralization
Fog computing decentralizes data processing by distributing computational resources across network nodes closer to end devices, reducing latency and bandwidth use. Edge mesh architecture expands this concept by interconnecting multiple edge nodes into a dynamic, cooperative network that enhances scalability and fault tolerance. Explore detailed comparisons to understand their impact on decentralized computing environments.
Data Processing Location
Fog computing distributes data processing tasks across decentralized nodes located between the cloud and edge devices, optimizing latency and bandwidth by processing data closer to its source. Edge mesh architecture further decentralizes this approach by creating a network of interconnected edge devices that collaboratively handle data processing, enhancing scalability and real-time responsiveness. Explore detailed comparisons and use cases to understand how these architectures impact data processing efficiency.
Source and External Links
Fog Computing: Definition, Explanation, and Use Cases - Fog computing is a decentralized computing infrastructure that processes data locally near the source rather than sending it to the cloud, reducing latency and improving security by operating independently of wider networks.
Fog computing - Wikipedia - Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by deploying computation, storage, and networking services close to IoT devices, minimizing latency and bandwidth usage by processing raw data locally before sending only processed data to the cloud.
What Is Fog Computing? Importance, Applications, Everything to Know - Fog computing brings computation and storage closer to IoT devices at the network edge to reduce latency and improve security; it differs from edge computing in that it extends cloud services closer to edge devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com