Quantum dots display technology leverages nanoscale semiconductor particles to produce vivid, highly saturated colors with improved energy efficiency and brightness compared to conventional displays. Digital Light Processing (DLP) utilizes micro-mirrors to project sharp, high-contrast images primarily in projectors and TVs, offering fast response times and excellent color accuracy. Explore the distinct advantages and application scenarios of Quantum dots display versus DLP technology to understand their impact on modern visual experiences.
Why it is important
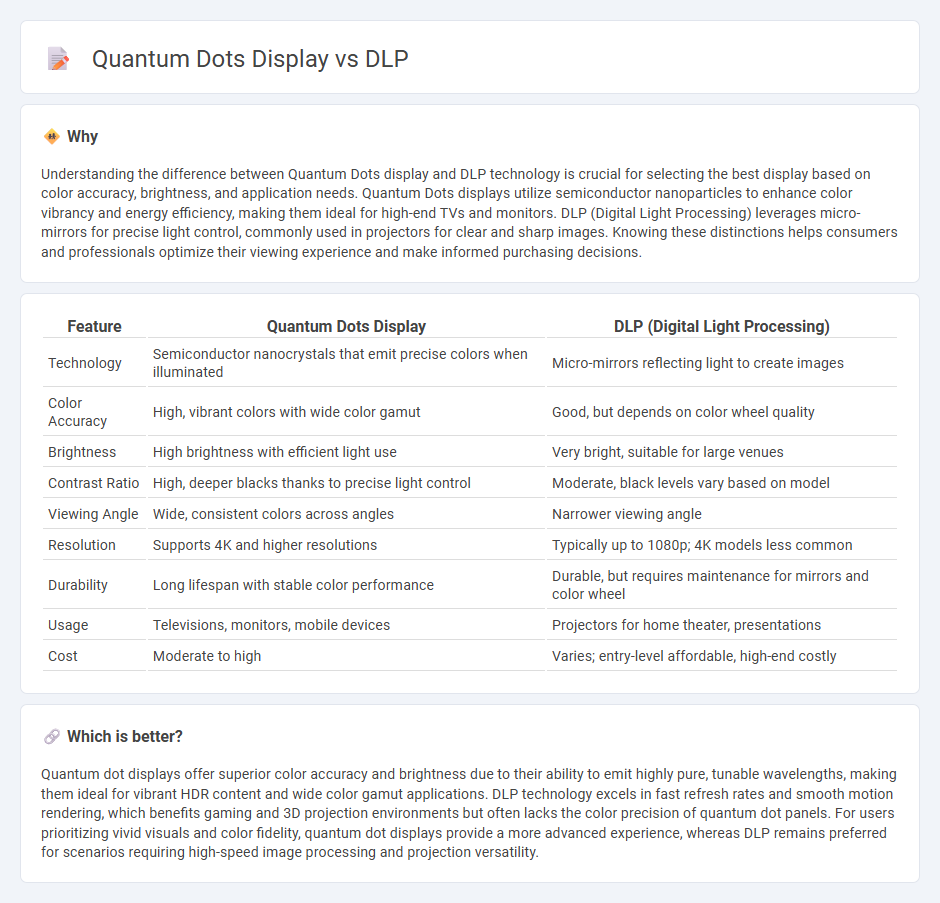
Understanding the difference between Quantum Dots display and DLP technology is crucial for selecting the best display based on color accuracy, brightness, and application needs. Quantum Dots displays utilize semiconductor nanoparticles to enhance color vibrancy and energy efficiency, making them ideal for high-end TVs and monitors. DLP (Digital Light Processing) leverages micro-mirrors for precise light control, commonly used in projectors for clear and sharp images. Knowing these distinctions helps consumers and professionals optimize their viewing experience and make informed purchasing decisions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Dots Display | DLP (Digital Light Processing) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Semiconductor nanocrystals that emit precise colors when illuminated | Micro-mirrors reflecting light to create images |
| Color Accuracy | High, vibrant colors with wide color gamut | Good, but depends on color wheel quality |
| Brightness | High brightness with efficient light use | Very bright, suitable for large venues |
| Contrast Ratio | High, deeper blacks thanks to precise light control | Moderate, black levels vary based on model |
| Viewing Angle | Wide, consistent colors across angles | Narrower viewing angle |
| Resolution | Supports 4K and higher resolutions | Typically up to 1080p; 4K models less common |
| Durability | Long lifespan with stable color performance | Durable, but requires maintenance for mirrors and color wheel |
| Usage | Televisions, monitors, mobile devices | Projectors for home theater, presentations |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Varies; entry-level affordable, high-end costly |
Which is better?
Quantum dot displays offer superior color accuracy and brightness due to their ability to emit highly pure, tunable wavelengths, making them ideal for vibrant HDR content and wide color gamut applications. DLP technology excels in fast refresh rates and smooth motion rendering, which benefits gaming and 3D projection environments but often lacks the color precision of quantum dot panels. For users prioritizing vivid visuals and color fidelity, quantum dot displays provide a more advanced experience, whereas DLP remains preferred for scenarios requiring high-speed image processing and projection versatility.
Connection
Quantum dot displays utilize semiconductor nanocrystals to emit precise, vibrant colors with high brightness and efficiency, enhancing the image quality compared to traditional displays. Digital Light Processing (DLP) uses micro-mirrors to project images, often benefiting from quantum dot technology when integrated as color converters to improve color accuracy and brightness. The synergy between quantum dots and DLP systems results in displays with superior color gamut and enhanced visual performance in projection technology.
Key Terms
Micro-mirrors (DLP)
Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology relies on micro-mirrors that rapidly tilt to modulate light and create images with high precision and brightness, distinct from Quantum Dots displays which utilize nanocrystals to enhance color accuracy and energy efficiency. The micro-mirrors in DLP offer faster response times and better motion clarity, especially beneficial for projectors and large-screen applications. Explore the intricate mechanics of micro-mirrors in DLP technology to understand how they reshape visual performance compared to Quantum Dot displays.
Quantum confinement (Quantum dots)
Quantum dots utilize quantum confinement to precisely control electron behavior, enabling vibrant colors and higher energy efficiency compared to traditional DLP displays. By manipulating the size of semiconductor nanocrystals, quantum dots emit pure, tunable light wavelengths that enhance color accuracy and brightness. Discover how quantum confinement technology in quantum dot displays revolutionizes visual performance and energy savings.
Color gamut
Quantum dots displays achieve a wider color gamut by utilizing nanocrystals that emit pure, highly saturated colors, surpassing the traditional DLP system's color performance limited by color wheel segments. DLP technology relies on sequential color filtering and LED or lamp sources, which typically result in narrower color ranges and less vibrant hues compared to quantum dot-enhanced LED displays. Explore the advanced color capabilities and applications of quantum dots in modern display technologies to understand the future of vivid visual experiences.
Source and External Links
What Is Data Loss Prevention (DLP)? [Guide] - CrowdStrike - Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a set of tools and processes that detect, prevent, and manage unauthorized access or leakage of sensitive data to protect organizations from breaches, regulatory penalties, and reputational harm.
What is Data Loss Prevention (DLP) - Check Point Software - DLP involves strategies, procedures, and tools including network, endpoint, cloud, and email DLP systems designed to monitor, classify, and control sensitive data flow with features like real-time alerts and encryption enforcement.
Data loss prevention software - Wikipedia - DLP software detects and prevents data breaches by monitoring sensitive data in use, in motion, and at rest, aiming to stop data loss or leaks through various monitoring and blocking techniques.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com