Generative audio utilizes AI algorithms to create unique soundscapes and music in real-time, offering personalized and dynamic listening experiences. In contrast, audio streaming delivers pre-recorded tracks from large libraries through the internet, providing vast selections instantly accessible to users. Explore deeper insights into how these technologies revolutionize the future of sound.
Why it is important
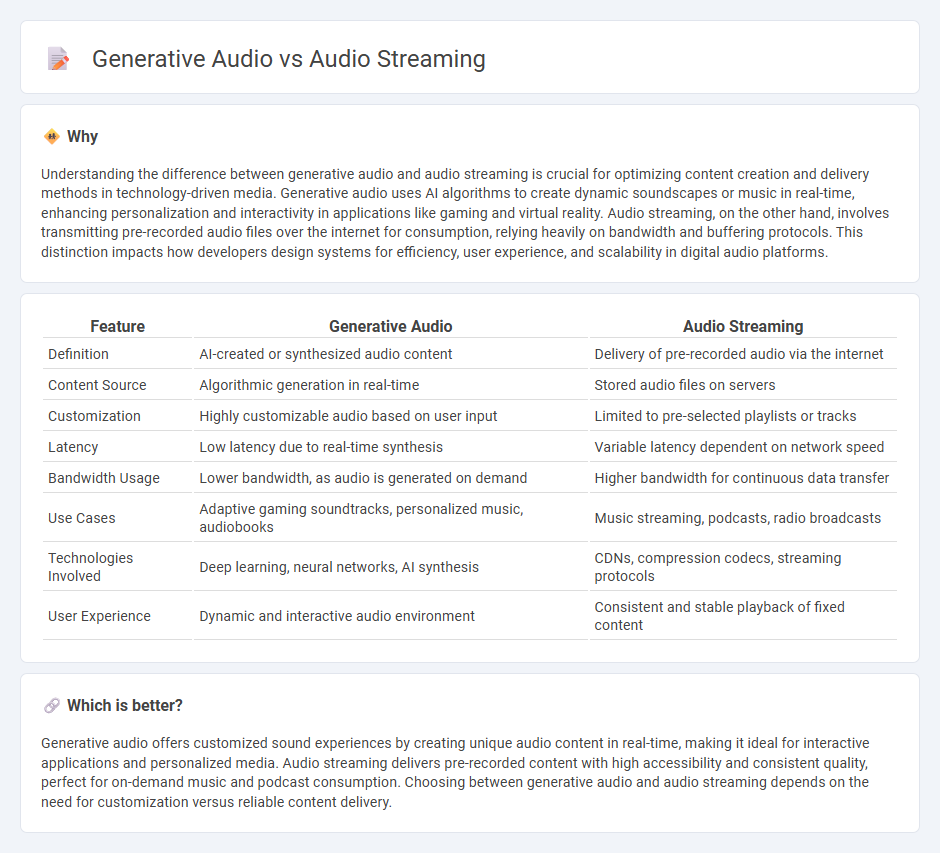
Understanding the difference between generative audio and audio streaming is crucial for optimizing content creation and delivery methods in technology-driven media. Generative audio uses AI algorithms to create dynamic soundscapes or music in real-time, enhancing personalization and interactivity in applications like gaming and virtual reality. Audio streaming, on the other hand, involves transmitting pre-recorded audio files over the internet for consumption, relying heavily on bandwidth and buffering protocols. This distinction impacts how developers design systems for efficiency, user experience, and scalability in digital audio platforms.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Generative Audio | Audio Streaming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI-created or synthesized audio content | Delivery of pre-recorded audio via the internet |
| Content Source | Algorithmic generation in real-time | Stored audio files on servers |
| Customization | Highly customizable audio based on user input | Limited to pre-selected playlists or tracks |
| Latency | Low latency due to real-time synthesis | Variable latency dependent on network speed |
| Bandwidth Usage | Lower bandwidth, as audio is generated on demand | Higher bandwidth for continuous data transfer |
| Use Cases | Adaptive gaming soundtracks, personalized music, audiobooks | Music streaming, podcasts, radio broadcasts |
| Technologies Involved | Deep learning, neural networks, AI synthesis | CDNs, compression codecs, streaming protocols |
| User Experience | Dynamic and interactive audio environment | Consistent and stable playback of fixed content |
Which is better?
Generative audio offers customized sound experiences by creating unique audio content in real-time, making it ideal for interactive applications and personalized media. Audio streaming delivers pre-recorded content with high accessibility and consistent quality, perfect for on-demand music and podcast consumption. Choosing between generative audio and audio streaming depends on the need for customization versus reliable content delivery.
Connection
Generative audio relies on advanced algorithms and machine learning to create unique soundscapes, which enhances the audio streaming experience by delivering personalized and adaptive content. Audio streaming platforms leverage generative audio to provide infinite variations of music and sound effects, optimizing listener engagement and satisfaction. The integration of generative audio into streaming technology drives innovation in real-time content creation and efficient bandwidth usage.
Key Terms
Codec
Audio streaming relies on codecs like AAC, Opus, and MP3 to compress and transmit audio efficiently over networks while maintaining quality. Generative audio utilizes advanced neural codecs such as WaveNet and Lyra, which synthesize audio content dynamically, enabling real-time creation with lower bandwidth requirements. Explore the latest advancements in codec technology to understand their impact on audio streaming and generative audio.
Latency
Audio streaming technology typically experiences latency ranging from 20 to 200 milliseconds, depending on network speed and buffering protocols, which can impact real-time interactions. Generative audio, leveraging AI models to create sound on-the-fly, often reduces latency by processing audio data locally or in optimized cloud environments, enabling near-instantaneous audio synthesis. Explore further to understand how latency differences shape user experiences in various applications.
Machine Learning
Machine learning plays a crucial role in both audio streaming and generative audio by enhancing user experiences through advanced data processing and content creation. Audio streaming leverages neural networks to optimize sound quality and personalize playlists in real-time, while generative audio uses deep learning models like GANs and transformers to synthesize novel sounds or music autonomously. Explore the latest machine learning breakthroughs driving innovation in audio technologies to understand their distinctive capabilities and future potential.
Source and External Links
Music Streaming 101: From Beginner to Audiophile - This article provides an overview of music streaming, discussing its basics and various platforms available for streaming music.
Best music streamers 2025 - This guide offers recommendations for the best network audio players that support high-quality audio streaming from various online services and local files.
Radio Mast - Radio Mast is a platform designed for creating and sharing live audio streams, suitable for professional broadcasters and offering reliable streaming solutions globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com