Edge intelligence leverages advanced AI algorithms directly on edge devices, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making without constant cloud dependency. Embedded systems are specialized computing units designed for dedicated functions within larger systems, often with limited processing power and no AI capabilities. Explore the differences between edge intelligence and embedded systems to understand their unique roles in modern technology.
Why it is important
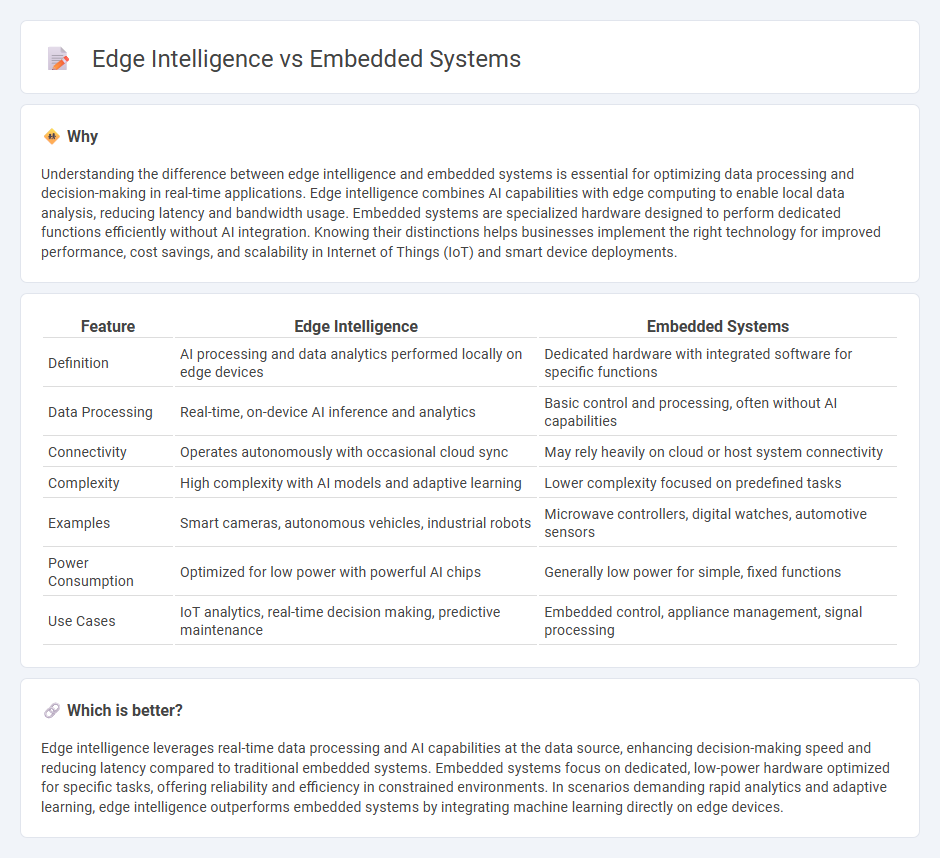
Understanding the difference between edge intelligence and embedded systems is essential for optimizing data processing and decision-making in real-time applications. Edge intelligence combines AI capabilities with edge computing to enable local data analysis, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Embedded systems are specialized hardware designed to perform dedicated functions efficiently without AI integration. Knowing their distinctions helps businesses implement the right technology for improved performance, cost savings, and scalability in Internet of Things (IoT) and smart device deployments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Intelligence | Embedded Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI processing and data analytics performed locally on edge devices | Dedicated hardware with integrated software for specific functions |
| Data Processing | Real-time, on-device AI inference and analytics | Basic control and processing, often without AI capabilities |
| Connectivity | Operates autonomously with occasional cloud sync | May rely heavily on cloud or host system connectivity |
| Complexity | High complexity with AI models and adaptive learning | Lower complexity focused on predefined tasks |
| Examples | Smart cameras, autonomous vehicles, industrial robots | Microwave controllers, digital watches, automotive sensors |
| Power Consumption | Optimized for low power with powerful AI chips | Generally low power for simple, fixed functions |
| Use Cases | IoT analytics, real-time decision making, predictive maintenance | Embedded control, appliance management, signal processing |
Which is better?
Edge intelligence leverages real-time data processing and AI capabilities at the data source, enhancing decision-making speed and reducing latency compared to traditional embedded systems. Embedded systems focus on dedicated, low-power hardware optimized for specific tasks, offering reliability and efficiency in constrained environments. In scenarios demanding rapid analytics and adaptive learning, edge intelligence outperforms embedded systems by integrating machine learning directly on edge devices.
Connection
Edge intelligence integrates artificial intelligence capabilities directly into embedded systems, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making at the data source. Embedded systems equipped with edge intelligence reduce latency and bandwidth usage by minimizing the need to transmit data to centralized cloud servers. This synergy enhances performance and efficiency in applications such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation.
Key Terms
Microcontroller (MCU)
Microcontrollers (MCUs) are fundamental in embedded systems, providing efficient real-time control with limited computational resources and low power consumption. Edge intelligence enhances MCUs by integrating AI processing capabilities directly on the device, enabling faster data analysis and decision-making near the data source. Explore the advancements in MCU-based edge intelligence to understand its impact on IoT and smart device innovation.
AI Inference
Embedded systems integrate dedicated hardware and software to perform AI inference with low latency and power efficiency, often in constrained environments. Edge intelligence leverages AI models directly on edge devices, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making without cloud dependency, enhancing privacy and reducing bandwidth usage. Explore the latest advancements in AI inference to understand how embedded systems and edge intelligence are transforming intelligent applications.
Real-time Processing
Embedded systems excel in real-time processing by executing dedicated tasks with minimal latency and high reliability in constrained hardware environments. Edge intelligence enhances these capabilities by incorporating advanced machine learning algorithms and data analytics directly at the network's edge, enabling faster decision-making and reduced dependency on cloud resources. Explore how integrating edge intelligence with embedded systems transforms real-time processing for critical applications.
Source and External Links
Embedded system - Embedded systems are specialized computer systems with dedicated functions, embedded as part of larger devices, and often feature real-time computing constraints and a wide range of applications from watches to industrial machines.
What is an Embedded System? | Definition from TechTarget - An embedded system is a combination of hardware and software designed for a specific task within a larger system, covering a broad spectrum from industrial controls to consumer electronics.
Introduction of Embedded Systems | Set-1 - Embedded systems integrate hardware like sensors and microcontrollers with software (firmware) to reliably perform dedicated tasks, often in real time, with examples including home appliances and automotive controls.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com