Quantum networking harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to enable ultra-secure communication and unprecedented computational power, while IoT networking connects vast arrays of devices to collect and exchange data efficiently across diverse platforms. Quantum networks utilize quantum entanglement and superposition to achieve instantaneous data transfer and enhanced security, contrasting with IoT's reliance on traditional IP-based protocols and wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi, LTE, and LPWAN. Explore the unique advantages and future potential of quantum networking compared to IoT networking to understand their evolving roles in the technology landscape.
Why it is important
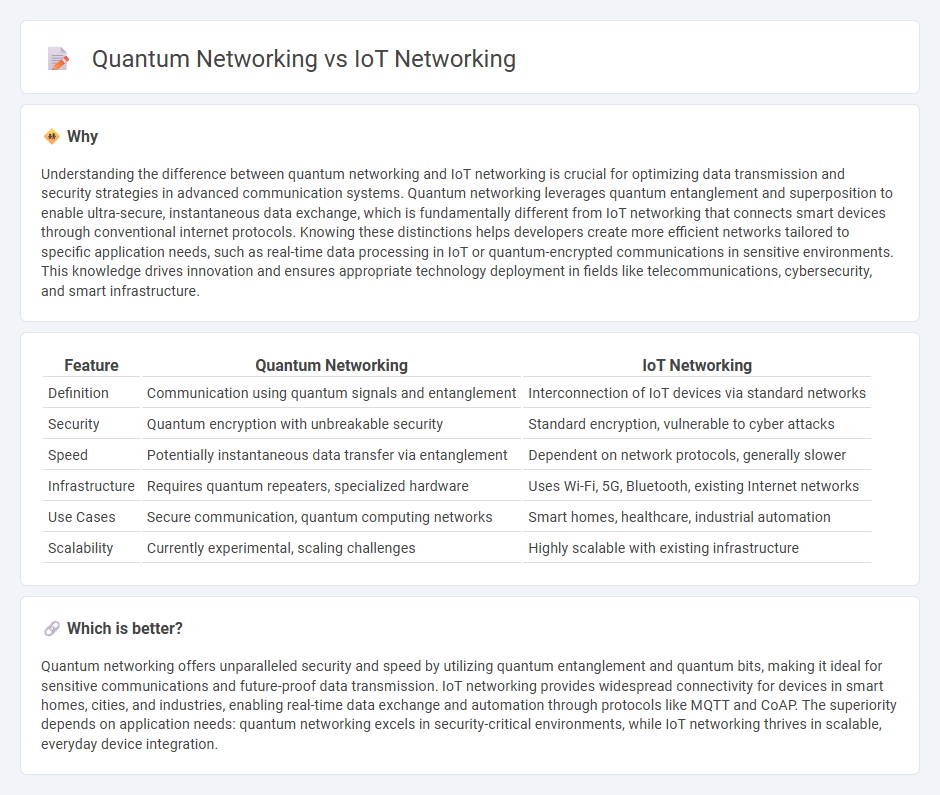
Understanding the difference between quantum networking and IoT networking is crucial for optimizing data transmission and security strategies in advanced communication systems. Quantum networking leverages quantum entanglement and superposition to enable ultra-secure, instantaneous data exchange, which is fundamentally different from IoT networking that connects smart devices through conventional internet protocols. Knowing these distinctions helps developers create more efficient networks tailored to specific application needs, such as real-time data processing in IoT or quantum-encrypted communications in sensitive environments. This knowledge drives innovation and ensures appropriate technology deployment in fields like telecommunications, cybersecurity, and smart infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Networking | IoT Networking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication using quantum signals and entanglement | Interconnection of IoT devices via standard networks |
| Security | Quantum encryption with unbreakable security | Standard encryption, vulnerable to cyber attacks |
| Speed | Potentially instantaneous data transfer via entanglement | Dependent on network protocols, generally slower |
| Infrastructure | Requires quantum repeaters, specialized hardware | Uses Wi-Fi, 5G, Bluetooth, existing Internet networks |
| Use Cases | Secure communication, quantum computing networks | Smart homes, healthcare, industrial automation |
| Scalability | Currently experimental, scaling challenges | Highly scalable with existing infrastructure |
Which is better?
Quantum networking offers unparalleled security and speed by utilizing quantum entanglement and quantum bits, making it ideal for sensitive communications and future-proof data transmission. IoT networking provides widespread connectivity for devices in smart homes, cities, and industries, enabling real-time data exchange and automation through protocols like MQTT and CoAP. The superiority depends on application needs: quantum networking excels in security-critical environments, while IoT networking thrives in scalable, everyday device integration.
Connection
Quantum networking enhances IoT networking by providing ultra-secure communication channels through quantum key distribution (QKD), which protects data integrity in IoT devices. The integration of quantum entanglement principles allows IoT networks to achieve faster and more reliable information transfer with minimal latency. These advancements in quantum communication protocols significantly improve the scalability and security of large-scale IoT ecosystems.
Key Terms
**IoT Networking:**
IoT networking connects billions of devices through low-power, wireless protocols like Zigbee, LoRa, and NB-IoT, enabling real-time data exchange and remote monitoring across smart homes, cities, and industries. It relies on scalable architectures such as edge computing and cloud platforms to manage vast amounts of sensor data securely and efficiently. Discover how innovations in IoT networking are transforming connectivity in the digital age.
IPv6
IoT networking relies heavily on IPv6 to provide a vast address space, enabling seamless connectivity for billions of devices with efficient routing and low latency. Quantum networking, though still emerging, explores integrating quantum communication protocols with IPv6 to enhance security and data transmission speeds through quantum entanglement and superposition principles. Discover how IPv6 serves as a foundational technology bridging IoT and quantum networking advancements.
MQTT
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol widely used in IoT networking for efficient, low-bandwidth communication between devices and cloud services, enabling real-time data exchange in smart homes and industrial automation. Quantum networking, still in experimental stages, leverages quantum entanglement and quantum key distribution for unbreakable security and ultra-fast data transmission but does not currently support MQTT natively. Discover how emerging quantum technologies could transform IoT protocols and reshape secure communication by exploring the future of MQTT in quantum networks.
Source and External Links
What Is IoT (Internet of Things)? - Cisco - IoT networking connects diverse devices through various means like wired Ethernet and Wi-Fi, providing necessary bandwidth, security, and scalability for effective IoT operation in industries, offices, and homes.
Understanding IoT Networks: A Beginner's Guide - Device Authority - IoT networks use a mix of cellular, LAN/PAN, LPWAN, and mesh network technologies to enable data exchange between smart devices and central systems for diverse applications, dictated by coverage, power, and data needs.
Types of IoT Networks - Tutorials Point - IoT networks consist of sensors, devices, and software interacting over connectivity options like Wi-Fi or cellular, often employing cloud or edge computing to analyze data and automate responses in real time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com