Decentralized identity allows users to control their personal data through blockchain technology, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and enhancing privacy and security. Centralized identity systems store user information on a single server or entity, increasing risks of data breaches and identity theft. Explore the advantages and challenges of each identity model to understand their impact on digital security.
Why it is important
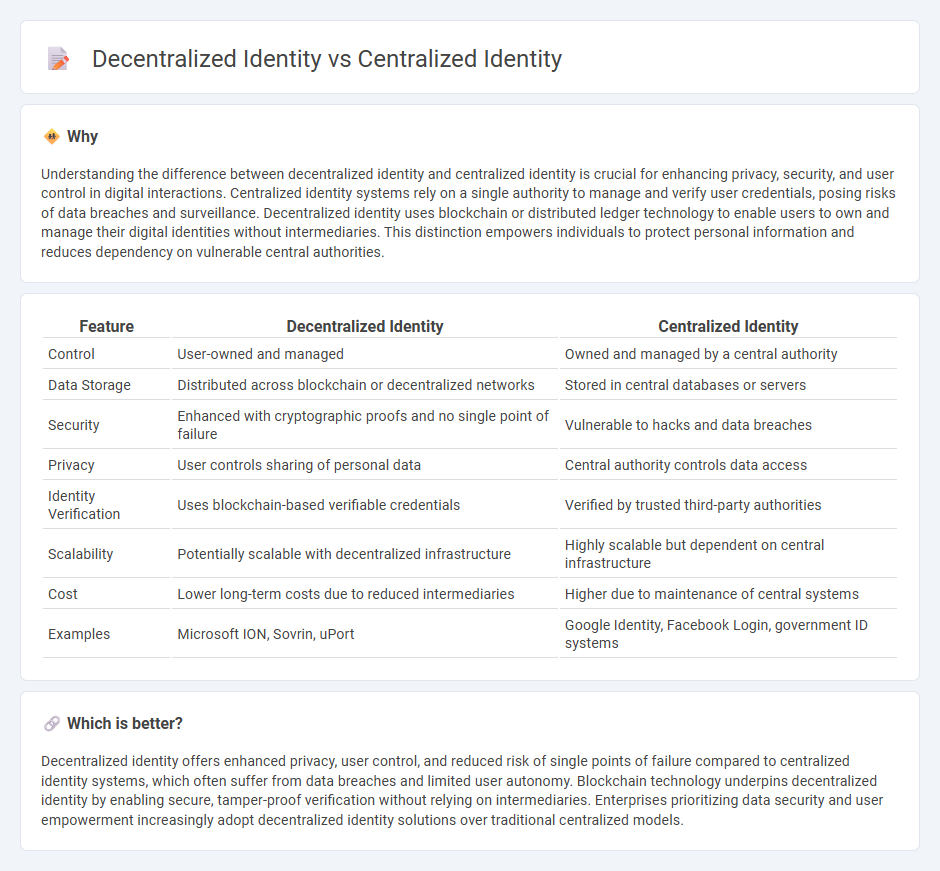
Understanding the difference between decentralized identity and centralized identity is crucial for enhancing privacy, security, and user control in digital interactions. Centralized identity systems rely on a single authority to manage and verify user credentials, posing risks of data breaches and surveillance. Decentralized identity uses blockchain or distributed ledger technology to enable users to own and manage their digital identities without intermediaries. This distinction empowers individuals to protect personal information and reduces dependency on vulnerable central authorities.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity | Centralized Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User-owned and managed | Owned and managed by a central authority |
| Data Storage | Distributed across blockchain or decentralized networks | Stored in central databases or servers |
| Security | Enhanced with cryptographic proofs and no single point of failure | Vulnerable to hacks and data breaches |
| Privacy | User controls sharing of personal data | Central authority controls data access |
| Identity Verification | Uses blockchain-based verifiable credentials | Verified by trusted third-party authorities |
| Scalability | Potentially scalable with decentralized infrastructure | Highly scalable but dependent on central infrastructure |
| Cost | Lower long-term costs due to reduced intermediaries | Higher due to maintenance of central systems |
| Examples | Microsoft ION, Sovrin, uPort | Google Identity, Facebook Login, government ID systems |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity offers enhanced privacy, user control, and reduced risk of single points of failure compared to centralized identity systems, which often suffer from data breaches and limited user autonomy. Blockchain technology underpins decentralized identity by enabling secure, tamper-proof verification without relying on intermediaries. Enterprises prioritizing data security and user empowerment increasingly adopt decentralized identity solutions over traditional centralized models.
Connection
Decentralized identity and centralized identity are connected through their roles in digital identity management systems, where centralized identity relies on a single authority to issue and control user credentials, while decentralized identity distributes control across multiple entities or blockchain networks. Both approaches aim to verify and authenticate users but differ in data ownership, security, and privacy, with decentralized identity enhancing user control and reducing reliance on intermediaries. Integration of these models can create hybrid systems that leverage centralized trust frameworks while enabling user-centric identity verification via decentralized methods.
Key Terms
Single Point of Control
Centralized identity systems rely on a single authority managing user credentials, creating a single point of control that can lead to vulnerabilities such as data breaches and identity theft. Decentralized identity leverages blockchain or distributed ledger technologies to distribute control among users, enhancing security and privacy by eliminating centralized failure points. Explore the benefits and challenges of these models to understand which identity management approach suits your needs.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Centralized identity systems rely on a single trusted authority to manage and verify user identities, often leading to privacy risks and limited user control. Decentralized identity, particularly Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), empowers individuals to own and control their digital identities without dependence on central authorities, using blockchain and cryptographic technologies for secure and verifiable credentials. Explore the benefits and implementations of SSI to understand how it revolutionizes identity management.
Trust Anchor
A centralized identity system relies on a single trusted authority, known as the trust anchor, to validate and manage user credentials, often creating a single point of control and potential failure. In contrast, decentralized identity distributes trust across multiple entities or blockchain validators, enhancing security and user autonomy by eliminating reliance on a central authority as the trust anchor. Explore the key differences and implications for digital identity management to understand which model best fits your needs.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Identity Management - Centralized identity management involves a single central authority collecting, storing, and managing identity data, used by governments and organizations for authentication, access control, and transactions, often implemented through directory services like Active Directory or cloud-based platforms.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Identity - ShareID - In centralized identity models, all user identity data is stored in one secure location, making them easy to manage and scale, with directory services authenticating users for resource access but posing risks such as a single point of failure.
The Importance of Centralized Identity Management - Okta - Centralized identity management consolidates user authentication in one environment, improving security visibility and reducing login friction, although decentralized models claim higher security by requiring multiple sign-ins.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com