Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated content such as deepfakes, manipulated images, and audio, using techniques like biometric analysis and machine learning classifiers. Fake news identification involves verifying the credibility of information by analyzing sources, cross-referencing facts, and detecting misinformation patterns through natural language processing and network analysis. Explore cutting-edge advancements to understand how these technologies combat digital misinformation effectively.
Why it is important
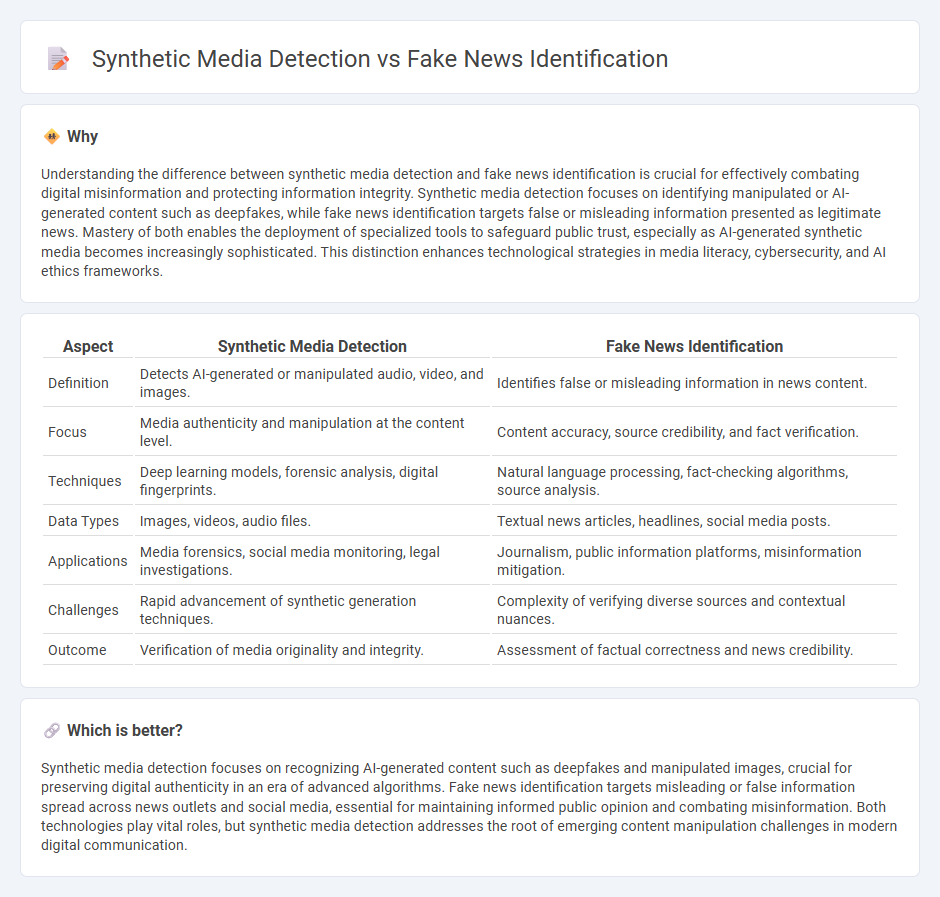
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and fake news identification is crucial for effectively combating digital misinformation and protecting information integrity. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content such as deepfakes, while fake news identification targets false or misleading information presented as legitimate news. Mastery of both enables the deployment of specialized tools to safeguard public trust, especially as AI-generated synthetic media becomes increasingly sophisticated. This distinction enhances technological strategies in media literacy, cybersecurity, and AI ethics frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Media Detection | Fake News Identification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detects AI-generated or manipulated audio, video, and images. | Identifies false or misleading information in news content. |
| Focus | Media authenticity and manipulation at the content level. | Content accuracy, source credibility, and fact verification. |
| Techniques | Deep learning models, forensic analysis, digital fingerprints. | Natural language processing, fact-checking algorithms, source analysis. |
| Data Types | Images, videos, audio files. | Textual news articles, headlines, social media posts. |
| Applications | Media forensics, social media monitoring, legal investigations. | Journalism, public information platforms, misinformation mitigation. |
| Challenges | Rapid advancement of synthetic generation techniques. | Complexity of verifying diverse sources and contextual nuances. |
| Outcome | Verification of media originality and integrity. | Assessment of factual correctness and news credibility. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection focuses on recognizing AI-generated content such as deepfakes and manipulated images, crucial for preserving digital authenticity in an era of advanced algorithms. Fake news identification targets misleading or false information spread across news outlets and social media, essential for maintaining informed public opinion and combating misinformation. Both technologies play vital roles, but synthetic media detection addresses the root of emerging content manipulation challenges in modern digital communication.
Connection
Synthetic media detection and fake news identification are interconnected through their reliance on advanced machine learning algorithms that analyze digital content authenticity. Techniques such as deepfake recognition and natural language processing enable the identification of manipulated videos and fabricated news stories by detecting inconsistencies and anomalies in multimedia and text data. Effective integration of these technologies strengthens the defense against misinformation dissemination across social media platforms and news outlets.
Key Terms
Misinformation classification
Fake news identification targets false or misleading information disseminated often through text, focusing on linguistic cues and factual inconsistencies to classify misinformation accurately. Synthetic media detection involves analyzing multimedia content, including deepfakes and AI-generated images or videos, to identify manipulated or fabricated content contributing to misinformation. Explore advanced methodologies in misinformation classification to enhance detection capabilities across both textual and synthetic media platforms.
Deepfake detection
Deepfake detection, a critical subset of synthetic media detection, employs advanced algorithms to identify manipulated video and audio content generated through AI techniques, contrasting with broader fake news identification which targets misleading textual information. Techniques such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and forensic analysis of digital artifacts enhance the accuracy of distinguishing authentic media from deepfakes. Explore the latest advancements and methodologies in deepfake detection to better understand the evolving landscape of synthetic media threats.
Content authenticity verification
Fake news identification primarily targets the verification of textual accuracy and source credibility to combat misinformation, while synthetic media detection emphasizes analyzing multimedia elements such as deepfakes and AI-generated images for signs of manipulation. Both approaches leverage machine learning models trained on large datasets to assess content authenticity through linguistic patterns, visual inconsistencies, and metadata examination. Explore advanced techniques in content authenticity verification to enhance detection capabilities across diverse media formats.
Source and External Links
Approaches to Identify Fake News: A Systematic Literature Review - Identifies five main approaches for fake news detection: language, topic-agnostic, machine learning, knowledge-based, and hybrid methods that can be combined for better results.
Fake News Infographic - Misinformation, Disinformation, and ... - Offers practical tips for spotting fake news including checking the source, author credibility, supporting sources, date, and considering personal biases.
Fake News Detection | European Data Protection Supervisor - Describes automated fake news detection using AI, natural language processing, and metadata analysis for text, images, and videos to improve accuracy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com