Ambient computing integrates smart devices seamlessly into daily environments, enabling continuous and intuitive user interaction without manual input. Edge computing processes data near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use by handling tasks locally rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. Explore how these technologies transform digital experiences and industry applications.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ambient computing and edge computing is crucial for optimizing technology deployment in smart environments. Ambient computing integrates seamless interactions between users and devices, enhancing user experience through context awareness. Edge computing processes data locally on devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, essential for real-time applications. This knowledge allows businesses to leverage the right approach for efficient, scalable, and responsive technology solutions.
Comparison Table
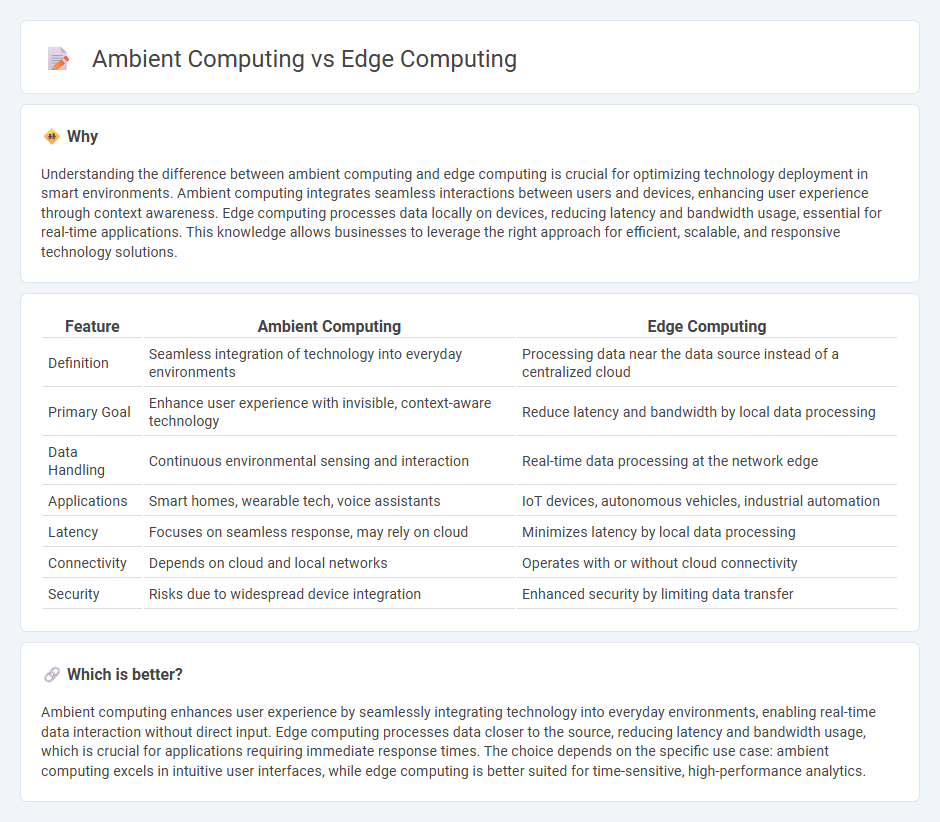
| Feature | Ambient Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seamless integration of technology into everyday environments | Processing data near the data source instead of a centralized cloud |
| Primary Goal | Enhance user experience with invisible, context-aware technology | Reduce latency and bandwidth by local data processing |
| Data Handling | Continuous environmental sensing and interaction | Real-time data processing at the network edge |
| Applications | Smart homes, wearable tech, voice assistants | IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation |
| Latency | Focuses on seamless response, may rely on cloud | Minimizes latency by local data processing |
| Connectivity | Depends on cloud and local networks | Operates with or without cloud connectivity |
| Security | Risks due to widespread device integration | Enhanced security by limiting data transfer |
Which is better?
Ambient computing enhances user experience by seamlessly integrating technology into everyday environments, enabling real-time data interaction without direct input. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage, which is crucial for applications requiring immediate response times. The choice depends on the specific use case: ambient computing excels in intuitive user interfaces, while edge computing is better suited for time-sensitive, high-performance analytics.
Connection
Ambient computing relies on Edge computing to process data locally on devices like sensors and smartphones, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness. By enabling seamless interaction between users and connected environments, Edge computing supports the pervasive and context-aware nature of ambient computing. This integration optimizes data handling and improves the efficiency of smart technologies in everyday settings.
Key Terms
Latency
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data close to the source, enabling real-time analytics and faster decision-making in applications such as autonomous vehicles and smart factories. Ambient computing, while also aiming for seamless interaction between users and devices, often relies on distributed sensors and cloud integration, potentially introducing variable latency. Explore the differences and benefits of each approach to enhance your understanding of latency optimization in modern computing environments.
Context-awareness
Edge computing processes data near the source, enhancing real-time context-awareness by minimizing latency and enabling quick decision-making in IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart factories. Ambient computing, also known as pervasive computing, creates an environment where context-aware systems seamlessly integrate into daily life, using sensors and AI to adapt to user behavior and surroundings dynamically. Discover more about how context-awareness drives innovation in edge and ambient computing paradigms.
Distributed processing
Distributed processing in edge computing involves data being processed near the source, typically on local devices or edge servers, which reduces latency and bandwidth use for real-time applications. Ambient computing distributes processing across a network of interconnected devices embedded in the environment, enabling seamless and context-aware interactions without user intervention. Explore how these distributed processing models transform technology integration and responsiveness in smart environments.
Source and External Links
What is edge computing? | Glossary | HPE - Edge computing stores and processes data near the user, reducing latency and improving speed by handling data at the network's edge via devices like IoT sensors, enabling real-time analysis for applications such as self-driving cars and smart cities.
What Is Edge Computing? | Microsoft Azure - Edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers, minimizing latency and bandwidth use by sending only relevant data to central datacenters, supporting real-time processing in environments with limited connectivity like factories and farms.
What Is Edge Computing? - IBM - Edge computing is a distributed framework that processes data closer to IoT devices or local servers, reducing latency and bandwidth demands while enabling faster insights and better user experiences, especially as data volume grows with 5G networks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com