Synthetic media detection leverages advanced algorithms and AI to identify manipulated or fabricated digital content by analyzing inconsistencies in audio, video, and images. Blockchain verification ensures data integrity and authenticity through decentralized, tamper-proof ledgers that securely record transactional history. Explore the innovative methodologies driving trust and security in digital media and data verification.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and blockchain verification is crucial for ensuring data authenticity and security in digital environments. Synthetic media detection identifies manipulated or AI-generated content to prevent misinformation and fraud. Blockchain verification uses decentralized ledger technology to confirm the integrity and provenance of transactions and data. Mastery of both technologies protects users and organizations from digital threats while enhancing trust in online communications.
Comparison Table
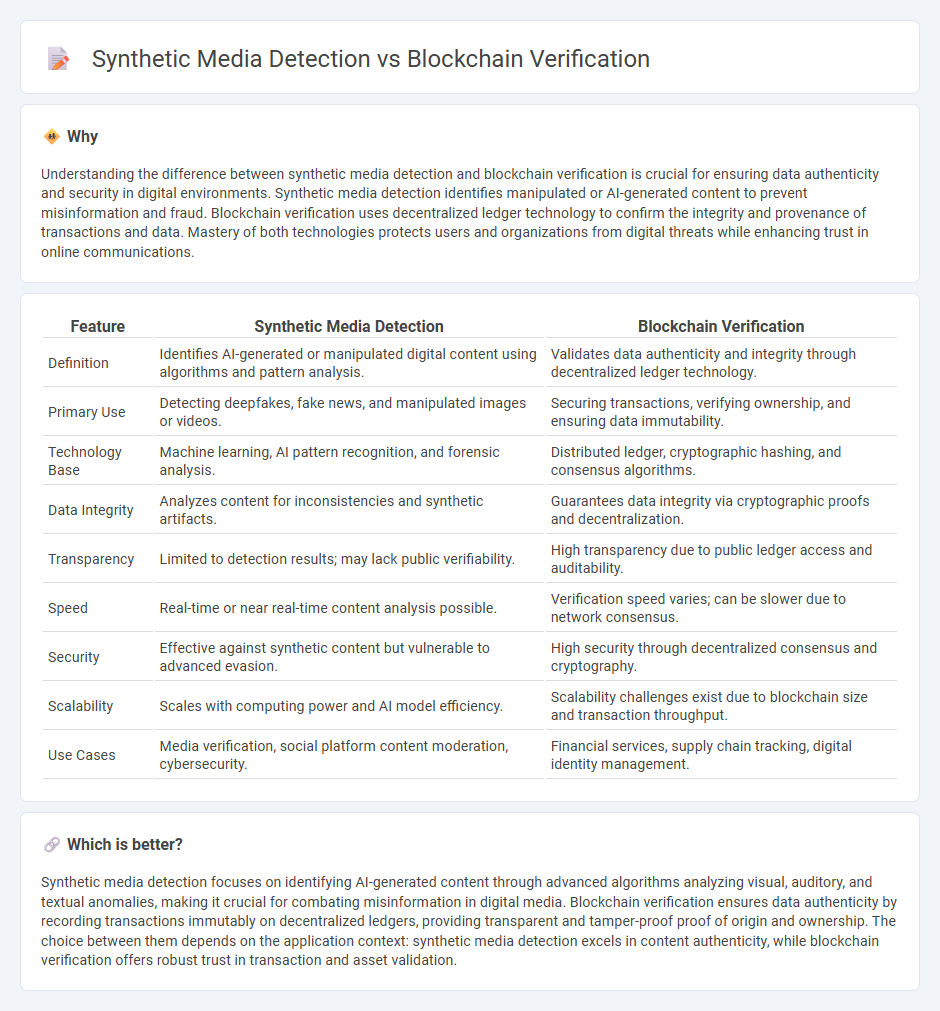
| Feature | Synthetic Media Detection | Blockchain Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies AI-generated or manipulated digital content using algorithms and pattern analysis. | Validates data authenticity and integrity through decentralized ledger technology. |
| Primary Use | Detecting deepfakes, fake news, and manipulated images or videos. | Securing transactions, verifying ownership, and ensuring data immutability. |
| Technology Base | Machine learning, AI pattern recognition, and forensic analysis. | Distributed ledger, cryptographic hashing, and consensus algorithms. |
| Data Integrity | Analyzes content for inconsistencies and synthetic artifacts. | Guarantees data integrity via cryptographic proofs and decentralization. |
| Transparency | Limited to detection results; may lack public verifiability. | High transparency due to public ledger access and auditability. |
| Speed | Real-time or near real-time content analysis possible. | Verification speed varies; can be slower due to network consensus. |
| Security | Effective against synthetic content but vulnerable to advanced evasion. | High security through decentralized consensus and cryptography. |
| Scalability | Scales with computing power and AI model efficiency. | Scalability challenges exist due to blockchain size and transaction throughput. |
| Use Cases | Media verification, social platform content moderation, cybersecurity. | Financial services, supply chain tracking, digital identity management. |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated content through advanced algorithms analyzing visual, auditory, and textual anomalies, making it crucial for combating misinformation in digital media. Blockchain verification ensures data authenticity by recording transactions immutably on decentralized ledgers, providing transparent and tamper-proof proof of origin and ownership. The choice between them depends on the application context: synthetic media detection excels in content authenticity, while blockchain verification offers robust trust in transaction and asset validation.
Connection
Synthetic media detection utilizes advanced algorithms to identify manipulated or AI-generated content by analyzing digital fingerprints and metadata. Blockchain verification leverages decentralized ledgers to securely record and authenticate original media ownership and provenance. Together, these technologies enhance content trustworthiness by providing reliable verification and tamper-evident records in digital ecosystems.
Key Terms
Consensus Algorithm
Consensus algorithms in blockchain verification ensure data integrity by enabling decentralized agreement on transaction validity, with prominent methods including Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance. Synthetic media detection leverages AI-driven pattern recognition and anomaly detection techniques to identify deepfakes and generated content, which fundamentally differ from consensus-driven validation in blockchains. Explore how consensus algorithms secure blockchain transactions and contrast these mechanisms with cutting-edge synthetic media detection methods.
Deepfake Identification
Blockchain verification leverages decentralized ledger technology to provide immutable records that authenticate the origin and integrity of digital content, ensuring trust in media provenance. Synthetic media detection uses advanced AI algorithms and machine learning models to analyze and identify manipulations in audio, video, and image files, specifically targeting deepfake content by detecting subtle inconsistencies and artifacts. Explore the latest techniques and tools to enhance deepfake identification and safeguard digital media authenticity.
Cryptographic Hashing
Cryptographic hashing plays a crucial role in blockchain verification by generating unique hash values that securely link data blocks, ensuring immutability and transparency in transaction records. In synthetic media detection, cryptographic hashes help identify manipulated content by verifying the integrity and authenticity of digital files, making it possible to spot alterations. Explore further to understand how cryptographic hashing bridges security in decentralized systems and media verification.
Source and External Links
How is a transaction verified on a cryptocurrency network? - Blockchain verification involves miners or stakers confirming transactions on a decentralized public ledger, with each new block added serving as a 'confirmation' that makes the transaction permanent and transparent.
What Are Blockchain Digital Credentials? An Expert Guide (2025) - Blockchain verification uses a tamper-proof digital ledger combined with cryptographic digital signatures and metadata to securely and instantly verify digital credentials.
Blockchain for Digital Identity and Credentials - IBM - Blockchain enables auditable, traceable, and verifiable identity information and credentials that are secure, allowing instant verification while preserving privacy through permissioned, tamper-proof transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com