Circular electronics emphasize designing devices for reuse, repair, and recycling to minimize electronic waste and resource consumption. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates sustainable production processes that recover and reuse materials within the manufacturing cycle, reducing dependency on virgin resources. Explore how these technologies redefine sustainability in the electronics industry.
Why it is important
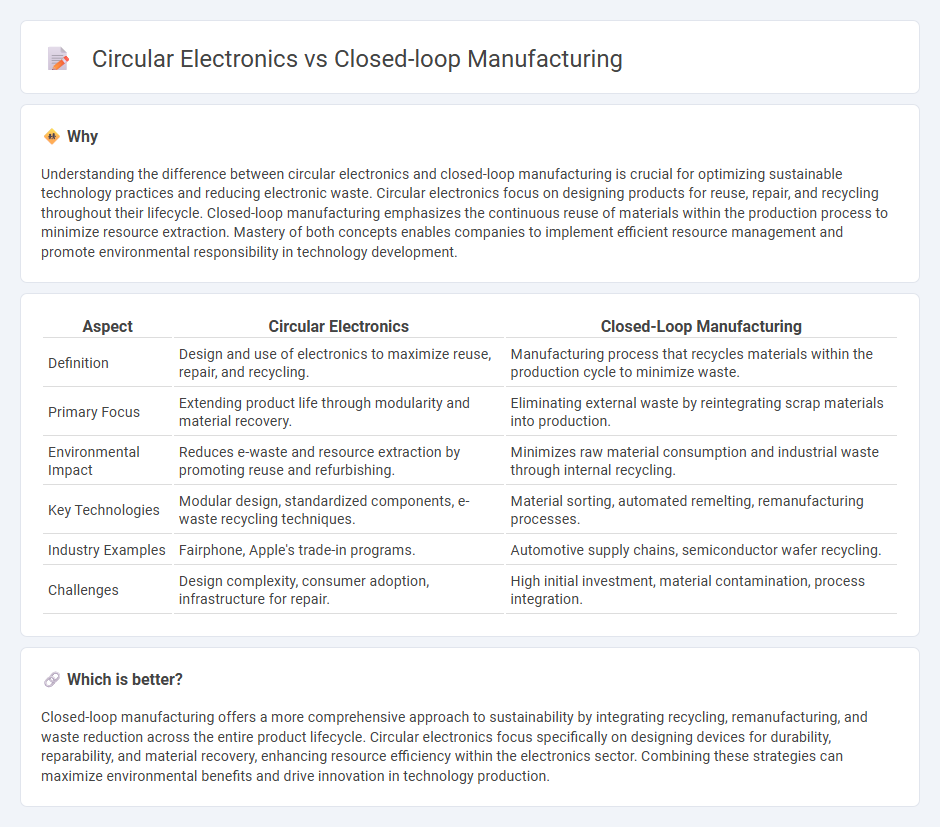
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and closed-loop manufacturing is crucial for optimizing sustainable technology practices and reducing electronic waste. Circular electronics focus on designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling throughout their lifecycle. Closed-loop manufacturing emphasizes the continuous reuse of materials within the production process to minimize resource extraction. Mastery of both concepts enables companies to implement efficient resource management and promote environmental responsibility in technology development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Closed-Loop Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design and use of electronics to maximize reuse, repair, and recycling. | Manufacturing process that recycles materials within the production cycle to minimize waste. |
| Primary Focus | Extending product life through modularity and material recovery. | Eliminating external waste by reintegrating scrap materials into production. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces e-waste and resource extraction by promoting reuse and refurbishing. | Minimizes raw material consumption and industrial waste through internal recycling. |
| Key Technologies | Modular design, standardized components, e-waste recycling techniques. | Material sorting, automated remelting, remanufacturing processes. |
| Industry Examples | Fairphone, Apple's trade-in programs. | Automotive supply chains, semiconductor wafer recycling. |
| Challenges | Design complexity, consumer adoption, infrastructure for repair. | High initial investment, material contamination, process integration. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing offers a more comprehensive approach to sustainability by integrating recycling, remanufacturing, and waste reduction across the entire product lifecycle. Circular electronics focus specifically on designing devices for durability, reparability, and material recovery, enhancing resource efficiency within the electronics sector. Combining these strategies can maximize environmental benefits and drive innovation in technology production.
Connection
Circular electronics rely on closed-loop manufacturing processes to minimize electronic waste by continuously recycling materials and components. This approach enhances resource efficiency, reduces environmental impact, and supports sustainable production cycles in the electronics industry. Implementing closed-loop systems enables the recovery of valuable metals and plastics, promoting a circular economy in technology manufacturing.
Key Terms
Feedback Control Systems
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback control systems to continuously monitor and adjust production processes, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Circular electronics emphasize material recovery and reuse, relying on feedback mechanisms for optimizing recycling loops and minimizing waste throughout the product lifecycle. Explore how feedback control systems drive innovation in both closed-loop manufacturing and circular electronics for sustainable industry transformation.
Product Life Cycle
Closed-loop manufacturing emphasizes the continuous reuse of materials within production cycles to minimize waste, enhancing resource efficiency throughout the Product Life Cycle. Circular electronics expands this concept by incorporating design for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, enabling extended product use and reducing environmental impact across all life stages. Explore how integrating these approaches optimizes sustainability in electronic product development and end-of-life management.
E-waste Recycling
Closed-loop manufacturing emphasizes the continuous reuse of materials within production cycles to minimize waste, while circular electronics target sustainable product lifecycle management to reduce e-waste through repair, refurbishment, and recycling. Electronic waste recycling focuses on recovering valuable metals and components such as gold, silver, and rare earth elements to prevent environmental contamination and resource depletion. Explore advanced e-waste recycling technologies and strategies to optimize circular economy practices in electronics.
Source and External Links
What is Closed Loop Manufacturing? - Clear Object - Closed-Loop Manufacturing is a holistic, circular approach that uses real-time data and technology to continuously monitor and optimize production for improved quality, reduced waste, cost savings, and sustainability.
Closed-loop manufacturing - Wikipedia - Closed-loop manufacturing (CLM) integrates production and in-machine measurement to iteratively manufacture parts with high accuracy, reducing tool costs and improving quality through continuous feedback.
Key Benefits and Challenges of Closed-Loop Manufacturing Systems - Closed-loop manufacturing enhances efficiency and sustainability by enabling material tracking, reuse, and process optimization through technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain, promoting a circular economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com